Abstract.
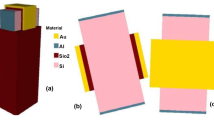
This paper was devoted to study the effects of some technological parameters (gate, oxide and doping density N a on the electrical properties of MOS structures. The conductance and capacitance were determined from a proposed admittance model. Results showed a frequency dispersion of C-V g and G-V g curves in inversion regime. This modeling takes into account the influence of series and parallel resistances (R s, R p), thickness of oxide layer, the work function of gate electrode and the doping density (N a). The C-V g and G-V g characteristics have been simulated at high frequency (100 kHz-1 MHz).With increasing frequency, the inversion capacitance is decreased whereas the conductance is strongly increased. A degradation of their shapes is shown in the operating accumulation and depletion modes. The accumulation capacitance seems to be strong for titanium oxide (TiO2) and for the oxide thickness is very small. Interestingly, the change of metal gate causes C-V g shifting and variation of the values of the flat band and threshold voltages. In the inversion mode, the C - V g and G-V g decreases with the increase of the doping density (N a). There is a shift of the flat-band and threshold voltage (V fb,V th) when N a increase. Excellent agreement was observed between the calculated and the measured C-V g curves obtained at high frequency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.E. Moore, in Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers. ISSCC. 2003 IEEE International, Vol. 1 (IEEE, 2003) pp. 20--23, DOI:10.1109/ISSCC.2003.1234194
G.E. Moore, in Proceedings of the International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM ’75), Vol. 21 (1975) pp. 11--13
A.I. Kingon, J.-P. Maria, S.K. Streiffer, Nature 406, 1032 (2000)
C. Jianjun, C. Shuming, L. Bin, L. Biwei, L. Zheng, T. Zheqian, J. Semiconduct. 31, 074006 (2010)
A. Godoy, J.A. López-Villanueva, J.A. Jiménez-Tejada, A. Palma, F. Gámiz, Solid-State Electron. 45, 391 (2001)
F.M. d’Heurle, M.O. Aboelfotoh, F. Pesavento, C.S. Petersson, Appl. Surf. Sci. 53, 237 (1991)
J.R. Hauser, K. Ahmed, AIP Conf. Proc. 235, 449 (1998)
A. Tataroğlu, S. Altindal, M.M. Bülbül, Microelectron. Eng. 81, 140 (2005)
M.M. Bülbül, S. Zeyrek, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 2522 (2006)
P. Chattopadhyay, B. RayChaudhuri, Solid State Electron. 36, 605 (1993)
V. Mikhaelashvili, Y. Betzer, I. Prudnikov, M. Orenstein, D. Ritter, G. Eisenstein, J. Appl. Phys. 84, 6747 (1998)
V. Misra, G.P. Heuss, H. Zhong, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 4166 (2001)
J. Lee, Y.-S. Suh, H. Lazar, R. Jha, J. Gurganus, Y. Lin, V. Misra, in Technical Digest - International Electron Devices Meeting (IEEE International, 2003) pp. 13.5.1--13.5.4
H. Kim, P.C. McIntyre, C.O. Chui, K.C. Saraswat, S. Stemmer, J. Appl. Phys. 96, 3468 (2004)
S. Abermann, J.K. Efavi, G. Sjoblom, M.C. Lemme, J. Olsson, E. Bertagnolli, Microelectron. Eng. 84, 1635 (2007)
E. Atanassova, A. Paskaleva, N. Novkovski, M. Georgieva, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 094104 (2005)
E. Atanassova, D. Spassov, A. Paskaleva, Microelectron. Reliab. 47, 2088 (2007)
O. Rejaiba, M. Ben Amar, A. Matoussi, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 80 (2015)
H. Mathieu, Physique de semi-conducteurs et des composantes électroniques (Masson S.A., Paris, 1998)
E.H. Nicollian, J.R. Brews, MOS Physics and Technology (Willey Interscience Publication, USA, 1982)
A. Dimoulas, G. Mavrou, G. Vellianitis, E. Evangelou, N. Boukos, M. Houssa, M. Caymax, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 032908 (2005)
