Abstract
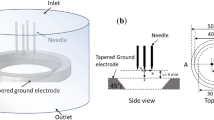
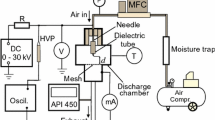
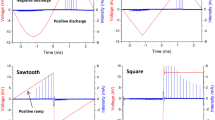
Miniaturization and high integration of electronic devices demand effective removal of heat flux, which requires an efficient cooling system. Corona wind discharge system (CWDS) with CNT-coated electrode is an attractive option for efficient cooling with low power consumption. The flow and heat transfer characteristics of the CWDS with CNT-coated electrode were experimentally investigated in the present work. Water-assisted CVD apparatus was used for the coating of CNT on needles, with Iron as catalyst. The interaction between the electrodes was experimentally studied by flow visualization method. The heat transfer characteristics of the CWDS were estimated using Mach–Zehnder interferometry, which is a powerful nonintrusive method for the measurement of heat transfer. The effect of number of electrodes, input power and the distance between the electrodes were studied experimentally and the results were compared. CWDS with CNT-coated electrode decreases the initiation voltage while increasing the velocity by 140%. The power consumption was decreased by 60% and heat transfer coefficient was found to be enhanced by 12% for CNT-coated electrode, as compared to uncoated electrodes.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.H. Shin, J.S. Yoon, H.S. Ko, Experimental optimization of ion wind generator with needle to parallel plates for cooling device. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 84, 35–45 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.01.018
Y. Zhang, L. Liu, Y. Chen, J. Ouyang, Characteristics of ionic wind in needle-to-ring corona discharge. J. Electrostat. 74, 15–20 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2014.12.008
I.Y. Chen, M.Z. Guo, K.S. Yang, C.C. Wang, Enhanced cooling for LED lighting using ionic wind. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 57, 285–291 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.10.015
J. Qu, J. Zhang, M. Li, W. Tao, Heat dissipation of electronic components by ionic wind from multi-needle electrodes discharge: experimental and multi-physical analysis. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120406
T.H. Wang, M. Peng, X.D. Wang, W.M. Yan, Investigation of heat transfer enhancement by electrohydrodynamics in a double-wall-heated channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 113, 373–383 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.05.079
S. Wang, J.G. Qu, L.J. Kong, J.F. Zhang, Z.G. Qu, Numerical and experimental study of heat-transfer characteristics of needle-to-ring-type ionic wind generator for heated-plate cooling. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 139, 176–185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2019.01.032
J. Wang, R. Fu, X. Hu, Experimental study on EHD heat transfer enhancement with a wire electrode between two divergent fins. Appl. Therm. Eng. 148, 457–465 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.11.058
A.R. Mahmoudi, F. Pourfayaz, A. Kasaeian, A simplified model for estimating heat transfer coefficient in a chamber with electrohydrodynamic effect (corona wind). J. Electrostat. 93, 125–136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2018.04.007
X. Li, D. Li, Q. Zhang, Y. Li, X. Cui, T. Lu, The detailed characteristics of positive corona current pulses in the line-to-plane electrodes. Plasma Sci. Technol. 20, 54014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-6272/aaa66b
E. Moreau, P. Audier, N. Benard, Ionic wind produced by positive and negative corona discharges in air. J. Electrostat. 93, 85–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2018.03.009
J. Wang, R. Fu, X. Hu, Comparison of EHD-enhanced convection heat transfer in two divergent fins between positive and negative voltage polarities. J. Electrostat. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2019.103358
J. Feng, C. Wang, Q. Liu, C. Wu, Enhancement of heat transfer via corona discharge by using needle-mesh and needle-fin electrodes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 130, 640–649 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.10.103
J. Zhang, F.C. Lai, Heat transfer enhancement using corona wind generator. J. Electrostat. 92, 6–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2018.01.001
I.Y. Chen, C.J. Chen, C.C. Wang, Influence of electrode configuration on the heat transfer performance of a LED heat source. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 77, 795–801 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.06.023
D.H. Shin, D.K. Jang, D.K. Sohn, H.S. Ko, Control of boundary layer by ionic wind for heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 131, 189–195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.11.058
A. Ongkodjojo-Ong, A.R. Abramson, N.C. Tien, Electrohydrodynamic microfabricated ionic wind pumps for thermal management applications. J. Heat Transf. 136, 061703 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4026807
J. Wang, T. Zhu, J. bo Wang, Y. xi Cai, X. hua Li, Optimization of a green solid-state fan for electronics cooling applications, Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments. 39 (2020) 100703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100703.
