Abstract
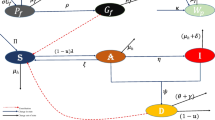
In this study, we present a novel mathematical model that comprehensively addresses the mechanics of hepatitis B infection propagation, caused by the hepatitis B virus, which represents a significant global health concern. This viral infection encompasses various stages, including chronic and acute carrier phases, each playing a pivotal role in the progression and transmission of hepatitis B. Notably, individuals in the chronic phase, despite being asymptomatic, can still transmit the virus, posing a substantial public health challenge. Our study develops an endemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate to better understand the infectiousness of hepatitis B at various phases of the illness. To achieve this, we refine the infectious group into two distinct subclasses: those acutely infected and chronic carriers, both capable of transmitting the virus both horizontally and vertically. We provide an in-depth description of the fundamental characteristics of the proposed model. Furthermore, in order to determine the reproduction number \(R_0\), we use the next-generation matrix approach. We study the biological relevance of the threshold state in great detail shedding light on its implications for disease control and spread. We also establish criteria for analyzing all potential equilibria of the model based on the fundamental reproduction number. To assess the sensitivity of the model’s outcomes to various parameters, we conduct a comprehensive sensitivity analysis, identifying the most influential factors. Estimation of parameter values is achieved using robust least square curve-fitting techniques, further enhancing the model’s practical applicability. Additionally, we complement our analytical findings with numerical simulations to gain deeper insights into the dynamics of hepatitis B transmission. Furthermore, we extend our investigation by formulating a fractional-order model, employing the Atangana–Baleanu derivative. Finally, we establish the existence and uniqueness of the model by employing the ABC fractional-order derivative, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the model’s behavior.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.]
References
J. Mann, M. Roberts, Modelling the epidemiology of hepatitis B in New Zealand. J. Theor. Biol. 21(269), 266–272 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.10.028
WHO, Hepatitis B. Fact sheet No. 204. Updated June 2014(http://www.who.int/meadiacenter/ factsheet/fs204/en/index.html)(revised Agust 2014)
L. Zou, S. Ruan, W. Zhang, On the sexual transmission dynamics of hepatitis B virus in China. J. Theor. Biol. 21(369), 1–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.01.005
L. Pang, S. Ruan, S. Liu, Z. Zhao, X. Zhang, Transmission dynamics and optimal control of measles epidemics. Appl. Math. Comput. 1(256), 131–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2014.12.096
G. Zaman, Y.H. Kang, I.H. Jung, Stability analysis and optimal vaccination of an SIR epidemic model. BioSystems 30(93), 240–249 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2008.05.004
A. Zeb, G. Zaman, S. Momani, Square-root dynamics of a giving up smoking model. Appl. Math. Modell. 1(37), 5326–5334 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2012.10.005
N. Ahmed, A. Raza, A. Akgul, Z. Iqbal, M. Rafiq, M.O. Ahmad, F. Jarad, New applications related to hepatitis C model. AIMS Math. 7(6), 11362–11381 (2022)
M.A. ur Rehman, M. Kazim, N. Ahmed, A. Raza, M. Rafiq, A. Akgul, M. Inc, C. Park, M. Zakarya, Positivity preserving numerical method for epidemic model of hepatitis B disease dynamic with delay factor. Alexandria Eng. J. 64, 505–515 (2023)
S. Jamil, M. Farman, A. Akgul, M.U. Saleem, E. Hincal, S.M. El Din, Fractional order age dependent Covid-19 model: an equilibria and quantitative analysis with modeling. Res. Phys. 53, 106928 (2023)
C. Xu, M. Farman, A. Hasan, A. Akgul, M. Zakarya, W. Albalawi, C. Park, Lyapunov stability and wave analysis of Covid-19 omicron variant of real data with fractional operator. Alexandria Eng. J. 61(12), 11787–11802 (2022)
M. Farman, A. Akgul, K.S. Nisar, D. Ahmad, A. Ahmad, S. Kamangar, C.A. Saleel, Epidemiological analysis of fractional order COVID-19 model with Mittag-Leffler kernel. AIMS Math. 7(1), 756–783 (2022)
R. Zarin, A. Khan, M. Inc, U.W. Humphries, T. Karite, Dynamics of five grade leishmania epidemic model using fractional operator with Mittag–Leffler kernel. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1(147), 110985 (2021)
