Abstract
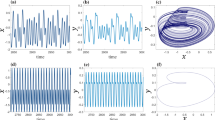
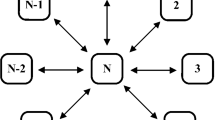
The information processing and encoding of nervous system requires complete collaboration of a large number of neurons in different functional regions of the brain, and the synchronization stability indicates the cooperative and competitive behaviors among neurons. Unusual synchronization is the main manifestation of brain functional diseases. It is an effective method to adjust the synchronization state of neurons by applying external stimulation. Indeed, quick creation and connection of synapses to neurons with appropriate intensity can regulate the collective behaviors of neurons effectively, and then, the energy diversity can be decreased to achieve energy balance. In this paper, a phototube is incorporated into a simple FitzHugh–Nagumo neural circuit for obtaining a light-sensitive neuron model, which is capable for simulating the neural activities in visual neurons. A star network is designed by connecting four photosensitive neurons with electric synapse. The coupling channel is controlled with an adaptive criterion and the coupling intensity is exponentially enhanced to a saturation threshold before the energy diversity between neurons reaches a tiny threshold. It is found that all identical neurons realize complete synchronization and energy balance no matter whether the neurons are presented in spiking, bursting, or chaotic patterns. Nevertheless, phase lock phenomenon occurs in the network when neurons are activated with showing different firing modes, and energy is pumped continuously along the coupling channels even the coupling intensity is further increased.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Strogatz, Exploring complex networks. Nature 401(6825), 268–276 (2001)
R. Albert, A.L. Barabasi, Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Modern Phys. 74(1), 47–97 (2002)
M.E.J. Newman, The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 45(2), 167–256 (2003)
A.L. Hodgkin, A.F. Huxley, A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500–544 (1952)
R.E. Plant, M. Kim, Mathematical description of a bursting pacemaker neuron by a modification of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Biophys. J. 16(3), 227–244 (1976)
J.L. Hindmarsh, R.M. Rose, A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853), 162–164 (1982)
J. Nagumo, S. Arimoto, S. Yoshizawa, An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc. IRE 50(10), 2061–2070 (1962)
K. Tsumoto, H. Kitajima, T. Yoshinaga et al., Bifurcations in Morris-Lecar neuron model. Neurocomputing 69(4–6), 293–316 (2006)
B.C. Bao, Y.X. Zhu, J. Ma et al., Memristive neuron model with an adapting synapse and its hardware experiments. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64(5), 1107–1117 (2021)
Y. Liu, W. Xu, J. Ma et al., A new photosensitive neuron model and its dynamics. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 21(9), 1387–1396 (2020)
P. Zhou, Z. Yao, J. Ma et al., A piezoelectric sensing neuron and resonance synchronization between auditory neurons under stimulus. Chaos Solit. Fractals 145, 110751 (2021)
Y. Xu, Y. Guo, G. Ren et al., Dynamics and stochastic resonance in a thermosensitive neuron. Appl. Math. Comput. 385, 125427 (2020)
W. Wei, Synchronization of coupled chaotic Hindmarsh Rose neurons: an adaptive approach. Chin. Phys. B 10(24), 97–104 (2015)
W.Q. She, M.H. Ma, Tracking synchronization of networked lagrangian systems via impulsive control and its applications. J. Syst. Sci. Complexity 32(4), 1093–1103 (2019)
F. Al Shargie, T.B. Tang, M. Kiguchi, Stress assessment based on decision fusion of EEG and fnirs signals. IEEE Access 8(5), 19889–19896 (2017)
X. Sun, G. Li, Synchronization transitions induced by partial time delay in a excitatory-inhibitorycoupled neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(4), 2509–2520 (2017)
G. Rigatos, Robust synchronization of coupled neural oscillators using the derivative-free nonlinear Kalman filter. Cogn. Neurodyn. 8(6), 465–478 (2014)
