Abstract
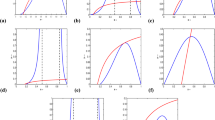
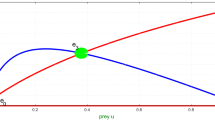
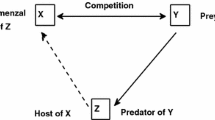
The present article concerns itself with the theoretical investigation on an interacting species model system with special emphasis on the species growth followed by Smith and a constant proportion of prey refuge. The prime objective of the study is to provide an adequate mathematical framework in order to carry out a comprehensive analytical investigation of the dynamical complexity between predator and prey species. The proposed model system is not only explored in the perception of diverse local bifurcations in a two-dimensional plane but also of the global bifurcations about coexistence equilibria under specific parametric conditions. For the purpose of validation of all the analytical outcomes together with the applicability of the model concerned, a quantitative sensitivity analysis based on numerical simulation is performed. The evolution of diffusion-driven pattern formation in two-dimensional plane in terms of spot, stripe, labyrinthine, stripe-hole mixture and hole replication as well is patently exhibited. These patterns are all influenced by both the Smith growth principle and prey refuge of the diffusive system. Finally, the influence of model parameters of significance on the dynamics of the proposed model system is, however, not ruled out to depict graphically from the present study.




























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
This research paper does not fall within the definition of “data sharing” because no code or dataset has been created or examined during the current investigation.
References
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/jan/04/lethal-algae-blooms-an-ecosystem-out-of-balance
E. Shao, Those Seaweed Blobs Headed for Florida? See How Big They Are, The New York Times, ISSN 0362-4331, April 19, (2023)
J.T. Turner, P.A. Tester, Toxic marine phytoplankton zooplankton grazers and pelagic food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 425(2), 1203–1213 (1997)
J. Norberg, D. DeAngelis, Temperature effects on stocks and stability of a phytoplankton-zooplankton model and the dependence on light and nutrients. Ecol. Model. 95(1), 75–86 (1997)
E. Beltrami, T. Carroll, Modeling the role of viral disease in recurrent phytoplankton blooms. J. Math. Biol. 32, 857–863 (1994)
J. Li, Y. Song, H. Wan, H. Zhu, Dynamical analysis of a toxin-producing phytoplankton-zooplankton model with refuge. Math. Biosci. Eng. 14(2), 529–557 (2017)
Y. Lv, Y. Pei, S. Gao, C. Li, H. Zhu, Harvesting of a phytoplankton-zooplankton model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(5), 3608–3619 (2010)
Y. Lv, Y. Pei, S. Gao, C. Li, H. Zhu, Role of toxin and nutrient for the occurrence and termination of plankton bloom-Results drawn from field observations and a mathematical model. Biosystems 90(1), 87–100 (2007)
J. Chattopadhayay, R.R. Sarkar, S. Mandal, Toxin-producing plankton may act as a biological control for planktonic blooms-field study and mathematical modelling. J. Theor. Biol. 215(3), 333–344 (2002)
E. Granéli, N. Johansson, Effects of the toxic haptophyte Prymnesium parvum on the survival and feeding of a ciliate: the influence of different nutrient conditions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 254, 49–56 (2003)
E. Granéli, N. Johansson, A phytoplankton-toxic phytoplankton-zooplankton model. Ecol. Complex 8(3), 239–248 (2011)
R. Han, G. Mandal, L.N. Guin, S. Chakravarty, Dynamical response of a reaction-diffusion predator-prey system with cooperative hunting and prey refuge. J. Stat. Mech: Theory Exp. 2022(10), 103502 (2022)
L.N. Guin, S. Djilali, S. Chakravarty, Cross-diffusion-driven instability in an interacting species model with prey refuge. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 153, 111501 (2021)
J.G. Wang, X.Y. Meng, L. Lv, J. Li, Stability and bifurcation analysis of a Beddington-DeAngelis Prey-Predator model with fear effect, prey refuge and harvesting. Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos 33(01), 2350013 (2023)
L.N. Guin, P.J. Pal, J. Alzahrani, N. Ali, K. Sarkar, S. Djilali, A. Zeb, I. Khan, S.M. Eldin, Influence of Allee effect on the spatiotemporal behaviour of a diffusive predator-prey model with Crowley-Martin type response function. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 4710 (2023)
D. Xiao, S. Ruan, Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J. Math. Biol. 43, 268–290 (2001)
W.E.I. Fengying, W. Ke, Economic harvesting model with variable price and cost for population with Smith growth and Cui Lawson growth. Int. J. Biomath. 19(3), 328–336 (2004)
F.E. Smith, Population dynamics in Daphnia magna and a new model for population growth. Ecology 44(4), 651–663 (1963)
Z. Ma, W. Li, Y. Zhao, W. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. Li, Effects of prey refuges on a predator-prey model with a class of functional responses: the role of refuges. Math. Biosci. 218(2), 73–79 (2009)
S. Samaddar, M. Dhar, P. Bhattacharya, Effect of fear on prey-predator dynamics Exploring the role of prey refuge and additional food. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary J. Nonlinear Sci. 30(6), 063129 (2020)
J. Ghosh, B. Sahoo, S. Poria, Prey-predator dynamics with prey refuge providing additional food to predator. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 96, 110–119 (2017)
