Abstract
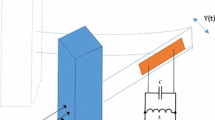
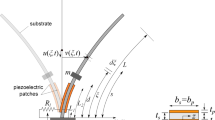
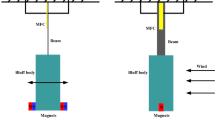
Modeling and comparative analysis of galloping-based hybrid piezoelectric-inductive energy harvesting systems are investigated. Both piezoelectric and electromagnetic transducers are attached to the transverse degree of freedom of the prismatic structure in order to harvest energy from two possible sources. A fully-coupled electroaeroelastic model is developed which takes into account the coupling between the generated voltage from the piezoelectric transducer, the induced current from the electromagnetic transducer, and the transverse displacement of the bluff body. A nonlinear quasi-steady approximation is employed to model the galloping force. To determine the influences of the external load resistances that are connected to the piezoelectric and electromagnetic circuits on the onset speed of galloping, a deep linear analysis is performed. It is found that the external load resistances in these two circuits have significant effects on the onset speed of galloping of the harvester with the presence of optimum values. To investigate the effects of these transduction mechanisms on the performance of the galloping energy harvester, a nonlinear analysis is performed. Using the normal form of the Hopf bifurcation, it is demonstrated that the hybrid energy harvester has a supercritical instability for different values of the external load resistances. For well-defined wind speed and external load resistance in the electromagnetic circuit, the results showed that there is a range of external load resistances in the piezoelectric circuit at which the output power generated by the electromagnetic induction is very small. On the other hand, there are two optimal load resistances at which the output power by the piezoelectric transducer is maximum. Based on a comparative study, it is demonstrated the hybrid piezoelectric-inductive energy harvester is very beneficial in terms of having two sources of energy. However, compared to the classical piezoelectric and electromagnetic energy harvesters, the results show that, considering a hybrid energy harvester leads to an increase in the onset speed of galloping and a decrease in the levels of the harvested power in both the piezoelectric and electromagnetic circuits which is explained by the additional resistive shunt damping effects in the hybrid energy harvester.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Muralt, J. Micromech. Microeng. 10, 136 (2000)
S.P. Gurav, A. Kasyap, M. Sheplak, L. Cattafesta, R.T. Haftka, J.F.L. Goosen, F.V. Keulen, Proceedings 10th AIAA/ISSSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, 3559 (2004)
D.J. Inman, B.L. Grisso, Smart Struct. Mater. Conf. SPIE 6174, 61740T (2006)
A. Abdelkefi, M. Ghommem, Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 3, 052001 (2013)
N. Sharpes, A. Abdelkefi, S. Priya, Ener. Harv. Syst. 1, 209 (2014)
H.A. Sodano, G. Park, D.J. Inman, Shock Vib. Dig. 36, 197 (2004)
S. Priya, J. Electrocera. 19, 167 (2007)
S.R. Anton, H.A. Sodano, Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 1 (2007)
G. Litak, M.I. Friswell, S. Adhikari, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 214103 (2010)
A. Abdelkefi, F. Najar, A.H. Nayfeh, S. Ben Ayed, Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 115007 (2011)
A. Abdelkefi, A.H. Nayfeh, M.R. Hajj, Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1147 (2011)
M.I. Friswell, S.F. Ali, O. Bilgen, S. Adhikari, L.W. Lees, G. Litak, J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Struct. 23, 1505 (2012)
M. Bryant, E. Garcia, Proceedings of SPIE 7493, 74931W (2009)
A. Erturk, W.G.R. Vieira, C. De Marqui, D.J. Inman, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 184103 (2010)
C. De Marqui, A. Erturk, D.J. Inman, J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Struct. 21, 983 (2010)
H.D. Akaydin, N. Elvin, Y. Andrepoulos, Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 025007 (2012)
H.L. Dai, A. Abdelkefi, L. Wang, J. Intel. Mater. Sys. Struct. 25, 1861 (2014)
H.L. Dai, A. Abdelkefi, L. Wang, Nonlinear Dyn. 77, 967 (2014)
J. Sirohi, R. Mahadik, J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Struct. 22, 2215 (2011)
A. Abdelkefi, M.R. Hajj, A.H. Nayfeh, Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 015014 (2013)
A. Abdelkefi, Z. Yan, M.R. Hajj, The Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 222, 1483 (2013)
Y. Yang, L. Zhao, L. Tang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 064105 (2013)
A. Bibo, M. Daqaq, Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 023901 (2014)
H.J. Jung, S.W. Lee, Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 055022 (2011)
A. Abdelkefi, A. Hasanyan, J. Montgomery, D. Hall, M.R. Hajj, Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 4, 022002 (2014)
A. Abdelkefi, A.H. Nayfeh, M.R. Hajj, Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 925 (2011)
A. Abdelkefi, M.R. Hajj, A.H. Nayfeh, Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1377 (2012)
J. Sirohi, R. Mahadik, ASME J. Vib. Acoust. 134, 1 (2012)
A. Abdelkefi, M.R. Hajj, A.H. Nayfeh, Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1355 (2012)
A. Abdelkefi, Z. Yan, M.R. Hajj, Smart Mater. Struct. 22(2), 025016 (2013)
A. Abdelkefi, Z. Yan, M.R. Hajj, J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Struct. 25, 246 (2014)
D. Zhu, S. Beeby, J. Tudor, N. White, N. Harris, Proc. IEEE Sens. Kona, HI 1, 1415 (2010)
C. De Marqui, A. Erturk, J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Struct. 24, 846 (2012)
J.A.C. Dias, C. De Marqui, A. Erturk, AIAA J. (2014)
J.A.C. Dias, C. De Marqui, A. Erturk, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 044101 (2013)
M. Ali, M. Arafa, M. Elaraby, Proc. World Cong. Eng., WCE , London, UK 3, 5 (2013)
D. Vicente-Ludlam, A. Barrero-Gil, A. Velazquez, J. Flui. Struct. (2014) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2014.09.007i
H.L. Dai, A. Abdelkefi, U. Javed, L. Wang, Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 045012 (2015)
R.D. Belvins, Flow-Induced Vibration Malabar (FL: Krieger, 1990)
A. Barrero-Gil, G. Alonso, A. Sanz-Andres, J. Soun. Vib. 329, 2873 (2010)
G.V. Parkinson, J.D. Smith, Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 17, 225 (1964)
J.D. Kraus, Electromagnetics (McGraw-Hill), p. 420
A.H. Nayfeh, Method of Normal Forms (Wiley Interscience, Berlin, 2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, U., Dai, H. & Abdelkefi, A. Nonlinear dynamics and comparative analysis of hybrid piezoelectric-inductive energy harvesters subjected to galloping vibrations. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 224, 2929–2948 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2015-02599-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2015-02599-y