M.M. El-Bahy, M.A.A. El-Ata, Onset voltage of negative corona on dielectric-coated electrodes in air. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 38, 3403–3411 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/38/18/013
M. Abdel-Salam, H. Singer, A. Ahmed, Effect of the dielectric barrier on discharges in non-uniform electric fields. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 34, 1219–1234 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/34/8/313
Y.C. Bao, Y.X. Cai, J. Wang, Y.F. Shi, J.B. Wang, Experimental study on LED heat dissipation based on enhanced corona wind by graphene decoration. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47, 4121–4126 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2019.2924287
K. Kordás, G. Tóth, P. Moilanen, M. Kumpumäki, J. Vähäkangas, A. Uusimäki, R. Vajtai, P.M. Ajayan, Chip cooling with integrated carbon nanotube microfin architectures. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2714281
R. Vyas, P.J. Herr, T. Aloui, K. Horvath, M.P. Kirley, C.B. Parker, A.D. Keil, J.B. Carlson, J. Keogh, R.P. Sperline, M.B. Denton, M.L. Sartorelli, B.R. Stoner, M.E. Gehm, J.T. Glass, J.J. Amsden, Comparison of thermionic filament and carbon nanotube field emitter-based electron ionization sources in cycloidal coded aperture mass analyzers. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 457, 116415 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2020.116415
S. Hong, J. Lee, K. Do, M. Lee, J.H. Kim, S. Lee, D.H. Kim, Stretchable electrode based on laterally combed carbon nanotubes for wearable energy harvesting and storage devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201704353
W. Yishan, J. Li, J. Ye, X. Chen, H. Li, S. Huang, R. Zhao, W. Ou-Yang, Greener Corona Discharge for Enhanced Wind Generation with a Simple Dip-coated Carbon Nanotube Decoration. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 50, 395304 (2017)
J. Wang, T. Zhu, Y. Xi-Cai, Y. Chao-Bao, J. Bo-Wang, Comparison of the generation characteristics and application performance of nanomaterials-enhanced ionic wind. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104734
D.N. Futaba, K. Hata, T. Yamada, K. Mizuno, M. Yumura, S. Iijima, Kinetics of water-assisted single-walled carbon nanotube synthesis revealed by a time-evolution analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 1–4 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.056104
R. Smajda, J.C. Andresen, M. Duchamp, R. Meunier, S. Casimirius, K. Hernádi, L. Forró, A. Magrez, Synthesis and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes produced by the water assisted CVD process. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 246, 2457–2460 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.200982269
T. Yamada, A. Maigne, M. Yudasaka, K. Mizuno, D.N. Futaba, M. Yumura, S. Iijima, K. Hata, Revealing the secret of water-assisted carbon nanotube synthesis by microscopic observation of the interaction of water on the catalysts. Nano Lett. 8, 4288–4292 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl801981m
S.P. Patole, P.S. Alegaonkar, H.C. Lee, J.B. Yoo, Optimization of water assisted chemical vapor deposition parameters for super growth of carbon nanotubes. Carbon N. Y. 46, 1987–1993 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.08.009
Y.Y. Tsui, Y.X. Huang, C.C. Lan, C.C. Wang, A study of heat transfer enhancement via corona discharge by using a plate corona electrode. J. Electrostat. 87, 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2017.02.003
S. Ohyama, R. Ohyama, Ionic wind characteristics of an EHD micro gas pump constructed with needle-ring electrode system, Annu. Rep. Conf. Electr. Insul. Dielectr. Phenomena, CEIDP. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/CEIDP.2011.6232638.
A. Niewulis, A. Berendt, J. Podliński, J. Mizeraczyk, Electrohydrodynamic flow patterns and collection efficiency in narrow wire-cylinder type electrostatic precipitator, J. Electrostat. 71 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2013.02.002.
G.A. Kallio, D.E. Stock, Flow Visualization Inside A Wire-Plate Electrostatic Precipitator, 26 (1990).
