Abstract
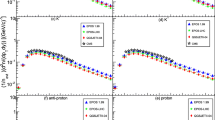
In this research article, we studied the behavior of the yields and Nuclear Modification Factors (NMFs) of the π±, K± mesons, and for the protons/antiprotons in the mid rapidity region as a function of pT (in the pT < 20 GeV/c region). Additionally, we analyzed the ratios of yields of K± mesons and protons/antiprotons to the yields of π± mesons as a function of pT in the most central Pb-Pb collisions at center of mass energy, \(\sqrt{{s}_{NN}}\)= 2.76 TeV. Our results were obtained using the EPOS-1.99, DPMJETIII-2017.1, and EPOS-LHC models, which were compared with the experimental data from the ALICE experiment. We found that the models gave similar results and effectively described the experimental data, which we attributed to the fact that the models used similar dynamics (string fragmentation) to describe the data in the considered pT region. We observed several regions for the distribution of NMFs, with the boundary values being approximately the same as those reported in a previous study, which we explained as a signal of string fragmentation and decay. We also confirmed the existence of these regions using the ratios of the yields for the particles, which showed that physics in the second and third pT regions differed from that in the first region. Lastly, our results suggested that the parton structure of matter dominated in the second and third pT regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data available online on data repository. [Authors’ comment: The ALICE experimental data are taken from http://www.hepdata.net/ from the paper https://doi.org/10.17182/hepdata.71310].
References
I. Arsene et al., Nucl. Phys. A 757, 1 (2005)
B.B. Back et al., Nucl. Phys. A 757, 28 (2005)
K. Adcox et al., Nucl. Phys. A 757, 184
J. Adams et al., Nucl. Phys. A 757, 102 (2005)
K. Aamodt et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 1 (2010)
K. Aamodt et al., Phys. Lett. B 696, 30 (2011)
B. Abelev et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 1 (2012)
G. Aad et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 1 (2010)
S. Chatrchyan et al., Phys. Rev. C-Nucl. Phys. 84, 26 (2011)
M. Gyulassy et al., Phys. Lett. B 243, 432 (1990)
M. Gyulassy et al., Nucl. Phys. B 420, 583 (1994)
E. Wang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 16 (2002)
K. Adcox et al., Nucl. Phys. 88, 6 (2001)
C. Adler et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 20 (2002)
J. Adams et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 172302 (2003)
B. Abelev et al., Phys. Lett. B 720, 52 (2013)
S. Chatrchyan et al., EPJ C 72, 1945 (2012)
C. Atlas et al., J. High Energy Phys. 9, 50 (2015)
X.N. Wang, Phys. Rev. C 58, 2321 (1998)
T. Renk et al., Phys. Rev. C. 76, 027901 (2007)
P. Abreu et al., EPJ C 17, 207 (2000)
B. Abelev et al., Phys. Lett. 736, 196 (2014)
A.O. Velasquez et al., Nucl. Phys. A 904, 763 (2013)
J. Adam et al., Phys. Rev. C 93, 034913 (2016)
K. Werner et al., Phys. Rev. C 74, 1 (2006)
K. Werner et al., Phys. Rev. C 85, 6 (2012)
R. Engel et al., Prog. Part. And Nucl. Phys. 61, 551 (2008)
K. Werner et al., Nucl. Phys. B 175, 81 (2008)
G. Aad et al., J. Instrum. 3, 8 (2013)
T. Pierog et al., Phys. Rev. C 92, 3 (2015)
S. Chatrchyan et al., J. Eur. Phys. J. C 72, 1945 (2012)
M. Suleymanov et al., Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 27, 1850008 (2018)
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Qurtuba University of Science and Information Technology, Peshawar, Kpk, Pakistan, which provided all possible facilities and a suitable platform to perform the simulations and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, Q., Ali, Y., Bashir, S. et al. Distributions of the nuclear modification factor of pions, kaons and protons in the most central Pb–Pb collisions at \(\sqrt{{s}_{NN}}\) = 2.76 TeV. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 749 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04351-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04351-0