Abstract
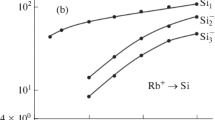
Measurements of Si2+ and Si+ ions sputtered due to bombardment of 3–5 keV Ar+ ions on silicon substrate have been performed for understanding exact charge-state formation mechanisms. Examination on the penetration depth dependence of incident particle on secondary ion formation has been performed. A closure look at the energetics of the secondary ions from their kinetic energy distributions suggests that Si+ ions are predominantly formed in the upper surface layer and Si2+ ions are produced due to target-target symmetric collision-induced Si 2p shell vacancy creation following the Auger electron emission. Furthermore, the increase in the oxygen-induced impurity in the silicon substrate enables us to explore the gradual transition from the dominating symmetric to asymmetric collision channel for production of Si2+ ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Sarkar, P. Chakraborty, H. Gnaser, Phys. Rev. B 70, 195427 (2004)
B. Saha, S. Sarkar, P. Chakraborty, H. Gnaser, Surf. Sci. 602, 1061 (2008)
A. Wucher, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 1194 (2008)
X. Chen, Z. Sroubek, J.A. Yarmoff, Phys. Rev. B 73, 132408 (2006)
X. Chen, Z. Sroubek, J.A. Yarmoff, Phys. Rev. B 71, 245412 (2005)
S.F. Belykh, V.V. Palitsin, A. Adriaens, F. Adams, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 203, 172 (2003)
Z. Sroubek, J. Lorincik, Surf. Rev. Lett. 6, 257 (1999)
D.V. Klushin, M.Y. Gusev, S.A. Lysenko, I.F. Urazgil’din, Phys. Rev. B 54, 7062 (1996)
S.N. Schauer, P. Williams, Phys. Rev. B 46, 15452 (1992)
M. Minniti et al., Phys. Rev. B 75, 045424 (2007)
X. Chen, Z. Sroubek, J.A. Yarmoff, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 264, 23 (2007)
R. Whaley, E.W. Thomas, J. Appl. Phys. 56, 1505 (1984)
N. Mandarino, P. Zoccali, A. Oliva, M. Camarca, A. Bonanno, F. Xu, Phys. Rev. A 48, 2828 (1993)
R.A. Baragiola, L. Nair, T.E. Madey, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 58, 322 (1991)
S. Kyoh, K. Takakuwa, M. Sakura, M. Umezawa, A. Itoh, N. Imanishi, Phys. Rev. A 51, 554 (1995)
M.H. Shapiro, T.A. Tombrello, J. Fine, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 74, 385 (1993)
Y. Sakuma, M. Kato, N. Shinde, S. Yagi, K. Soda, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 908 (2008)
Y. Sakuma, N. Shinde, M. Kato, S. Yagi, K. Soda, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 258, 230 (2007)
P. Williams, C.A. Evans, Surf. Sci. 78, 324 (1978)
J.F. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, M.D. Ziegler, The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter (SRIM Co., Chester, 2008), www.srim.org
Y. Sakuma, M. Kato, S. Yagi, K. Soda, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 269, 999 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, S., Gnaser, H. & Chakraborty, P. Symmetric and asymmetric collision effects on the formation of singly and doubly-charged ions in sputtering process. Eur. Phys. J. D 66, 197 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2012-30107-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2012-30107-4