Abstract
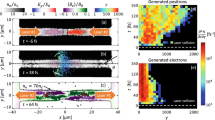
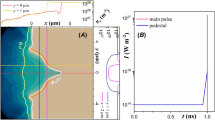
By using two counter-propagating ultra-intense lasers interaction with a solid aluminum (Al) target, an all-optical scheme was demonstrated with the generation of high-bright GeV photons and high energy density electron–positron pairs. The multi-photon Breit–Wheeler (BW) process is simulated by Particle-in-cell (PIC) code EPOCH with a quantum electrodynamics (QED) module implemented. The target front side keeps still due to the involvement of hot electrons in the target in two colliding laser schemes. High-frequency photons are produced by hot electrons colliding with the reflected laser pulse at the front of the target, followed by electron and positron pairs production. On the lateral side of the target, electron bunches are extracted from the target by the p-polarized laser electromagnetic field and accelerated by the laser pondermotive force to collide with the counter-propagating laser. By modulating the target transversal size, the pulse energy is allocated to the target front side and lateral side. It is found that on the lateral side the laser will be more efficient in the generation of gamma photons and positrons, which may helpful for investigating high-energy pair production and gamma-ray emission. The generated positrons are as dense as 40 nc and can be accelerated to over 1 GeV. On the target longitudinally front side, the participation of hot electrons in the target plays an important role in the generation of photons and positrons. When the target length is set to the corrected skin depth of the plasma, electrons are fully involved in photon production. The pairs yield reaches 1.68 × 1011, whose density is 90 nc. These findings propose a feasible scheme to produce high-energy and high-density pair plasma for extensive scientific research and applications.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Date Availability Statement
“This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request].
References
D. Strickland, G. Mourou, Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 55(6), 447–449 (1985)
A. Dubietis, G. Jonušauskas, A. Piskarskas, Powerful femtosecond pulse generation by chirped and stretched pulse parametric amplification in BBO crystal. Opt. Commun. 88(4–6), 437–440 (1992)
S. Gales et al., The extreme light infrastructure—nuclear physics (ELI-NP) facility: new horizons in physics with 10 PW ultra-intense lasers and 20 MeV brilliant gamma beams. Rep. Prog. Phys. 81(9), 094301 (2018)
I.B. Mukhin et al., Design of the front-end system for a subexawatt laser of the XCELS facility. Quantum Electron. 51(9), 759 (2021)
J. Kataoka et al., Multiwavelength Observations of the powerful gamma-ray quasar PKS 1510–089: Clues on the jet composition. Astrophys. J. 672(2), 787 (2008)
B.W. Stappers et al., An X-ray nebula associated with the millisecond pulsar B1957+ 20. Science 299(5611), 1372–1374 (2003)
B. Cerutti, A.A. Philippov, G. Dubus, Dissipation of the striped pulsar wind and non-thermal particle acceleration: 3D PIC simulations. Astron. Astrophys. 642, A204 (2020)
A.D. Piazza et al., Extremely high-intensity laser interactions with fundamental quantum systems. Rev. Modern Phys. 84(3), 1177–1228 (2011)
H. Chen et al., Making relativistic positrons using ultraintense short pulse lasers. Phys. Plasmas 16(12), 105001 (2009)
E.P. Liang, S.C. Wilks, M. Tabak, Pair production by ultraintense lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(22), 4887 (1998)
S.V. Bulanov et al., On the problems of relativistic laboratory astrophysics and fundamental physics with super powerful lasers. Plasma Phys. Rep. 41(1), 1–51 (2015)
C. Müller, C.H. Keitel, Abundant positron production. Nat. Photonics 3(5), 245–246 (2009)
O.J. Pike et al., A photon–photon collider in a vacuum hohlraum. Nat. Photonics 8(6), 434–436 (2014)
G. Breit, J.A. Wheeler, Collision of two light quanta. Phys. Rev. 46(12), 1087 (1934)
X.L. Zhu, T.P. Yu, Z.M. Sheng, Y. Yin, I.C. Turcu, A. Pukhov, Dense GeV electron–positron pairs generated by lasers in near-critical-density plasmas. Nat. Commun. 7(1), 1–8 (2016)
W.H. Furry, On bound states and scattering in positron theory. Phys. Rev. 81(1), 115 (1951)