C. Xiang, J. Huang, H. Wang, Bifurcations in Holling-Tanner model with generalist predator and prey refuge. J. Differential Equ. 343, 495–529 (2023)
R. Han, L.N. Guin, S. Acharya, Complex dynamics in a reaction-cross-diffusion model with refuge depending on predator-prey encounters. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137(1), 134 (2022)
Z. Wei, F. Chen, Dynamics of a Delayed Predator-Prey Model with Prey Refuge, Allee Effect and Fear Effect. Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos 33(03), 2350036 (2023)
R. Han, L.N. Guin, B. Dai, Consequences of refuge and diffusion in a spatiotemporal predator-prey model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 60, 103311 (2021)
J. Maynard-Smith, Models in Ecology (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1974)
M.P. Hassell, The Dynamics of Arthopod Predator-Prey System (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2020)
J.N. McNair, The effects of refuges on predator-prey interactions: a reconsideration. Theor. Popul. Biol. 29(1), 38–63 (1986)
J.B. Collings, Bifurcation and stability analysis of a temperature-dependent mite predator-prey interaction model incorporating a prey refuge. Bull. Math. Biol. 57, 63–76 (1995)
E. González-Olivares, R. Ramos-Jiliberto, Dynamic consequences of prey refuges in a simple model system: more prey, fewer predators and enhanced stability. Ecol. Model 166(1–2), 135–146 (2003)
Y. Huang, F. Chen, L. Zhong, Stability analysis of a prey-predator model with Holling type III response function incorporating a prey refuge. Appl. Math. Comput. 182(1), 672–683 (2006)
P.D.N. Srinivasu, I.L. Gayatri, Influence of prey reserve capacity on predator-prey dynamics. Ecol. Model. 181(2–3), 191–202 (2002)
L.N. Guin, S. Pal, S. Chakravarty, S. Djilali, Pattern dynamics of a reaction-diffusion predator-prey system with both refuge and harvesting. Int. J. Biomath. 14(1), 2050084 (2021)
M.M. Mullin, E.F. Stewart, F.J. Fuglister, Ingestion by planktonic grazers as a function of concentration of food 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20(2), 259–262 (1975)
A.M. Turing, The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philosop. Trans. Royal Series B 237(64), 37–72 (1952)
X.Y. Tao, L.H. Zhu, Study of periodic diffusion and time delay induced spatiotemporal patterns in a predator-prey system. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 150, 111101 (2021)
W.S. Burnside, A.W. Panton, The theory of equations: with an introduction to the theory of binary algebraic forms (Dublin University Press Series, Dublin, 1892)
L. Perko, Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems (Springer, New York, 2001)
S. Wiggins, Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos (Springer, New York, 2003)
Y.A. Kuznetsov, Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory (Springer, New York, 1988)
R.I. Bogdanov, Bifurcation of the limit cycle of a family of plane vector field. Sel. Math. Sov. 4, 373–387 (1981)
R.I. Bogdanov, Versal deformations of a singular point on the plane in the case of zero eigenvalues. Nonlinear Functional Anal. Appl. 9, 144–145 (1975)
F. Takens, Forced Oscillations and Bifurcations Applications of Global Analysis (Institute of Utrecht, Netherlands, 1974)
J.C. Helton, F.J. Davis, J.D. Johnson, A comparison of uncertainty and sensitivity analysis results obtained with random and Latin hypercube sampling. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 89(3), 305–330 (2005)
N. Chitnis, J.M. Hyman, J.M. Cushing, Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bull. Math. Biol. 5, 1272–1296 (2008)
M.D. Samsuzzoha, M. Singh, D. Lucy, Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the basic reproduction number of a vaccinated epidemic model of influenza. Appl. Math. Model. 37(3), 903–915 (2014)
J. Shen, Y.M. Jung, Geometric and stochastic analysis of reaction-diffusion patterns. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 19(2), 195–244 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the learned reviewers and the journal editors for their valuable suggestions and comments, which significantly improved the quality of the paper. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India, New Delhi, is gratefully acknowledged by Mr. G. Mandal, for providing financial support in the shape of a Junior Research Fellowship (File No.: 09/0202(16462)/2023-EMR-I Dated 14.03.2023).
Funding
This research has no funding at all.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S Chakravarty and LN Guin visualized the presented idea. LN Guin and G Mandal developed the analytical theory and performed numerical simulations. S Das, G Mandal, and S Dutta verified the analytical methods. All authors discussed the simulated outcomes and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that the publishing of this paper does not involve any conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All the researchers have adhered to the accepted ethical standards of a genuine research study. No animals are harmed during this research study. This research has been conducted by maintaining the balance of bio-diversity and practicing honesty in all professional relationships and endeavours.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guin, L.N., Das, S., Mandal, G. et al. Isolating patterns in a reaction-diffusion system with Smith population growth. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 829 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04466-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04466-4