Abstract
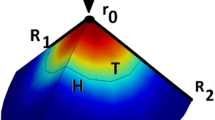
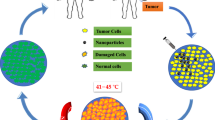
The efficient thermal damage of the malignant tissues (tumors) is the main goal in the Magnetic Hyperthermia method. The magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) transport is strongly related to the tissue parameters as the porosity and the permeability. When an external time-dependent magnetic field is applied, the spatial and temporal distributions of MNPs have a fundamental role in the thermal damage of the malignant tissues. This paper describes the influence of the tissues’ porosity on the therapeutic temperature field which determines the thermal damage of the malignant tissues. The supplementary effects related to the spatial re-distribution of the nanoparticles as a result of thermal damage-dependent porosity were discussed for the case of the constant tissue porosity. The optimum (MNP) doses needed to obtain the therapeutic temperature range (42 ÷ 46 °C) are computed for the malignant tissues. In the numerical model, the frequency f(kHz) and amplitude of the AC magnetic field are optimized to obtain the therapeutic temperature range with the maximum thermal damage. The model contains a complex analysis regarding the injection of the ferrofluid, the spatial distribution of MNPs (after their injection) and the thermal damage of the malignant tissues.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that supports the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
S. Dutz, R. Hergt, Int. J. Hyperth. 29, 790 (2013)
J. Carrey, B. Mehdaoui, M. Respaud, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 083921 (2011)
Y.-D. Tang, T. Jin, R.C.C. Flesch, Appl. Math. Model. 83, 122–135 (2020)
M. Lahonian, A.A. Golneshan, IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 10, 262 (2011)
I. Astefanoaei, A. Stancu, J. Appl. Phys. 122, 164701 (2017)
M. Salloum, R. Ma, L. Zhu, Int. J. Hyperth. 25, 309 (2009)
I. Aștefănoaei, A. Stancu, H. Chiriac, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(2), 1–12 (2017)
M. Singh, R. Ma, L. Zhu, in Theoretical Evaluation of Temperature Elevation, Thermal Damage, Tumor Porosity Enhancement and Magnetic Nanoparticle Migration in Tumors during Local Heating, Conference Paper – June (2019)
N.T. Wright, On a relationship between the Arrhenius parameters from thermal damage studies. J. Biomech. Eng. 125, 300–304 (2003)
A.W. El-Kareh, S.L. Braunstein, T.W. Secomb, Effect of cell arrangement and interstitial volume fraction on the diffusivity of monoclonal antibodies in tissue. Biophys. J. 64(5), 1638–1646 (1993)
A. Zhang, X. Mi, G. Yang, L.X. Xu, Numerical study of thermally targeted liposomal drug delivery in tumor. J Heat Transfer 131(4), 043209–043219 (2009)
Y. Tang, R.C.C. Flesch, T. Jin, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51(3), 035401 (2017)
COMSOL Multiphysics, Reference Manual, Version 5.5.
Y. Tang, R. C. C. Flesch, T. Jin, Y. Gao, M. He J. M. M. M. 517(167391) (2021)
Y. Tang, R.C.C. Flesch, T. Jin, J. Appl. Phys. 122, 034702 (2017)
I. Astefanoaei, I. Dumitru, H. Chiriac, A. Stancu, IEEE Trans Magn. 50, 11 (2014)
I. Astefanoaei, A. Stancu, J. Appl. Phys. 125, 194701 (2019)
M. Salloum, R.H. Ma, D. Weaks, L. Zhu, Int. J. Hyperth. 24, 337 (2008)
I. Astefanoaei and A. Stancu, “Numerical simulations in engineering and science,” in Modeling of the Temperature Field in the Magnetic Hyperthermia, edited by S. P. Rao (IntechOpen, 2018).
I. Astefanoaei, H. Chiriac, A. Stancu, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131(9), 1–9 (2016)
A. Golneshan, M. Lahonian, Int. J. Hyperth. 27, 266 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Astefanoaei, I., Stancu, A. Thermo-fluid porosity-related effects in the magnetic hyperthermia. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 1216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-02229-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-02229-7