Abstract
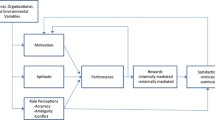
The study develops and tests a model of salespeople’s job stress relative to its proposed determinants and outcomes. The study findings shed light on four questions concerning possible links between job stress and its precursors. The evidence gained suggests that job stress may influence intention to leave through reduced organizational commitment and that job satisfaction intervenes between salespeople’s role perceptions and job stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacharach, Samuel and Peter Bamberger. 1992. “Causal Models of Role Stressor Antecedents and Consequences: The Importance of Occupational Differences.”Journal of Vocational Behavior 41 (August): 13–34.
Bagozzi, Richard P. 1978. “Salesforce Performance and Satisfaction as a Function of Individual Differences, Interpersonal, and Situational Factors.”Journal of Marketing Research 15 (November): 517–531.
Bagozzi, Richard P. and Youjae, Yi. 1988. “On the Evaluation of Structural Equation Models.”Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 16 (Spring): 74–94.
Bateman, Thomas S. and Stephen Strasser. 1983. “A Cross-Lagged Regression Test of the Relationships between Job Tension and Employee Satisfaction.”Journal of Applied Psychology 68 (August): 439–445.
Bedeian, Arthur G. and Achilles A. Armenakis. 1981. “A Path-Analytic Study of the Consequences of Role Conflict and Ambiguity.”Academy of Management Journal 24 (June): 417–424.
Behrman, Douglas N. and William D. Perreault, Jr. 1984. “A Role Stress Model of the Performance and Satisfaction of Industrial Salespersons.”Journal of Marketing 48 (Fall): 9–21.
Bluedorn, Alan C. 1982a. “The Theories of Turnover: Causes, Effects, and Meaning.”Research in the Sociology of Organizations 1: 75–128.
Bluedorn, Alan C. 1982b. “A Unified Model of Turnover from Organizations.”Human Relations 35 (February): 135–153.
Bollen, Kenneth A. 1989.Structural Equations with Latent Variables. New York: Wiley.
Brooke, Paul P., Jr., Daniel W. Russell, and James L. Price. 1988. “Discriminant Validation of Measures of Job Satisfaction, Job Involvement, and Organizational Commitment.”Journal of Applied Psychology (April): 139–145.
Brown, Steven P. and Robert W. Peterson. 1993. “Antecedents and Consequences of Salesperson Job Satisfaction: Meta-Analysis and Assessment of Causal Effects.”Journal of Marketing Research 30 (February): 63–77.
Curry, James P., Douglas S. Wakefield, James L. Price, and Charles W. Mueller. 1986. “On the Causal Ordering of Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment.”Academy of Management Journal 29 (December): 847–858.
Dunham, Randall B. and Jeanne B. Herman. 1975. “Development of Female Faces Scale for Measuring Job Satisfaction.”Journal of Applied Psychology 60 (October): 629–631.
Eden, Dov. 1990. “Acute and Chronic Job Stress, Strain, and Vacation Relief.”Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 45 (April): 175–193.
Edwards, Jeffrey R. 1992. “A Cybernetic Theory of Stress, Coping, and Well-Being in Organizations.”Academy of Management Review 17 (April): 238–274.
Fisher, Cynthia D. and Richard Gitelson. 1983. “A Meta-Analysis of the Correlates of Role Conflict and Ambiguity.”Journal of Applied Psychology 68 (May): 320–333.
Ford, Neil M., Orville C. Walker, Jr., and Gilbert A. Churchill, Jr. 1976. “The Psychological Consequences of Role Conflict and Ambiguity in the Industrial Salesforce.” InMarketing: 1776–1976 and Beyond. Ed. Kenneth L. Bernhardt. Chicago: American Marketing Association, 403–408.
Fowler, H. W. 1965.A Dictionary of Modern English Usage. Second Edition. New York: Oxford University Press.
Fried, Yitzhak, Kendrith M. Rowland, and Gerald R. Ferris. 1984. “The Physiological Measurement of Work Stress: A Critique.”Personnel Psychology 37 (Winter): 583–615.
Fry, Louis W., Charles M. Futrell, A. Parasuraman, and M. A. Chmielewski. 1986. “An Analysis of Alternative Causal Models of Salesperson Role Perceptions and Work-related Attitudes.”Journal of Marketing Research 23 (May): 153–163.