T. Khan, G. Zaman, Classification of different Hepatitis B infected individuals with saturated incidence rate. SpringerPlus 15(5), 1082 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2706-3
T. Khan, G. Zaman, M.I. Chohan, The transmission dynamic and optimal control of acute and chronic hepatitis B. J. Biol. Dyn. 1(11), 172–189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/17513758.2016.1256441
R. Zarin, I. Ahmed, P. Kumam, A. Zeb, A. Din, Fractional modeling and optimal control analysis of rabies virus under the convex incidence rate. Res. Phys., p. 104665 (2021)
S. Thornley, C. Bullen, M. Roberts, Hepatitis B in a high prevalence New Zealand population: a mathematical model applied to infection control policy. J. Theor. Biol. 7(254), 599–603 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.06.022
L. Zou, W. Zhang, S. Ruan, Modeling the transmission dynamics and control of hepatitis B virus in China. J. Theor. Biol. 21(262), 330–338 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.09.035
M. Fan, M.Y. Li, K. Wang, Global stability of an SEIS epidemic model with recruitment and a varying total population size. Math. Biosci. 30(170), 199–208 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S00255564(00)00067-5
J. Li, Z. Ma, Qualitative analyses of SIS epidemic model with vaccination and varying total population size. Math. Comput. Modell. 1(35), 1235–1243 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S08957177(02)00082-1
A.A. shari, K. Hattaf, G. Zaman, X.Z. Li, Backward bifurcation and optimal control of a vector borne disease. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 1(7):301–309 (2013). https://doi.org/10.12785/amis/070138
M. Toufik, A. Atangana, New numerical approximation of fractional derivative with non-local and non-singular kernel: application to chaotic models. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(10), 144 (2017)
T. Khan, G. Zaman, Alshomrani A. Saleh, Spreading dynamic of acute and carrier hepatitis B with nonlinear incidence. PloS One 13(4), e0191914 (2018)
A. Khan, R. Zarin, M. Inc et al., Stability analysis of leishmania epidemic model with harmonic mean type incidence rate. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 528 (2020)
K. Khan, R. Zarin, A. Khan et al., Stability analysis of five-grade Leishmania epidemic model with harmonic mean-type incidence rate. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 86 (2021)
A. Khan, R. Zarin, I. Ahmed, A. Yusuf, U.W. Humphries, Numerical and theoretical analysis of Rabies model under the harmonic mean type incidence rate. Res. Phys., p. 104652 (2021)
C. Castillo-Chavez, Z. Feng, W. Huang, Mathematical approaches for emerging and reemerging infectious diseases: an introduction. In: Proceedings of the IMA vol. 125, pp. 229-250, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg New York
M.Y. Li, J.S. Muldowney, A geometric approach to global-stability problems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 27(4), 1070–1083 (2006)
R.H. Martin, Logarithmic norms and projections applied to linear differential systems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 45(2), 432–454 (1974)
K. Khan, R. Zarin, A. Khan, A. Yusuf, M. Al-Shomrani, A. Ullah, Stability analysis of five-grade Leishmania epidemic model with harmonic mean-type incidence rate. Adv. Differ. Eqn. 2021(1), 1–27 (2021)
A. Khan, R. Zarin, G. Hussain, A.H. Usman, U.W. Humphries, J.F. Gomez-Aguilar, Modeling and sensitivity analysis of HBV epidemic model with convex incidence rate. Res. Phys. 22, 103836 (2021)
A. Khan, R. Zarin, G. Hussain, N.A. Ahmad, M.H. Mohd, A. Yusuf, Stability analysis and optimal control of covid-19 with convex incidence rate in Khyber Pakhtunkhawa (Pakistan). Res. Phys. 20, 103703 (2021)
A. Khan, R. Zarin, Akgül, A., Saeed, A. and Gul, T., Fractional optimal control of COVID-19 pandemic model with generalized Mittag-Leffler function. Adv. Differe. Eqn. 2021(1), 1–22 (2021)
S. Allegretti, I.M. Bulai, R. Marino, M.A. Menandro, K. Parisi, Vaccination effect conjoint to fraction of avoided contacts for a Sars-Cov-2 mathematical model. Math. Modell. Numer. Simul. Appl. 1(2), 56–66 (2021)
P. Veeresha, Wei Gao, D. G. Prakasha, N. S. Malagi, E. Ilhan, Haci Mehmet Baskonus, New dynamical behaviour of the coronavirus (2019-ncov) infection system with non-local operator from reservoirs to people. Inf. Sci. Lett. 10(2), 17 (2021)
C. Ravichandran, D. Baleanu, On the controllability of fractional functional integro-differential systems with an infinite delay in Banach spaces. Adv. Differ. Eqn. 2013(1), 1–13 (2013)
