Abstract
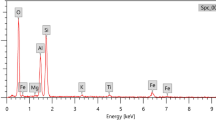
This study discusses the synergy created by mixing two different materials, which is the primary motivation for producing composites, from a different perspective. In this context, it is aimed to investigate how much a desired feature of a matrix can be improved by adding reinforcing particles to a main matrix. Following this purpose, epoxy matrix and silver particles have been chosen as the components of the composites, and the ability to protect from ionizing radiation was considered as the physical property to be developed. To obtain the highest ionizing radiation shielding ability, three different composite families have been tested: composites containing only micro-sized Ag particles (2%, 4%, 8%, 16%, and 32% by mass), containing only nano-sized Ag particles (2%, 4%, 8%, and 16% by mass), and those containing half the mass of micro- and nano-sized Ag particles (1% nano + 1% micro, 2% nano + 2% micro, 4% nano + 4% micro, 8% nano + 8% micro, and 16% nano + 16% micro by mass). The main motivation for the preparation of a composite family containing micro/nano-reinforcing particle mixtures was to examine whether there could be a synergistic effect of combining the large volume advantage of microparticles and the large surface area advantage of nanoparticles in one structure. The radiation shielding performances of the samples have been experimentally investigated in the context of linear attenuation coefficient (µ), half value layer (HVL), and mean free path (λ) parameters for photons with energies ranging from 81 to 356 keV. Finally, the particle size effect (PSE) has been discussed. PSE discussion has figured out that the greatest PSE values greater than 1 have been obtained for micro/nano-Ag particle mixtures. All available experimental data have shown that the highest µ values (1.520 cm−1 for 81 keV and 0.171 cm−1 for 356 keV) and therefore the shortest HVL (0.454 cm for 81 keV and 4.039 cm−1 for 356 keV) and λ (0.655 cm for 81 keV and 5.289 cm−1 for 356 keV) values are obtained for the epoxy-based composite having 16% micro-Ag/16% nano-Ag particle mixtures in both photon energies studied.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Brumfiel, I. Fuyuno, Nature 483, 138 (2012)
M. Almurayshid, Y. Alssalim, F. Aksouh, R. Almsalam, M. ALQahtani, M. Sayyed, F. Almasoud, Materials 14, 4957 (2021)
M. Ambika, N. Nagaiah, V. Harish, N. Lokanath, M. Sridhar, N. Renukappa, S. Suman, Radiat. Phys. Chem. 130, 351 (2017)
C.V. More, Z. Alsayed, M. Badawi, A. Thabet, P.P. Pawar, Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 2057 (2021)
K. Yue, W. Luo, X. Dong, C. Wang, G. Wu, M. Jiang, Y. Zha, Radiat. Prot. Dosim 133, 256 (2009)
L. Yu, P.L. Yap, A. Santos, D. Tran, D. Losic, A.C.S. Appl, Nano Mater. 4, 7471 (2021)
Y. Karabul, O. İçelli, Results Phys. 26, 104423 (2021)
M.J. Aldhuhaibat, M.S. Amana, N.J. Jubier, A. Salim, Radiat. Phys. Chem. 179, 109183 (2021)
Y. Ergin, Y. Karabul, Z.G. Özdemir, M. Kılıç, EJEST 16, 256 (2019)
R. Li, Y. Gu, Y. Wang, Z. Yang, M. Li, Z. Zhang, Mater. Res. Exp. 4, 035035 (2017)
M.I. Abbas, A.H. Alahmadi, M. Elsafi, S.A. Alqahtani, S. Yasmin, M.I. Sayyed, M.M. Gouda, A.M. El-Khatib, Polymers 14, 4801 (2022)
R.A. Abu Saleem, N. Abdelal, A. Alsabbagh, M. Aljarrah, F. Aljawarneh, Polymers 13, 3699 (2021)
Y. Thooyavan, L.A. Kumaraswamidhas, R.D.E. Raj, J.S. Binoj, B. Brailson Mansingh, Polym. Compos. 43, 2574 (2022)
W. Wang, Y. Yang, Sci. Rep. 7, 1 (2017)
K. Shameli, M.B. Ahmad, S.D. Jazayeri, P. Shabanzadeh, P. Sangpour, H. Jahangirian, Y. Gharayebi, Chem. Cent. J. 6, 1 (2012)
M. Zargar, A.A. Hamid, F.A. Bakar, M.N. Shamsudin, K. Shameli, F. Jahanshiri, F. Farahani, Molecules 16, 6667 (2011)
H. Klug, L. Alexander, X-Ray Diffraction Procedures 2nd edn, Ch. 9, Wiley, 1974.
G. Nelson, D. Reilly, Passive Nondestruct. Anal. Nuclear Mater. 2, 27 (1991)
A.M. El-Khatib, M.I. Abbas, M.A. Elzaher, M.S. Badawi, M.T. Alabsy, G.A. Alharshan, D.A. Aloraini, Sci. Rep. 9, 1 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by the Yildiz Technical University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Department with the Project Number of FYL-2022-5187.
Funding
Data available on request from the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalkan, N.E., İç, S., Karabul, Y. et al. Synergistic effect achieved in ionizing radiation shielding with epoxy-based composites blended with nature-inspired micro- and nanoparticle mixtures. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 628 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04262-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04262-0