Y. Xu, Y. Jia, J. Ma et al., Synchronization between neurons coupled by memristor. Chaos Solit. Fractals 104, 435–442 (2017)
H.D.I. Abarbanel, R. Huerta, M.I. Rabinovich et al., Synchronized action of synaptically coupled chaotic model neurons. Neural Comput. 8(8), 1567–1602 (1996)
Y. Zhang, C.N. Wang, J. Tang et al., Phase coupling synchronization of FHN neurons connected by a Josephson junction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63(11), 2328–2338 (2020)
Z. Yao, P. Zhou, Z. Zhu et al., Phase synchronization between a light-dependent neuron and a thermosensitive neuron. Neurocomputing 423, 518–534 (2021)
Y. Guo, Z. Zhu, C. Wang et al., Coupling synchronization between photoelectric neurons by using memristive synapse. Optik 218, 164993 (2020)
Y. Xie, Z. Yao, X. Hu et al., Enhance sensitivity to illumination and synchronization in light-dependent neurons. Chinese Phys. B (2021)
Z. Zhu, G. Ren, X. Zhang et al., Effects of multiplicative-noise and coupling on synchronization in thermosensitive neural circuits. Chaos Solit. Fractals 151, 111203 (2021)
J.T. Fossi, V. Deli, H.C. Edima et al., Phase synchronization between two thermo-photoelectric neurons coupled through a Josephson Junction. Eur. Phys. J. B 95(4), 1–17 (2022)
A. Calim, J.J. Torres, M. Ozer et al., Chimera states in hybrid coupled neuron populations. Neural Netw. 126, 108–117 (2020)
R.M.G. Reinhart, J.A. Nguyen, Working memory revived in older adults by synchronizing rhythmic brain circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 22(5), 820–827 (2019)
A. Calim, P. Hövel, M. Ozer et al., Chimera states in networks of type-I Morris-Lecar neurons. Phys. Rev. E 98(6), 062217 (2018)
M.S. Kafraj, F. Parastesh, S. Jafari, Firing patterns of an improved Izhikevich neuron model under the effect of electromagnetic induction and noise. Chaos Solit. Fractals 137, 109782 (2020)
M.M. Ibrahim, M.A. Kamran, M.M.N. Mannan et al., Lag synchronization of coupled time-delayed FitzHugh-Nagumo neural networks via feedback control. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–15 (2021)
W. Du, L. Xiao, Coherence resonance and noise-induced synchronization in Hindmarsh-Rose neural network with different topologies. Commun. Theor. Phys. 48(4), 759–762 (2007)
M. Masoliver, C. Masoller, A. Zakharova, Control of coherence resonance in multiplex neural networks. Chaos Solit. Fractals 145, 110666 (2021)
C. Phan, Y. You, Synchronization of boundary coupled Hindmarsh-Rose neuron network. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 55, 103139 (2020)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, J.B. Kirunda et al., Propagation of firing rate by synchronization in a feed-forward multilayer Hindmarsh-Rose neural network. Neurocomputing 320, 60–68 (2018)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, Y. Xu et al., Wave propagation and synchronization induced by chemical autapse in chain Hindmarsh-Rose neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 352, 136–145 (2019)
C.B. Tabi, A.S. Etémé, A. Mohamadou et al., Unstable discrete modes in Hindmarsh-Rose neural networks under magnetic flow effect. Chaos Solit. Fractals 123, 116–123 (2019)
Y.H. Zheng, Q.S. Lu, Spatiotemporal patterns and chaotic burst synchronization in a small-world neuronal network. Physica A 387(14), 3719–3728 (2008)
M. Wang, Z. Hou, H. Xin, Ordering spatiotemporal Chaos in small-world neuron networks. ChemPhysChem 7(3), 579–582 (2006)
B. Percha, R. Dzakpasu, M. Żochowski et al., Transition from local to global phase synchrony in small world neural network and its possible implications for epilepsy. Phys. Rev. E 72(3), 031909 (2005)
F. Li, S. Liu, X. Li, Pattern selection in thermosensitive neuron network induced by noise. Physica A 589, 126627 (2022)
Y. Xu, J. Ma, Pattern formation in a thermosensitive neural network. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 111, 106426 (2022)
