Abstract
Graphic Abstract
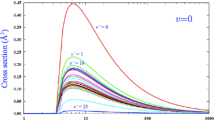
We report a detailed study of features of electron impact excitation (EIE) of Ca IV (Ca IV + e \(\rightarrow \) Ca IV* + \(e' \rightarrow \) Ca IV + h\(\nu + e'\)), for the first time using the relativistic Breit–Pauli R-matrix method with a large close-coupling wave function expansion of 54 fine structure levels belonging to \(n=2,3,4\) complexes. Calcium lines in the infrared (IR) region are expected to be observed by the high-resolution James Webb Space Telescope. Our study predicts the presence of a strong 3.2 \(\upmu \)m emission line in IR formed due to EIE of \(3p^{5~ 2}P^o_{3/2}-3p^{5~2}P^o_{1/2}\) in Ca IV. The EIE collision strength (\(\Omega \)) for the transition shows extensive resonance with enhanced background (top panel, Figure below), resulting in an effective collision strength (\(\Upsilon \)) of 2.2 at about 10\(^4\) K that increases to 9.66 around 3\(\times 10^5\) k (lower panel, Figure below). The present results include \(\Omega \) for all 1431 excitations among the 54 levels and \(\Upsilon \) for a limited number of transitions of possible interest. We found extensive resonances in the low-energy region of \(\Omega \), and convergence of the resonances and of the partial waves with the 54-level wave function. At high energy, \(\Omega \) decreases beyond the resonance region for forbidden transitions and is almost constant or decreases slowly for dipole-allowed transitions with low oscillation strength (f-values) and increases with Coulomb–Bethe behavior of ln(E) to almost a plateau for transitions with high f-values. The wave function of Ca IV was obtained from optimization of 13 configurations \(3s^23p^5, 3s3p^6, 3s^23p^43d, 3s^23p^44s, 3s^23p^44p, 3s^23p^44d, 3s^23p^44f, 3s^23p^45s, 3s3p^53d, 3s3p^54s, 3s3p^54p, 3p^63d, 3s3p^43d^2\), each with the core configuration of \(1s^22s^22p^6\), using the SUPERSTRUCTURE atomic structure program. They produce 387 fine structure levels. We report transition parameters—oscillator strength, line strength (S) and A-values-for a total of 93,296 electric dipole (E1), quadrupole (E2), octupole (E3), magnetic dipole (M1) and quadrupole (M2) transitions among these levels. The lifetimes of these levels are also presented.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: All atomic data for energies, radiative transitions, collisional excitations, and effective collision strengths of a set of transitions are available online at the NORAD-Atomic-Data database at the Ohio State University at: https://norad.astronomy.osu.edu/.]
References
S.N. Shore, T. Augusteijn, A. Ederoclite, H. Uthas, A &A 533, L8 (2011)
M. Asplund, N. Grevesse, A.J. Sauval, P. Scott, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 47, 481–52 (2009)
J. Shepherd (2019) https://www.astrobin.com/full/406485/0/
W.V. Jacobson-Galan et al., Astrophys. J. 898, 166 (2020)
H. Feuchtgruber et al., ApJ 487, 962 (1997)
R. Ignanc, J.P. Cassinelli, M. Quigley, B. Babler, ApJ 558, 771–779 (2001)
H. Feuchtgruber, D. Lutz, D.A. Beintema, ApJS 136, 221 (2001)
B. Zuckerman, D. Koester, I.N. Reid, M. Hunsch, ApJ 596, 477 (2003)
A.K. Pradhan, S.N. Nahar, Atomic Astrophysics and Spectroscopy (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2011)
J. Sugar, C. Corliss, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 14(Suppl. 2), 1–664 (1985)
A.M. Naqvi, PhD Thesis Harvard University (1951) (data available at NIST)
C.M. Varsavsky, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 6, 75–107 (1961)
B.C. Fawcett, A.H. Gabriel, Proc. Phys. Soc. 88, 262 (1966)
K.-N. Huang, Y.-K. Kim, K.T. Cheng, J.P. Desclaux, ADNDT28, 355–377 (1983)
N.J. Wilson, A. Hibbert, K.L. Bell, Phys. Scr. 61, 603–610 (2000)
A.H. Gabriel, B.C. Fawcett, C. Jordan, Proc. Phys. Soc. 87, 825 (1966)
D.G. Hummer, K.A. Berrington, W. Eissner, A.K. Pradhan, H.E. Saraph, J.A. Tully, Astron. Astrophys. 279, 298–309 (1993)
K.A. Berrington, W. Eissner, P.H. Norrington, Comput. Phys. Commun. 92, 290–420 (1995)
W. Eissner, M. Jones, H. Nussbaumer, Comput. Phys. Commun. 8, 270–306 (1974)
S.N. Nahar, W. Eissner, G.X. Chen, A.K. Pradhan, A &A 408, 789 (2003)
P.G. Burke, W.D. Robb, Adv. At. Mol. Phys. 11, 143–214 (1975)
N.S. Scott, P.G. Burke, J. Phys. B 12, 4299 (1980)
N.S. Scott, K.T. Taylor, Comput. Phys. Commun. 25, 347 (1982)
A. Burgess, J.A. Tully, J. Phys. B 11, 4271 (1978)
S.N. Nahar, Written in, unpublished (2013)
S.N. Nahar, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 127, 253 (2000)
NORAD-Atomic-Data, https://norad.astronomy.osu.edu/
Acknowledgements
All computations were carried on the high-performance computers of the Ohio Supercomputer Center. BS acknowledges the IRSIP fellowship from the Government of Pakistan to carry out the research at the Ohio State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors, S.N. Nahar and B. Shafique, contributed equally to the contents of the paper. While SNN trained BS, set up the project, wrote necessary program, and remained engaged in studying the project, BS picked up all aspects of computations, carried out computations, and was engaged in the analysis.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nahar, S., Shafique, B. Collisional excitation and photoexcitation of Ca IV including a strong 3.2 \(\upmu \)m emission line. Eur. Phys. J. D 77, 45 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00622-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00622-8