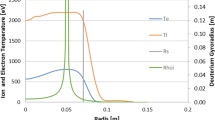
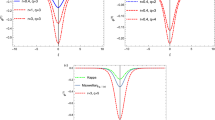
Abstract
Effects of energetic particles (EPs) on m/n = 3/1 magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instabilities have been investigated via hybrid simulations for reversed magnetic shear configurations. The simulation results shown that a global instability, energetic particle modes (EPMs), can be excited by the strong energetic particle drive with the frequency lying into the Alfvén continuum. In the linear growth stage, EPs not only induce radial broadening of mode structures but also enhance toroidal mode coupling when EP beta is large enough. In the nonlinear saturation stage, the good flux surfaces are still kept over the entire plasma area in a long time evolution of EPMs. To clarify nonlinear saturation of the mode, effects of the energetic particle beta values, the width of the particle distribution, the beam energy and the initial pitch angle on the saturation amplitude of the EPMs are discussed in detail. Furthermore, MHD nonlinearity is found to reduce the saturation level of the EPM compared to linear MHD case, while the high-n harmonics have less impact.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: All data included in this manuscript are available upon request by contacting with the corresponding author.]
References
J.F. Drake, M.A. Shay, W. Thongthai, M. Swisdak, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 095001 (2005)
F. Porcelli et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 44, B389 (2002)
Z. Chang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3553 (1996)
F.M. Levinton, S.H. Batha, M.C. Zarnstorff, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4417 (1995)
P.L. Pritchett, Y.C. Lee, J.F. Drake, Phys. Fluids 23, 1368 (1980)
J.Q. Dong, S.M. Mahajan, W. Horton, Phys. Plasmas 10, 3151 (2003)
A. Otto, G.T. Birk, Phys. Fluids B 4, 3811 (1992)
L. Ofman, Phys. Fluids B 4, 2751 (1992)
R.L. Dewar, M. Persson, Phys. Fluids B 5, 4273 (1993)
Q. Yu, Phys. Plasmas 3, 2898 (1996)
X. Wang, Z.W. Ma, A. Bhattacharjee, Phys. Plasmas 3, 2129 (1996)
Q. Yu, Phys. Plasmas 4, 1047 (1997)
Y. Ishii, M. Azumi, Y. Kishimoto, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 205002 (2002)
Z.X. Wang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 185004 (2007)
C.L. Zhang, Z.W. Ma, Phys. Plasmas 16, 122113 (2009)
A. Fasoli et al., Progress in the ITER physics basis chapter 5: physics of energetic ions. Nucl. Fusion 47, S264 (2007)
K. McGuire et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 891 (1983)
L. Chen, R.B. White, M.N. Rosenbluth, Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 1122 (1984)
L. Chen, F. Zonca, Rev. Mod. Phys. 88, 015008 (2016)
F. Zonca et al., Nucl. Fusion 47, 1588 (2007)
X.Q. Wang, X.G. Wang, Nucl. Fusion 57, 016039 (2017)
B. Gao et al., Phys. Plasmas 28, 012104 (2021)
S. Wang, Z.W. Ma, Phys. Plasmas 22(12), 122504 (2015)
J. Zhu, Z.W. Ma, S. Wang, Phys. Plasmas 23, 122506 (2016)
W. Zhang, Z.W. Ma, J. Zhu, H.W. Zhang, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion. 61(7), 075002 (2019)
W. Zhang, Z.W. Ma, X.Q. Lu, H.W. Zhang, Nucl. Fusion 60(12), 126022 (2020)
Y. Todo, Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 3, 1 (2019)
C. Cheng, M. Chance, J. Comput. Phys. 71(1), 124–146 (1987)
H. Cai et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 075002 (2011)
Y. He et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 175001 (2014)
X.Q. Wang, EPL 115, 45003 (2016)
X. Zhang, H. Cai, Z.X. Wang, Phys. Plasmas 26, 062505 (2019)
X.L. Zhu, W. Chen, F. Wang, Z.X. Wang, Nucl. Fusion 60, 046023 (2020)
W. Shen et al., Nucl. Fusion 60, 106016 (2020)
G. Meng, X.Q. Wang, X.G. Wang, R.B. Zhang, Phys. Plasmas 22, 092510 (2015)
P. Maget et al., Nucl. Fusion 46, 797 (2006)
E. Joffrin et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 44, 1203 (2002)
K. Toi et al., Nucl. Fusion 39, 1929 (1999)
K.L. Wong et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 996 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. X. G. Wang, Prof. Z. W. Ma for useful suggestions. M. Li acknowledge CLT-K team for supporting the code. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11975188, U22A20262, and the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant Nos. 2019YFE03020002, 2022YFE03070000, 2022YFE03070001 and the Science and Technology Plan Project in Sichuan Province of China under Grant Nos. 2022JDJQ0036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Wang, X.Q., Zhang, B. et al. Nonlinear simulations of energetic particle modes in tokamak plasmas with reversed magnetic shear. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 558 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04198-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04198-5