Abstract.
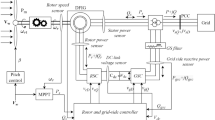
The aim of this study is to enhance DFIG based Wind Energy Conversion Systems (WECS) dynamics during grid coupling. In this paper, a system modelling and a starting/coupling procedure for this generator to the grid are proposed. The proposed non-linear system is a variable structure system (VSS) and has two different states, before and after coupling. So, two different state models are given to the system to analyse transient stability during the coupling. The given model represents well the transient state of the machine, through which, a behaviour assessment of the generator before, during and after connection is given based on simulation results. For this, a 300 kW DFIG based wind generation system model was simulated on the Matlab/SIMULINK environment. We judge the proposed procedure to be practical, smooth and stability improved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renewables 2017 Global Status Report, accessed Sep 2017, http://www.ren21.net/gsr-2017/
Ming Cheng, Ying Zhu, Energy Convers. Manag. 88, 332 (2014)
Alshehri Abdullah, Afef Fekih, An Overview of the Current State of Wind Energy Technology Development in the US, in 2013 IEEE Green Technologies Conference, 4-5 April 2013, Denver, CO, USA (IEEE, 2013) pp. 120--126, https://doi.org/10.1109/GreenTech.2013.26
Wind Report, Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), 2016, accessed on September 2016, available on-line at the following link: http://gwec.net/publications/global-wind-report-2/global-wind-report-2016/
V.N. Pande, U.M. Mate, Shailaja Kurode, Electr. Power Syst. Res. 100, 73 (2013)
S. Abdeddaim, A. Betka, Electr. Power Energy Syst. 49, 234 (2013)
Arjang Yousefi-Talouki, Edris Pouresmaeil, Bo Nørregaard Jørgensen, Electr. Power Energy Syst. 63, 600 (2014)
F. Akela, T. Ghennam, E.M. Berkouk, M. Laour, Energy Convers. Manag. 78, 584 (2014)
W. Yi, X. Lie, IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 25, 367 (2010)
S. Lei, H. Jiabing, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 27, 362 (2012)
M.I. Martinez, G. Tapia, A. Susperregui, H. Camblong, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 27, 328 (2012)
G. Abad, M.A. Rodriguez, G. Iwanski, J. Poza, IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25, 442 (2010)
M. Kenan Döşoğlu, Ali Öztürk, Adv. Eng. Softw. 45, 292 (2012)
Ali Öztürk, Kenan Döşoğlu, Investigation of the control voltage and reactive power in wind farm load bus by STATCOM and SVC, in International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering - ELECO 2009, 5--8 Nov. 2009, Bursa, Turkey, (2009) pp. I-60-I-64, https://doi.org/10.1109/ELECO.2009.5355356
M. Kenan Döşoğlu, Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 83, 251 (2016)
M. Kenan Döşoğlu, Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 78, 655 (2016)
M. Kenan Döşoğlu, Ayşen Basa Arsoy, Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 78, 414 (2016)
R. Pena, J.C. Clare, G.M. Asher, IEEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 143, 231 (1996)
S.A. Gomez, J.L.R. Amenedo, Grid synchronisation of doubly fed induction generators using direct torque control, in IEEE 2002 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society, IECON 02, 5--8 Nov. 2002, Sevilla, Spain, Vol. 4, pp. 3338-3343, https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMDC.2007.382704
Ahmed G. Abo-Khalil, Renew. Energy 44, 193 (2012)
S. Kammoun, A. Marrekchi, S. Sallem, M. Kammoun, Int. J. Mod. Nonlinear Theory Appl. 3, 77 (2014)
Gonzalo Abad, Jesús López, Miguel A. Rodríguez, Luis Marroyo, Grzegorz Iwanski, Doubly fed induction machine: modeling and control for wind energy generation (IEEE Press, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New Jersey, 2011) https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118104965
Hüseyin Altun, Sedat Sünter, Electr. Eng. 95, 157 (2013)
Rishabh Dev Shukla, Ramesh Kumar Tripathi, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 37, 69 (2014)
Eduard Muljadi, Mohit Singh, Vahan Gevorgian, Doubly Fed Induction Generator in an Offshore Wind Power Plant Operated at Rated V/Hz, in IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exhibition Raleigh, North Carolina September 15-20, Conference Paper NREL/CP-5500-55573, June 2012 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2013.2261043
A. Mechter, K. Kemih, M. Ghanes, Backstepping control of a wind turbine for low wind speeds, Nonlinear Dyn., (2016) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2655-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kammoun, S., Sallem, S. & Ben Ali Kammoun, M. Modelling and analysis of transient state during improved coupling procedure with the grid for DFIG based wind turbine generator. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11737-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11737-8