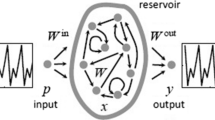
Abstract
High-performance reservoir computing has to rely on its highly rich internal dynamic. Chaotic systems based on memristors are widely employed in reservoir computing because of their wealthy nonlinear dynamic behaviors, but there are few studies and applications related to discrete memristor models compared to continuous memristor models. This paper proposes a brand new discrete memristor model, and a two-dimensional hyper chaotic maps is constructed by coupling the discrete memristor model and a sinusoidal function. The map has rich nonlinear dynamic behaviors which cater to the need for RC, therefore, we apply this map to enhance the richness of the state of the reservoir, and test the reservoir’s computing capability by the emulation of NARMA and Santa Fe time series prediction task. For this purpose, using the method of the single node with delayed feedback, the proposed reservoir can avoid the selection of meta-parameters, and fully exploits the time dependence of the map states to replace the interactions between the internal nodes. As far as we know, this is the first time that time series analysis using the discrete memristive map, and the experimental results demonstrate that the hyperchaotic map based on the discrete memristor can effectively optimize the performance of the reservoir computing. Moreover, the proposed reservoir shows several attractive features including simple design, ease to calculate, and robustness.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
L. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. 18(5), 507–519 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337
F. Corinto, M. Forti, Memristor circuits: bifurcations without parameters. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 64(6), 1540–1551 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2016.2642112
S. Sun, H. Shi, S. Duan, L. Wang, Memristor-based time-delay hyperchaotic system with circuit simulation and image encryption. Phys. Scr. 97(3), 035204 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ac4cfb
H. Shi, D. Yan, L. Wang, S. Duan, A novel memristor-based chaotic image encryption algorithm with hash process and s-box. Eur. Phys. J.-Spec. Top. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00365-w
Y. Peng, K. Sun, S. He, A discrete memristor model and its application in hénon map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 137, 109873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109873
S. Kong, C. Li, S. He, S. Çiçek, Q. Lai, A memristive map with coexisting chaos and hyperchaos. Chin. Phys. B 30(11), 110502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/abf4fb
H. Li, Z. Hua, H. Bao, L. Zhu, M. Chen, B. Bao, Two-dimensional memristive hyperchaotic maps and application in secure communication. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(10), 9931–9940 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3022539
Y. Deng, Y. Li, A 2d hyperchaotic discrete memristive map and application in reservoir computing. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II-Express Briefs (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2021.3118646
H. Jaeger, The “echo state’’ approach to analysing and training recurrent neural networks-with an erratum note. Bonn German.: German Natl. Res. Center Inf. Technol. GMD Tech. Rep. 148(34), 13 (2001)
B. Schrauwen, D. Verstraeten, J. Van Campenhout, An overview of reservoir computing: theory, applications and implementations. In Proceedings of the 15th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks. p. 471–482 2007, pages 471–482, (2007). http://hdl.handle.net/1854/LU-416607
M.R.E.U. Shougat, X.F. Li, T. Mollik, E. Perkins, A hopf physical reservoir computer. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98982-x
K. Nakajima, H. Hauser, T. Li, R. Pfeifer, Information processing via physical soft body. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10487
Y. Zhong, J. Tang, X. Li, B. Gao, H. Qian, W. Huaqiang, Dynamic memristor-based reservoir computing for high-efficiency temporal signal processing. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20692-1
New motor neuroscience and brain-machine interfaces, D.J. O’shea, E. Trautmann, C. Chandrasekaran, S. Stavisky, J. C. Kao, M. Sahani, S. Ryu, K. Deisseroth, and K. V. Shenoy, The need for calcium imaging in nonhuman primates. Exp. Neurol. 287, 437–451 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.08.003
W. Sun, N. Akashi, Y. Kuniyoshi, K. Nakajima, The 32nd 2021 international symposium on micro-nanomechatronics and human science. pages 1–6, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS53471.2021.9767178
M. Cucchi, C. Gruener, L. Petrauskas, P. Steiner, H. Tseng, A. Fischer, B. Penkovsky, C. Matthus, P. Birkholz, H. Kleemann, K. Leo, Reservoir computing with biocompatible organic electrochemical networks for brain-inspired biosignal classification. Sci. Adv. 7(34), eabh0693 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abh0693
S.J. Weddell, S. Ayyagari, R.D. Jones, Reservoir computing approaches to microsleep detection. J. Neural Eng. 18(4), 046021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/abcb7f
M. Lukoševičius, A practical guide to applying echo state networks. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, pages 659–686. Springer, (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8_36
G. Dion, S. Mejaouri, J. Sylvestre, Reservoir computing with a single delay-coupled non-linear mechanical oscillator. J. Appl. Phys. 124(15), 152132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5038038
J. Jensen , G. Tufte, Reservoir computing with a chaotic circuit. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Artificial Life 2017. MIT Press, (2017). http://hdl.handle.net/11250/2456968
L. Appeltant, M. Cornelles Soriano, G. Van der Sande, J. Danckaert, S. Massar, J. Dambre, B. Schrauwen, C.R. Mirasso, I. Fischer, Information processing using a single dynamical node as complex system. Nat. Commun. 2(1), 1–6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1476
Y. Suzuki, Q. Gao, K.C. Pradel, K. Yasuoka, N. Yamamoto, Natural quantum reservoir computing for temporal information processing. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 1–15 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05061-w
S.P. Adhikari, M.P. Sah, H. Kim, L.O. Chua, Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 60(11), 3008–3021 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2013.2256171
D.R. Rigney, A.L. Goldberger, W.C. Ocasio, Y. Ichimaru, G.B. Moody, R.G. Mark, Multichannel physiological data description and analysis. Time Series Prediction: Forecasting the Future and Understanding the Past, pages 697–709, (1994). https://doi.org/10.9774/GLEAF.978-1-909493-38-4_2
Y. Ichimaru, G.B. Moody, Development of the polysomnographic database on cd-rom. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 53(2), 175–177 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1819.1999.00527.x
A.F. Atiya, A.G. Parlos, New results on recurrent network training: unifying the algorithms and accelerating convergence. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 11(3), 697–709 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/72.846741
T. Liu, J. Mou, L. Xiong, X. Han, H. Yan, Y. Cao, Hyperchaotic maps of a discrete memristor coupled to trigonometric function. Phys. Scr. 96(12), 125242 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ac3153
Y. Peng, S. He, K. Sun, A higher dimensional chaotic map with discrete memristor. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 129, 153539 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2020.153539
M. Ma, Y. Yang, Z. Qiu, Y. Peng, Y. Sun, Z. Li, M. Wang, A locally active discrete memristor model and its application in a hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-07132-5
A. Elbedwehy, A. El-Mohandes, A. Elnakib, M. Abou-Elsoud, FPGA-based reservoir computing system for ECG denoising. Microprocess. Microsyst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2022.104549
Z. Liang, S. He, H. Wang, K. Sun, A novel discrete memristive chaotic map. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 137(3) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02512-1
Q. Lai, L. Yang, Y. Liu, Design and realization of discrete memristive hyperchaotic map with application in image encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112781
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62076208, 62076207, U20A20227), and in part by the National Key R &D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB1306600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Ji’e, M., Xu, S. et al. RC-MHM: reservoir computing with a 2D memristive hyperchaotic map. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 232, 663–671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-023-00773-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-023-00773-0