Abstract
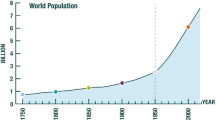
We analyze the growth rates of human population and of atmospheric carbon dioxide by comparing the relative merits of two benchmark models, the exponential law and the finite-time-singular (FTS) power law. The later results from positive feedbacks, either direct or mediated by other dynamical variables, as shown in our presentation of a simple endogenous macroeconomic dynamical growth model describing the growth dynamics of coupled processes involving human population (labor in economic terms), capital and technology (proxies by CO2 emissions). Human population in the context of our energy intensive economies constitutes arguably the most important underlying driving variable of the content of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Using some of the best databases available, we perform empirical analyses confirming that the human population on Earth has been growing super-exponentially until the mid-1960s, followed by a decelerated sub-exponential growth, with a tendency to plateau at just an exponential growth in the last decade with an average growth rate of 1.0% per year. In contrast, we find that the content of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has continued to accelerate super-exponentially until 1990, with a transition to a progressive deceleration since then, with an average growth rate of approximately 2% per year in the last decade. To go back to CO2 atmosphere contents equal to or smaller than the level of 1990 as has been the broadly advertised goals of international treaties since 1990 requires herculean changes: from a dynamical point of view, the approximately exponential growth must not only turn to negative acceleration but also negative velocity to reverse the trend.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Akaev, V. Sadovnichy, A. Korotayev, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 205, 355 (2012)
J.M. Barnola, M. Anklin, J. Porcheron, D. Raynaud, J. Schwander, B. Stauffer, Tellus B 47(1–2), 264 (1995)
R. Biggs, S.R. Carpenter, W.A. Brock, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106(3), 826 (2009)
J.G. Canadell, C. Le Quere, M.R. Raupach, C.B. Field, E.T. Buitenhuis, P. Ciais, T.J. Conway, N.P. Gillett, R.A. Houghton, G. Marland, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104(47) 18866 (2007)
M.R. Chertow, J. Industr. Ecol. 4(4), 13 (2000)
C.W. Cobb, P.H. Douglas, Amer. Econ. Rev. 18(1), 139 (1928)
V. Dakos, M. Scheffer, E.H. van Nes, V. Brovkin, V. Petoukhov, H. Held, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105(38), 14308 (2008)
J.M. Drake, B.D. Griffen, Nature 456(September), 456 (2010)
T. Garrett, Climatic Change 104(3), 437 (2011)
S. Gluzman, D. Sornette, Phys. Rev. E 6601(016134), U315 (2002)
N. Goldenfeld, Lectures on Phase Transitions and the Renormalization Group (Perseus Publishing, 1992)
A. Goriely, J. Differen. Eqns. 161(2), 422 (2000)
C.A.S. Hall, J.W. Day, Jr., Amer. Scientist 97, 230 (2009)
K. Ide, D. Sornette, Physica A 307(1–2), 63 (2002)
A. Johansen, D. Sornette, Physica A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 294(3-4), 465 (2001)
A. Korotayev, J. World-Syst. Res. 11(1), 79 (2005)
A. Korotayev, A.S. Malkov, D. Khaltourina, Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Secular Cycles and Millennial Trends (URSS, 2006)
M. Kremer, Q. J. Econ. 108, 681 (1993)
D.H. Meadows, The Limits to Growth; a Report for the Club of Rome’s Project on the Predicament of Mankind (Universe Books, 1972)
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, World Energy Outlook 2011
R. Pielke, T. Wigley, C. Green, Nature 452(7187), 531 (2008)
M.R. Raupach, J.G. Canadell, C. Le Quéré, Biogeosci. Discuss. 5(4), 2867 (2008)
J. Rockstrom, W. Steffen, K. Noone, A. Persson, F.S. Chapin, E.F. Lambin, T.M. Lenton, M. Scheffer, C. Folke, H.J. Schellnhuber, B. Nykvist, C.A. de Wit, T. Hughes, S. van der Leeuw, H. Rodhe, S. Sorlin, P.K. Snyder, R. Costanza, U. Svedin, M. Falkenmark, L. Karlberg, R.W. Corell, V.J. Fabry, J. Hansen, B. Walker, D. Liverman, K. Richardson, P. Crutzen, J.A. Foley, Nature 461(7263), 472 (2009)
D. Romer, Advanced Macroeconomics, 2nd ed. (McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2000)
Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, Climate Change: Evidence & Causes
S.G. Sammis, D. Sornette, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99(Supp1), 2501 (2002)
M. Scheffer, J. Bascompte, W.A. Brock, V. Brovkin, S.R. Carpenter, V. Dakos, H. Held, E.H. van Nes, M. Rietkerk, G. Sugihara, Nature 461(7260), 53 (2009)
D. Sornette, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99(Supp1), 2522 (2002)
D. Sornette, Why Stock Markets Crash (Critical Events in Complex Financial Systems), (Princeton University Press, 2003)
D. Sornette, Critical Phenomena in Natural Sciences: Chaos, Fractals, Self-organization and Disorder: Concepts and Tools (Springer Series in Synergetics), 2nd ed. (Springer, 2006)
P.A. Stephens, W.J. Sutherland, R.P. Freckleton, Oikos 87, 185 (1999)
S.A. Umpleby, Population Env. 11(3), 159 (1990)
P.-F. Verhulst, Mém. de l’Academie Royale des Sci. et Belles-Lettres de Bruxelles 18, 1 (1845)
P.-F. Verhulst, Mém. de l’Academie Royale des Sci. et Belles-Lettres de Bruxelles 20, 1 (1847)
H. von Foerster, P.M. Mora, L.W. Amiot, Science 132(3436), 1291 (1960)
P.E. Waggoner, J.H. Ausubel, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99(12), 7860 (2002)
S.R. Weart, The Discovery of Global Warming: Revised and Expanded Edition (New Histories of Science, Technology, and Medicine) (Harvard University Press, revised and expanded edition, 2008)
V.I. Yukalov, E.P. Yukalova, D. Sornette, Physica D 238, 1752 (2009)
V.I. Yukalov, E.P. Yukalova, D. Sornette, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 205, 313 (2012)
V.I. Yukalov, E.P. Yukalova, D. Sornette, Physica D 241, 1270 (2012)
V.I. Yukalov, E.P. Yukalova, D. Sornette, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24(2), 1450021 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hüsler, A., Sornette, D. Human population and atmospheric carbon dioxide growth dynamics: Diagnostics for the future. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 223, 2065–2085 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2014-02250-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2014-02250-7