I. Hussain, S. Jafari, D. Ghosh et al., Synchronization and chimeras in a network of photosensitive FitzHugh-Nagumo neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(3), 2711–2721 (2021)
Z. Yao, C. Wang, Control the collective behaviors in a functional neural network. Chaos Solit. Fractals 152, 111361 (2021)
S. Dong, H. Zhu, S. Zhong et al., New study on fixed-time synchronization control of delayed inertial memristive neural networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 399, 126035 (2021)
F. Kong, Q. Zhu, R. Sakthivel et al., Fixed-time synchronization analysis for discontinuous fuzzy inertial neural networks with parameter uncertainties. Neurocomputing 422, 295–313 (2021)
Y. Cao, W. Jiang, J. Wang, Anti-synchronization of delayed memristive neural networks with leakage term and reaction-diffusion terms. Knowl.-Based Syst. 233, 107539 (2021)
R. Li, J. Cao, C. Xue et al., Quasi-stability and quasi-synchronization control of quaternion-valued fractional-order discrete-time memristive neural networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 395, 125851 (2021)
Q. Lai, C. Lai, P.D.K. Kuate et al., Chaos in a simplest cyclic Memristive Neural Network. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 32(03), 2250042 (2022)
A. Kashkynbayev, A. Issakhanov, M. Otkel et al., Finite-time and fixed-time synchronization analysis of shunting inhibitory memristive neural networks with time-varying delays. Chaos Solit. Fractals 156, 111866 (2022)
H. Bao, Y. Zhang, W. Liu et al., Memristor synapse-coupled memristive neuron network: synchronization transition and occurrence of chimera. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(1), 937–950 (2020)
D. Premraj, K. Suresh, K. Thamilmaran, Effect of processing delay on bifurcation delay in a network of slow-fast oscillators. Chaos: Interdisciplin. J. Nonlinear Sci. 29(12), 123127 (2019)
D. Premraj, K. Suresh, T. Banerjee et al., Bifurcation delay in a network of locally coupled slow-fast systems. Phys. Rev. E 98(2), 022206 (2018)
F. Parastesh, K. Rajagopal, S. Jafari et al., Blinking coupling enhances network synchronization. Phys. Rev. E 105(5), 054304 (2022)
K. Sathiyadevi, V.K. Chandrasekar, D.V. Senthilkumar, Inhomogeneous to homogeneous dynamical states through symmetry breaking dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(1), 327–340 (2019)
A. Foroutannia, M. Ghasemi, F. Parastesh et al., Complete dynamical analysis of a neocortical network model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(3), 2699–2714 (2020)
M. Shafiei, S. Jafari, F. Parastesh et al., Time delayed chemical synapses and synchronization in multilayer neuronal networks with ephaptic inter-layer coupling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 84, 105175 (2020)
S. Binczak, S. Jacquir, J.M. Bilbault et al., Experimental study of electrical FitzHugh-Nagumo neurons with modified excitability. Neural Netw. 19(5), 684–693 (2006)
R. FitzHugh, Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J . 1(6), 445–466 (1961)
I.M. Kyprianidis, V. Papachristou, I.N. Stouboulos et al., Dynamics of coupled chaotic Bonhoeffer-van der Pol oscillators. WSEAS Trans. Syst. 11(9), 516–526 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This research is partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 12062009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FY finished the numerical calculation and wrote the original draft. JM suggested this project and wrote the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that we have no competing financial interests in publishing this paper.
Additional information
Collective Behavior of Nonlinear Dynamical Oscillators. Guest editors: Sajad Jafari, Bocheng Bao, Christos Volos, Fahimeh Nazarimehr, Han Bao.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Ma, J. Synchronization and energy balance of star network composed of photosensitive neurons. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 4025–4035 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00698-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00698-0