Goolsby, Jerry R. 1992. “A Theory of Role Stress in Boundary Spanning Positions of Marketing Organizations.”Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 20 (Spring): 155–164.
Hayduk, Leslie A. 1987.Structural Equation Modeling with LISREL. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Hom, Peter W. and Rodger W. Griffeth. 1990. “Structural Equations Modeling Test of a Turnover Theory: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analyses.”Journal of Applied Psychology 76 (June): 350–366.
House, Robert J. and John R. Rizzo. 1972. “Role Conflict and Ambiguity as Critical Variables in a Model of Organizational Behavior.”Organizational Behavior and Human Performance 7 (June): 467–505.
James, Lawrence R., Stanley A. Mulaik, and Jeanne M. Brett. 1982.Causal Analysis. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Johnston, Mark W., A. Parasuraman, and Charles M. Futrell. 1989. “Extending a Model of Salesperson Role Perceptions and Workrelated Attitudes: Impact of Job Tenure.”Journal of Business Research 18 (June): 269–290.
Johnston, Mark W., A. Parasuraman, Charles M. Futrell, and William C. Black. 1990. “A Longitudinal Assessment of the Impact of Selected Organizational Influences on Salespeople’s Organizational Commitment during Early Employment.”Journal of Marketing Research 27 (August): 333–344.
Jöreskog, Karl G. and Dag Sörbom. 1989.LISREL 7: User’s Reference Guide. Mooresville, IN: Scientific Software.
Kahn, Robert L., Donald M. Wolfe, Robert P. Quinn, J. Dietrick Snoek, and Robert A. Rosenthal. 1964.Organizational Stress: Studies in Role Conflict and Ambiguity. New York: Wiley.
Keichel, Walter III. 1993. “How We Will Work in the Year 2000.”Fortune 127 (May 17): 38–52.
Kemery, Edward R., Arthur G. Bedeian, Kevin W. Mossholder, and John Touliatos. 1985. “Outcomes of Role Stress: A Multisample Constructive Replication.”Academy of Management Journal 28 (June): 363–375.
Klenke-Hamel, Karin E. and John E. Mathieu. 1990. “Role Strains, Tension, and Job Satisfaction Influences on Employees’ Propensity to Leave: A Multi-Sample Replication and Extension.”Human Relations 43: 791–807.
Locke, Edwin A. 1976. “The Nature and Causes of Job Satisfaction.” InHandbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology. Ed. Marvin D. Dunnette. Chicago: Rand McNally, 1328–1334.
Mathieu, John E. and Denny M. Zajac. 1990. “A Review and Meta-Analysis of the Antecedents, Correlates, and Consequences of Organizational Commitment.”Psychological Bulletin 108 (April): 171–194.
McGee, Gail W., Carl E. Ferguson, Jr., and Anson Seers. 1989. “Role Conflict and Role Ambiguity: Do the Scales Measure These Two Constructs?”Journal of Applied Psychology 74 (October): 815–818.
Miles, Robert H. 1975. “An Empirical Test of Causal Interference between Role Perceptions of Conflict and Ambiguity and Various Personal Outcomes.”Journal of Applied Psychology 60 (June): 334–339.
Mobley, William H. 1977. “Intermediate Linkages in the Relationship between Job Satisfaction and Employee Turnover.”Journal of Applied Psychology 62 (April): 237–240.
Mobley, William H., Rodger W. Griffeth, Herbert H. Hand, and Bruce M. Meglino. 1979. “Review and Conceptual Analysis of the Employee Turnover Process.”Psychological Bulletin 86 (May): 493–522.
Moncrief, William C. III. 1986. “Selling Activity and Sales Position Taxonomies for Industrial Salesforces.”Journal of Marketing Research 23 (August): 261–270.
Mowday, Richard T., Richard M. Steers, and Lyman W. Porter. 1979. “The Measurement of Organizational Commitment.”Journal of Vocational Behavior 14 (April): 224–247.
Netemeyer, Richard G., Mark W. Johnston, and Scott Burton. 1990. “Analysis of Role Conflict and Ambiguity in a Structural Equations Framework.”Journal of Applied Psychology 75 (April): 148–157.
