Abstract.
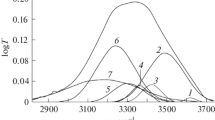
In order to explore the influence of nanoscopic confinement on the vibrational properties of H-bonded liquids, we performed a detailed Raman scattering study, as a function of temperature, on water confined in 75 Å and 200 Å pores of a Gelsil glass. A detailed evaluation of the observed changes in the O-H stretching profile has been achieved by decomposing the O-H band into individual components, corresponding to those found for bulk water and associated to different levels of water connectivity. As main result, a similar effect produced by enlarging pore diameter and lowering T has been put into evidence. Again, the “structure-breaker” role of the GelSil glass on physisorbed water is confirmed and shown to be enhanced by the diminishing of the pore size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.B. McKenna, Eur. Phys. J. E 12, 191–194 (2003)
V. Crupi, D. Majolino, V. Venuti, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 16, S5297–S5316 (2004)
C.M. Carbonaro, F. Clemente, R. Corpino, P.C. Ricci, A. Anedda, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 14441–14444 (2005)
G.E. Walrafen, J. Chem. Phys. 47, 114–126 (1967)
G.E. Walrafen, Y.C. Chu, J. Phys. Chem. 99, 11225–11229 (1995)
J.B. Brubach, A. Mermet, A. Filabozzi, A. Gerschel, P. Roy, J. Chem. Phys. 122, 184509 (2005)
N.V. Nucci, J.M. Vanderkooi, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 18301–18309 (2005)
P.A. Giguère, J. Chem. Phys. 87, 4835–4839 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crupi, V., Longo, F., Majolino, D. et al. Raman spectroscopy: Probing dynamics of water molecules confined in nanoporous silica glasses. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 141, 61–64 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2007-00018-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2007-00018-x