K. Jothimani, K. Kaliraj, S.K. Panda, K.S. Nisar, C. Ravichandran, Results on controllability of non-densely characterized neutral fractional delay differential system. Evol. Eqn. Control Theory 10(3), 619 (2021)
A. Das, B. Hazarika, S.K. Panda, V. Vijayakumar, An existence result for an infinite system of implicit fractional integral equations via generalized Darbo’s fixed point theorem. Comput. Appl. Math. 40(4), 1–17 (2021)
R. Zarin, Modeling and numerical analysis of fractional order hepatitis B virus model with harmonic mean type incidence rate. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng., pp. 1–16 (2022)
K. Kavitha, K.S. Nisar, A. Shukla, V. Vijayakumar, S. Rezapour, A discussion concerning the existence results for the Sobolev-type Hilfer fractional delay integro-differential systems. Adv. Differ. Eqn. 1, 1–18 (2021)
Williams, W. Kavitha, V. Vijayakumar, Discussion on the controllability results for fractional neutral impulsive Atangana-Baleanu delay integro-differential systems. Math. methods Appl. Sci. (2021)
R. Zarin, A. Khan, A. Yusuf, S. Abdel-Khalek, M. Inc, Analysis of fractional COVID-19 epidemic model under Caputo operator. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. (2021)
V. Vijayakumar, K.S. Nisar, D. Chalishajar, A. Shukla, M. Malik, A. Alsaadi, S.F. Aldosary, A note on approximate controllability of fractional semilinear integrodifferential control systems via resolvent operators. Fractal Fractional 6(2), 73 (2022)
C. Dineshkumar, R. Udhayakumar, V. Vijayakumar, K.S. Nisar, A. Shukla, A note concerning to approximate controllability of Atangana-Baleanu fractional neutral stochastic systems with infinite delay. Chaos Solitons Fractals 157, 111916 (2022)
Y.-K. Ma, K. Kavitha, W. Albalawi, A. Shukla, K.S. Nisar, V. Vijayakumar, An analysis on the approximate controllability of Hilfer fractional neutral differential systems in Hilbert spaces. Alexandria Eng. J. 61(9): 7291–7302 (2022)
R. Zarin, A. Khan, P. Kumar, Fractional-order dynamics of Chagas-HIV epidemic model with different fractional operators. AIMS Math. 7(10), 18897–18924 (2022)
K. Nisar, K.S. Sooppy, K. Jothimani, C. Ravichandran, An analysis of controllability results for nonlinear Hilfer neutral fractional derivatives with non-dense domain. Chaos Solitons Fractals 146, 110915 (2021)
E.F. Goufo, C.R. Doungmo, G.A. Birajdar, Self-similarity techniques for chaotic attractors with many scrolls using step series switching. Math. Modell. Anal. 26(4), 591–611 (2021)
C. Ravichandran, K. Logeswari, S.K. Panda, K.S. Nisar, On new approach of fractional derivative by Mittag-Leffler kernel to neutral integro-differential systems with impulsive conditions. Chaos Solitons Fractals 139, 110012 (2020)
I. Haq, N. Ali, K.S. Nisar, An optimal control strategy and Grünwald-Letnikov finite-difference numerical scheme for the fractional-order COVID-19 model. Math. Modell. Numer. Simul. Appl. 2(2), 108-116 (2022)
P. Liu, A. Din, R. Zarin, Numerical dynamics and fractional modeling of hepatitis B virus model with non-singular and non-local kernels. Res. Phys. 39, 105757 (2022)
B. Buonomo, D. Lacitignola, On the dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with a convex incidence rate. Ricerche di matematica 57, 261–281 (2008)
Y. Jin, W. Wang, S. Xiao, A SIRS model with a nonlinear incidence. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34, 1482–1497 (2007)
P. van den Driessche, J. Watmough, A simple SIS epidemic model with a backward bifurcation. J. Math. Biol. 40, 525–540 (2000)
P. van den Driessche, J. Watmough, Epidemic solutions and endemic catastrophies. In: Dynamical systems and their applications in biology, Cape Breton Island, NS, 2001. Fields Inst. Commun., vol. 36, pp. 247–257. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2003)
A. Korobeinikov, Lyapunov functions and global stability for SIR and SIRS epidemiological models with nonlinear transmission. Bull. Math. Biol. 30, 615–626 (2006)
A.E. Taylor, D.C. Lay, Introduction to Functional Analysis (Wiley, New York, 1980)
Acknowledgements
“The first author appreciates the support provided by Petchra Pra Jom Klao PhD Research Scholarship through grant no (50/2565), by King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, Thailand.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zarin, R., Raouf, A., khan, A. et al. Modeling hepatitis B infection dynamics with a novel mathematical model incorporating convex incidence rate and real data. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 1056 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04642-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04642-6