T. Grismayer et al., Laser absorption via quantum electrodynamics cascades in counter propagating laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 23(5), 056706 (2016)
X.L. Zhu, Y. Yin, T.P. Yu et al., Enhanced electron trapping and γ ray emission by ultra-intense laser irradiating a near-critical-density plasma filled gold cone. New J. Phys. 17(5), 053039 (2015)
Yu. Lu et al., Enhanced copious electron–positron pair production via electron injection from a mass-limited foil. Plasma Phys. Controll. Fusion 60(12), 125008 (2018)
J.X. Liu et al., Enhanced electron–positron pair production by ultra intense laser irradiating a compound target. Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 58(12), 125007 (2016)
T.P. Yu, A. Pukhov, Z.M. Sheng et al., Bright betatronlike x rays from radiation pressure acceleration of a mass-limited foil target. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(4), 45001–45001 (2013)
C.P. Ridgers et al., Dense electron-positron plasmas and ultraintense γ rays from laser-irradiated solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(16), 165006 (2012)
T. Yuan et al., Target transverse size and laser polarization effects on pair production during ultra-relativistic-intense laser interaction with solid targets. Phys. Plasmas 24(6), 063104 (2017)
C.S. Brady et al., Gamma-ray emission in near critical density plasmas. Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 55(12), 124016 (2013)
T.D. Arber et al., Contemporary particle-in-cell approach to laser-plasma modelling. Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 57(11), 113001 (2015)
D. Del Sorbo, D.R. Blackman, R. Capdessus, K. Small, C. Slade-Lowther, W. Luo, M.J. Duff, A.P. Robinson, P. McKenna, Z.M. Sheng, J. Pasley, Efficient ion acceleration and dense electron–positron plasma creation in ultra-high intensity laser-solid interactions. New J. Phys. 20(3), 033014 (2018)
D. Seipt et al., Polarized QED cascades. New J. Phys. 23(5), 053025 (2021)
A.R. Bell, J.G. Kirk, Possibility of prolific pair production with high-power lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(20), 2952–2965 (2008)
C.P. Ridgers et al., Dense electron-positron plasmas and bursts of gamma-rays from laser-generated quantum electrodynamic plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 20(5), 056701 (2013)
T.G. Blackburn et al., Scaling laws for positron production in laser–electron-beam collisions. Phys. Rev. A 96, 2 (2017)
J. Zhao, Y.T. Hu, Y. Lu et al., All-optical quasi-monoenergetic GeV positron bunch generation by twisted laser fields. Commun. Phys. 5, 15 (2022)
Z. Guo et al., Leveraging radiation reaction via laser-driven plasma fields. Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 61, 6 (2019)
X.Q. Yan et al., Generating high-current monoenergetic proton beams by a circularlypolarized laser pulse in the phase-stable acceleration regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(13), 135003–135003 (2008)
W. Zhou et al., High quality ion acceleration through the interaction of two matched counterpropagating transversely polarized Gaussian lasers with a flat foil target. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 21(2), 21301–21301 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11975308, 11805278, 11775305, 12005297, and 12075306), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant Nos.XDA25050200 and XDB16010600), The authors wish to acknowledge CFSA at the University of Warwick for allowing the usage of EPOCH. 32254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software. YM: Supervision, Project administration, Funding Acquisition, Writing-Review&Editing. XHY: Resources, Software. GBZ:Resources, Software. JXL: Supervision, Project administration, Funding Acquisition, Writing-Review&Editing. YY: Software,Validation. MP: Software,Validation. YC: Software,Validation. SK: Methodology.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
High Field QED Physics. Guest editors: Francesco Pegoraro, David A. eis, Gianluca Sarri, Tongpu Yu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zi, M., Ma, Y.Y., Yang, X.H. et al. High-energy–density positron and \({\upgamma }\)-photon generation via two counter-propagating ultra-relativistic laser irradiating a solid target. Eur. Phys. J. D 77, 41 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00597-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00597-6