J. Wang, X. Hu, X. Mo, Z. Sun, R. Fu, Flow and heat transfer characteristics of corona wind in two symmetric divergent fins. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 160, 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120210
J.R. Lee, E. Von Lau, Convective heat transfer enhancement of ionic wind under variable air pressures. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 160, 106657 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106657
M. Mirzaei, M. Saffar-Avval, Enhancement of convection heat transfer using EHD conduction method. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 93, 108–118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2017.12.022
M.E. Franke, K.E. Hutson, Effects of Corona Discharge on Free-Convection Heat transfer Inside a Vertical Hollow Cylinder. Heat Transf. 106, 346–351 (1984)
L.E. Hogue, M.E. Franke, Electrostatic cooling of a horizontal cylinder. J. Heat Transfer. 113, 544–548 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2910597
S.R. Mahmoudi, K. Adamiak, P. Castle, M. Ashjaee, The effect of corona discharge on free convection heat transfer from a horizontal cylinder. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 34, 528–537 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2009.11.006
M. Mohan, Convective heat transfer studies in dilute alumina and silica nanofluids flowing through a channel using Mach-Zehnder interferometry, (2020).
A. Vyas, A. Yadav, A. Srivastava, Flow and heat transfer measurements in the laminar wake region of semi- circular cylinder embedded within a rectangular channel. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 116, 104692 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104692
A. Krishnan, A.R. Ganesan, A. Mani, Interferometric analysis of flow around a horizontal tube falling film evaporator for MED systems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 161, 106745 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106745
N. Sheet, Interferometric Study of the Heat Transfer Phenomena Induced by Rapid Heating of Nickel Sheet, (2020).
J. Wang, T. Zhu, Y. xi Cai, J. fei Zhang, J. bo Wang, Review on the recent development of corona wind and its application in heat transfer enhancement, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 152 (2020) 119545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119545.
D. Naylor, Recent developments in the measurement of convective heat transfer rates by laser interferometry. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow. 24, 345–355 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-727X(03)00021-3
M. Joseph, V. Antony, V. Sajith, Characterisation of heat dissipation from PCM based heat sink using Mach-Zehnder Interferometry. Heat Mass Transf. Und Stoffuebertragung. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-021-03101-1
D. Naylor, N. Duarte, Direct temperature gradient measurement using interferometry. Exp. Heat Transf. 12, 279–294 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1080/089161599269609
J.P.Holman, Heat Transfer, Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2008.
B. Kwon, T. Foulkes, T. Yang, N. Miljkovic, W.P. King, Air Jet Impingement Cooling of Electronic Devices Using Additively Manufactured Nozzles, IEEE Trans. Components, Packag. Manuf. Technol. 10 (2020) 220–229. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCPMT.2019.2936852.
J. Wang, Y. jun Liu, T. Zhu, Y. qiang Chen, J. bo Wang, Magnetic field enhanced ionic wind for environment-friendly improvement and thermal management application, Appl. Therm. Eng. 194 (2021) 117054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117054.
E.T. Ring, I. Wind, Enhanced cooling of LED filament bulbs using an embedded tri-needle/ring ionic wind device. Energies 13, 1–20 (2020)
J. Ye, J. Li, X. Chen, S. Huang, W. Ou-Yang, Enhancement of corona discharge induced wind generation with carbon nanotube and titanium dioxide decoration. Chinese Phys. B. 28, 095202 (2019)
J. Wang, Y. Xi Cai, Y. Chao Bao, J. Bo Wang, X. Hua Li, Enhanced ionic wind generation by graphene for LED heat dissipation. Int. J. Energy Res. 43, 3746–3755 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4532
X. Yao, N. Jiang, B. Peng, H. Guo, N. Lu, K. Shang, J. Li, Y. Wu, Characteristics of a corona discharge ignited by a MgO/NiO/Ni sandwich cathode with high secondary electron emission for VOC degradation. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aadddd
J. Wang, Y. Xi Cai, X. Hua Li, X. Dong Zhao, J. Wang, Y. Fei Shi, Y. Xi Shi, Experimental investigation of high-power light-emitting diodes’ thermal management by ionic wind. Appl. Therm. Eng. 122, 49–58 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.084
J. Wang, Y. Xi Cai, X. Hua Li, Y. Fei Shi, Y. Chao Bao, Electrically-induced ionic wind flow distribution and its application for LED cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 138, 346–353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.04.091
J. Wang, T. Zhu, Y. Xi Cai, J. Bo Wang, J. Wang, Development and application of a solid-state fan for enhanced heat dissipation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 169, 114922 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.114922
D.H. Shin, S.H. Baek, H.S. Ko, Analysis of counter flow of corona wind for heat transfer enhancement. Heat Mass Transf. Und Stoffuebertragung. 54, 841–854 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-017-2183-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vibin Antony, P., Joseph, M., Ozden, S. et al. Heat transfer enhancement using CNT-coated needle electrodes in corona wind discharge system. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 524 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02723-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02723-6