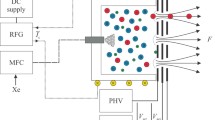
Abstract
We present a global model of a radio-frequency ion thruster. The model takes into account radial and axial density distributions for electrons and ions of the plasma inside the ionization vessel. These spatial distributions are based on analytical equations and heuristic assumptions and are used self-consistently in all conservation equations. They are considered in the 3D computation of electromagnetic fields and used to calculate the induced power generated by the coil current. We also consider the spatial ionization and excitation inside the plasma volume in the context of energy and charge conservation. Furthermore, the model includes effects of local charge and power losses on the walls. The extraction grid system is modeled in detail describing each extraction channel separately. The spatial dependence of the electron and ion density profile also leads to a radially varying ion beam current and ion focus across the grid system. Therefore, the parameters of each beamlet differ and need to be described individually by the 3D ion extraction code. An extension of the extraction code also simulates the neutral gas transmission coefficient of the aperture system. This approach enables us to determine the neutral gas density inside the ionization vessel as well as the neutral gas losses. The peripheral electric losses in the coil, the RF cables and the radio-frequency generator are derived by a circuit model.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Löb, Die Verwendungsmöglichkeit der Hochfrequenzionenquelle in elektrostatischen Raketentriebwerken, Professorial dissertation, Naturwissenschaftliche Fakulät derJustus Liebig-Universität, Gießen, Germany, 1967
H.R. Kaufman, Adv. Electron. Electron Phys. 36, 265 (1974)
H. Leiter, J. Kuhmann, R. Kukies, J.P. Porst, Results from the RIT-22 technology maturity demonstration activity, in Proceedings of the 50th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Cleveland, Ohio, 2014, Proceeding AIAA 2014-3421
R. Killinger, R. Kukies, M. Surauer, Orbit Raising with Ion Propulsion on ESA’s ARTEMIS Satellite, in Proceedings of the 38th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Joint Propulsion Conferences, Indianapolis, IN, 2002, Proceeding AIAA-2002-3672
P. Chabert, N. Braithwaite, Physics of Radio-Frequency Plasmas (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2011)
A. Lieberman, M. Lichtenberg, Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing, 2nd edn. (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2005)
D. Goebel, I. Katz, Fundamentals of Electric Propulsion: Ion and Hall Thrusters (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2008)
R.B. Piejak, V.A. Godyak, B.M. Alexandrovich, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 1, 179 (1992)
J.T. Gudmundsson, M.A. Liebermann, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 6, 540 (1997)
M.M. Tsay, Simple performance modeling of a radio-frequency ion thruster, in Proceedings of the 30th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Florence, Italy, 2007, Proceeding IEPC-2007-072
D.M. Goebel, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36, 2111 (2008)
C. Volkmar, U. Ricklefs, Eur. Phys. J. D 69, 227 (2015)
M. Dobkevicius, D. Feili, Eur. Phys. J. D 70, 227 (2016)
M. Dobkevicius, D. Feili, J. Propul. Power 44, 940 (2017)
C. Volkmar, A. Neumann, C. Geile, K. Hannemann, Real-time in situ determination of inductively coupled power and numerical prediction of power distribution in RF ion thrusters, in Proceedings of the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, Georgia, 2017, Proceeding IEPC-2017-161
Fortran program, MAGBOLTZ, S.F. Biagi, versions 8.97, Biagi database, http://www.lxcat.net
R.P. McEachran, A.D. Stauffer, Eur. Phys. J. D 68, 153 (2014), COP database, http://www.lxcat.net
R. Henrich, Development of a plasma simulation tool for Radio Frequency Ion Thrusters, Ph.D. dissertation, I. Physikalisches Institut, Justus Liebig-Universität, Giessen, Germany, 2013
A. Bondi, J. Phys. Chem. 68, 441 (1964)
R. Henrich, D. Feili, C. Heiliger, Self-consistent Simulation of the Coupling Between Plasma and Neutral Gas in μN-RIT, in , Proceedings of the 32nd International Electric Propulsion Conference, Wiesbaden, Germany, 2011, Proceeding IEPC-2011-323
K. Jousten (ed.), Wutz Handbuch Vakuumtechnik (Vieweg + Teubner, Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010)
D. Hanel, Molekulare Gasdynamik, Einfhrung in die kinetische Theorie der Gase und Lattice-Boltzmann-Methode (Springer, Berlin, Germany, 2004)
M. Schäfer, Plasmadiagnostik und Energiebilanzuntersuchung an dem HF-Ionentriebwerk RIT 10, Ph.D. dissertation, Naturwissenschaftliche Fakulät der Justus Liebig-Universität, Gießen, Germany, 1971
N.S. Mühlich, K. Holste, P.J. Klar, Near-field beam diagnostics for radio-frequency ion thrusters RIT, in Proceedings of the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017
V.A. Godyak, Soviet Radio Frequency Discharge Research (Delphic Associates, Falls Church, VA, 1986)
V. Godyak, N. Sternberg, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 17, 025004 (2008)
W.L. Briggs, H. Van Emden, S.F. McCormick, A Multigrid Tutorial, 2nd edn. (SIAM, 2000)
J.D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd edn. (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 1998)
A. Reeh, U. Probst, P.J. Klar, 3D ion extraction code incorporated self-consistently into a numerical model of a radio-frequency ion thruster, in Proceedings of the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, Georgia, 2017, Proceeding IEPC-2017-326
T. Kalvas, O. Tarvainen, T. Ropponen, O. Steczkiewicz, J. Ärje, H. Clar, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81, 02B703 (2010)
T. Kalvas, Development and use of computational tools for modelling negative hydrogen ion source extraction systems, Ph.D. dissertation, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland, 2013
C.C. Farnell, Performance and lifetime simulation of ion thruster optics, Ph.D. dissertation, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, 2007
C.K. Birdsall, A.B. Langdon, Plasma Physics via Computer Simulation, 1st edn. (Adam Hilger, Bristol, Philadelphia, New York, 1991)
J. Simon, U. Probst, P.J. Klar, Trans. JSASS Aerospace Tech. Jpn. 14, Pb_33 (2016)
J. Simon, Entwicklung und Aufbau eines Radiofrequenzgenerators zur Versorgung und elektrischen Charakterisierung induktiv-gekoppelter Plasmen in Radiofrequenz-Ionentriebwerken, Ph.D. dissertation, I. Physikalisches Institut, Justus Liebig-Universität, Giessen, Germany, 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reeh, A., Probst, U. & Klar, P.J. Global model of a radio-frequency ion thruster based on a holistic treatment of electron and ion density profiles. Eur. Phys. J. D 73, 232 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2019-100002-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2019-100002-3