Abstract
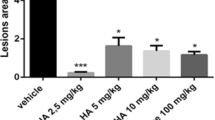
Previous studies have suggested that rebamipide, a gastroprotective drug, might be effective for the treatment of aphthous oral ulcers in Behçet's disease patients. The aim of this study was to confirm the effect of rebamipide on experimentally induced stomatitis in a rat acetic acidinduced oral ulcer model. Buccal mucosal lesions were induced by local injection of 50 μl of 99.7% acetic acid into the buccal mucosa, which produced a single large ulcer in each of the treated rats. The ulcer remained up to 14 days. Repeated dose of rebamipide (3-100 mg/kg) dose-dependently decreased the ulcer area. Histopathologically, increased fibrosis and regenerated epithelium were observed in the rebamipide-treated group. In contrast, indomethacin, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, impaired the healing of ulcers. We have successfully established an improved method for the administration of acetic acid to induce oral ulcers, and rebamipide accelerated the ulcer healing.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arakawa, T., Kobayashi, K., Yoshikawa, T., et al. (1998). Rebamipide: overview of its mechanism of action and efficacy in mucosal protection and ulcer healing, Dig. Dis. Sci. 43, 5S–13S.
Ishihara, K., Komuro, Y., Nishiyama, N., et al. (1992). Effect of rebamipide on mucus secretion by endogenous prostaglandin-independent mechanism in rat gastric mucosa, Arzneim-Forsch. Drug Res. 42, 1462–1466.
Ishiyama, H., Yamasaki, K., Imaizumi, T., et al. (1985). Effect of OPC-12759, a new anti-ulcer agent, on the healing, recurrence and relapse of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats, Dig. Dis. Sci. 30, 381.
Kaklamani, V. G., Vaiopoulos, G. and Kaklamanis, P. G. (1998). Behçet's disease, Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 27, 197–217.
Matsuda, T., Yamada, H., Hoshi, K., et al. (1994). The beneficial effect of rebamipide on recurrent oral aphthous ulcers in Behçet's disease, J. Clin. Exp. Med. 170, 773–774.
Naito, Y., Yoshikawa, T., Tanigawa, T., et al. (1995). Hydroxyl radical scavenging by rebamipide and related compounds: electron paramagnetic resonance study, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 18, 117–123.
Ogino, K., Hobara, T., Ishiyama, H., et al. (1992). Antiulcer mechanism of action of rebamipide, a novel antiulcer compound, on diethyldithiocarbamate-induced antral gastric ulcers in rats, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 212, 9–13.
Shigeta, J., Takahashi, S. and Okabe, S. (1998). Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in the healing of gastric ulcers in rats, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 286, 1383–1390.
Shiraki, M., Yamasaki, K., Ishiyama, H., et al. (1988). Healing promoting effect of proamipide, a novel drug that increase gastric defense mechanisms, on acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in the rat, Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 92, 389–395.
Slomiany, B. L., Piotrowski, J. and Slomiany, A. (1999). Role of endothelin-1 and interleukin-4 in buccal mucosal ulcer healing: Effect of chronic alcohol ingestion, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 373–377.
Suetsugu, H., Ishihara, S., Moriyama, N., et al. (2000). Effect of rebamipide on prostaglandin EP4 receptor gene expression in rat gastric mucosa, J. Lab. Clin. Med. 136, 50–57.
Sun, W., Tsuji, S., Tsujii, M., et al. (2000). Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat gastric mucosa by rebamipide, a mucoprotective agent, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 295, 447–452.
Tarnawski, A. S., Arakawa, T. and Kobayashi, K. (1998). Rebamipide treatment activates epidermal growth factor and its receptor expression in normal and ulcerated gastric mucosa in rats: One mechanism for its ulcer healing action?, Dig. Dis. Sci. 43, 90S–98S.
Wallace, J. L., Mcknight, W., Reuter, B. K., et al. (2000). NSAID-induced gastric damage in rats: requirement for inhibition of both cyclooxygenase 1 and 2, Gastroenterology 119, 706–714.
Wang, J. Y., Yamasaki, S., Takeuchi, K., et al. (1989). Delayed healing of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats by indomethacin, Gastroenterology 96, 393–402.
Yamasaki, K., Ishiyama, H., Imaizumi, T., et al. (1989). Effect of OPC-12759, a novel antiulcer agent, on chronic and acute experimental gastric ulcer, and gastric secretion in rats, Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 49, 441–448.
Yoshikawa, T., Naito, Y., Tanigawa, T., et al. (1993). Free radical scavenging activity of novel anti-ulcer agent rebamipide studies by electron spin resonance, Arzeim-Forsh. Drug Res. 43, 363–366.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiyama, H., Kawai, K., Azuma, A. et al. Therapeutic effect of rebamipide in a modified acetic acid-induced buccal mucosal ulcer model. Inflammopharmacology 10, 391–399 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1163/156856002321544864
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156856002321544864