Parasuraman, A. and Charles M. Futrell. 1983. “Demographics, Job Satisfaction, and Propensity to Leave of Industrial Salesmen.”Journal of Business Research 11 (March): 33–48.
Parasuraman, Saroj and Joseph A. Alutto. 1984. “Sources and Outcomes of Stress in Organizational Settings: Toward the Development of a Structural Model.”Academy of Management Journal 27 (June): 330–350.
Parasuraman, Saroj, Jeffrey H. Greenhaus, and Cherlyn S. Granrose. 1992. “Role Stressors, Social Support, and Well-Being among Two-Career Couples.”Journal of Organizational Behavior 13 (July): 339–356.
Price, James L. 1977.The Study of Turnover. Ames: Iowa State University Press.
Reichers, Arnon E. 1985. “A Review and Reconceptualization of Organizational Commitment.”Academy of Management Review 10 (July): 465–476.
Rizzo, John R., Robert J. House, and Sidney I. Lirtzman. 1970. “Role Conflict and Ambiguity in Complex Organizations.”Administrative Science Quarterly 15 (June): 150–163.
Rosse, Joseph G. and Charles L. Hulin. 1985. “Adaptation to Work: An Analysis of Employee Health, Withdrawal, and Change.”Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 36 (December): 324–347.
Sager, Jeffrey K. 1991. “A Longitudinal Assessment of Change in Sales Force Turnover.”Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 19 (Winter): 25–36.
Sager, Jeffrey K. and Mark W. Johnston. 1989. “Antecedents and Outcomes of Organizational Commitment: A Study of Salespeople.”Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management 9 (Spring): 30–41.
Sager, Jeffrey K., P. R. Varadarajan, and Charles M. Futrell. 1988. “Understanding Salesperson Turnover: A Partial Evaluation of Mobley’s Turnover Process Model.”Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management 8 (May): 20–35.
Schriesheim, Chester A. 1978. “Development, Validation, and Application of New Leadership Behavior and Expectancy Research Instruments.” Dissertation. Ohio State University.
Schriesheim, Chester A. 1979. “The Similarity of Individual Directed and Group Directed Leader Behavior Descriptions.”Academy of Management Journal 22 (June): 345–355.
Schriesheim, Chester A., Angelo J. Kinicki, and Janet F. Schriesheim. 1979. “The Effect of Leniency on Leader Behavior Descriptions.”Organizational Behavior and Human Performance 23 (February): 1–29.
Schuler, Randall S. 1975. “Role Perceptions, Satisfaction, and Performance: A Partial Reconciliation.”Journal of Applied Psychology 60 (December): 683–687.
Selye, Hans. 1980. “Preface.” InSelye’s Guide to Stress Research. Volume 1. Ed. Hans Selye. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, v–xiii.
Teas, Richard K. 1983. “Supervisory Behavior, Role Stress, and the Job Satisfaction of Industrial Salespeople.”Journal of Marketing Research 20 (February): 84–91.
Tracy, Lance and Thomas W. Johnson. 1981. “What Do the Role Conflict and Role Ambiguity Scales Measure?”Journal of Applied Psychology 66 (August): 464–469.
Walker, Orville C., Jr., Gilbert A. Churchill, Jr., and Neal M. Ford. 1975. “Organizational Determinants of the Industrial Salesman’s Role Conflict and Ambiguity.”Journal of Marketing 39 (January): 32–39.
Walker, Orville C., Jr., Gilbert A. Churchill, Jr., and Neal M. Ford. 1977. “Motivation and Performance in Industrial Selling: Present Knowledge and Needed Research.”Journal of Marketing Research 14 (May): 156–168.
Williams, Larry J. and John T. Hazer. 1986. “Antecedents and Consequences of Satisfaction and Commitment in Turnover Models: A Reanalysis Using Latent Variable Structural Equation Methods.”Journal of Applied Psychology 71 (May): 219–231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
He researches primarily in the area of salesperson attitudes and behavior. He has published in theJournal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, Journal of Business Research, AMA Summer Educator’s Proceedings, Industrial Marketing Management, andAkron Business and Economic Review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sager, J.K. A structural model depicting salespeople’s job stress. JAMS 22, 74–84 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1177/0092070394221007
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0092070394221007