P. Batude, X. Garros, L. Clavelier, C. Le Royer, J.M. Hartmann, V. Loup, P. Besson, L. Vandroux, Y. Campidelli, S. Deleonibus, F. Boulanger, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 034514 (2007)
E.H. Nicollian, A. Goetzberger, Appl. Phys. Lett. 7, 216 (1965)
G.D. Wilk, R.M. Wallace, J.M. Anthony, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5243 (2001)
M. Maitri Mishra, G. Pradhan, F. Ashraf Ali, G. Bose, in Intelligent Computing, Communication and Devices, Proceedings of ICCD., Vol. 1 (2014) pp. 499--507
H. Wong, H. Iwai, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 1867 (2006)
I.-S. Park, T. Lee, H. Ko, J. Ahn, J. Korean. Phys. Soc. 49, 760 (2006)
S.S. Ullah, M. Robinson, J. Hoey, M.S. Driver, A. Caruso, D.L. Schulz, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 27, 065012 (2012)
P.V. Gray, D.M. Brown, Appl. Phys. Lett. 13, 247 (1968)
H. Watanabe, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 52, 2265 (2005)
P. Bouillon, T. Skotnicki, IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 19, 19 (1998)
G. Yaron, D. Frohman-Bentchkowsky, Solid State Electron. 23, 433 (1980)
P. Bouillon, R. Gwoziecki, Th. Skotnicki, Member, IEEE, J. Alieu, P. Gentil, IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 47, 871 (2000)
S.M. Sze, Physics of Semiconductors (Wiley Interscience, 1969)
B.E. Deal, E.H. Snow, C.A. Mead, J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 27, 1873 (1966)
A.S. Grove, B.E. Deal, E.H. Snow, C.T. Sah, Solid-State Electron. 8, 145 (1965)
E.H. Nicollian, J.R. Brews, Small-signal steady-state capacitance methods, in Mos (metal oxide semiconductor) physics and technology, Wiley Classics Library (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, N.J., 2003) pp. 334--336
V. Midili, Realization of a capacitance-voltage measurement system for semiconductor characterization, Thesis, Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering Degree Programme of Micro and Nanotechnology (2012)
G. Baccarani, S. Solmi, G. Soncini, Alta Frequenza 16, 113 (1972)
D.C. Wheeler, Dissertation submitted to the Graduate School of the University of Notre Dame, High-k-inas metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitors formed by atomic-layer deposition (India, 2009)
A. Paula, B. Ziliotto, Marcello Bellodi, VII Microelectronics Student Forum, SFORUM (2007) http://www.lbd.dcc.ufmg.br/colecoes/sforum/2008/0054.pdf
M. Shur, Surface charge in metal oxide semiconductor capacitor, in Physics of Semi-conductor devices, edited by Nick Holonyak Jr. (Prentice Hall New Jersey, Upper Saddle River, 1990) pp. 332--343
C. Chakraborty, J. Adv. Dielectr. 4, 1450023 (2014)
H. Chakraborty, D. Misra, Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 3, 1 (2013)
J.A. Luna-Lopez, M. Aceves-Mijares, O. Malik, Soc. Mex. Ciencia Superf. Vacío. 17, 1 (2004)
P. Fernández-Martínez, F.R. Palomo, S. Hidalgo, C. Fleta, F. Campabadal, D. Flores, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 5, 108 (2013)
E. Atanassova, D. Spassov, A. Paskaleva, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 1918 (2006)
D. Spassov, E. Atanassova, D. Virovska, Appl. Phys. A 82, 55 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11433-9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rejaiba, O., Braña, A. & Matoussi, A. Study of various technological parameters on the C-Vg and the G-Vg characteristics of MOS structures. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 281 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16281-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16281-5