Abstract
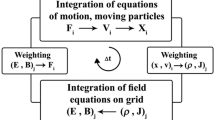
This paper is focused on the study of the electrical charging process of micron-sized particles immersed into low-temperature argon plasma by the methods of computer modelling. The hybrid computer simulations are performed for a set of particles with the radius up to \(20~{\rm \mu m}\) in order to determine the dependence of the electric charge on the surface of the particulate on its radius. This dependence seems to be linear. The distribution of the electric potential in the vicinity of the particulate is obtained from the fluid model. Afterwards, the non self-consistent particle simulation is performed in order to determine both the reaction rates and the electric charge on the surface of the particulate. The most important collision processes of charged particles in plasma and the appropriate dependence of the collision cross-section on the particle energy are considered (elastic scattering of electrons on neutrals, excitation of neutrals into all important energetic states, ionisation of Argon atoms by fast electrons, elastic scattering of positively charged ions etc.). The presented algorithm provides an effective way, how the key quantity in dusty plasma physics – electric charge on the surface of the particulate – can be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Kersten, H. Deutsch, G.M.V. Kroesen, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 233, 51 (2004)
E.B. Tomme, D.A. Law, J.E. Annaratone, J.E. Allen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2518 (2000)
V.E. Fortov, A.P. Nefedov, V.I. Molotkov, M.Y. Poustylnik, V.M. Torchinski, Phys. Rev. Lett. 233, 205002 (2001)
B. Walch, M. Horanyi, S. Robertson, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 22, 97 (1994)
B. Walch, M. Horanyi, S. Robertson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 838 (1995)
P. Bartoš, R. Hrach, P. Jelínek, Vacuum 82, 220 (2007)
P. Bartoš, R. Hrach, P. Jelínek, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 48, 406 (2008)
A. Bogaerts, R. Gijbels, W. Goedheer, J. Appl. Phys. 38, 4404 (1999)
M. Horváth, Ph.D. thesis, Charles University in Prague, 2002
H.R. Skulerud, Null collision method (Norwegian Inst. of Technology, Trondhaim, 1972)
P.K. Shukla, A.A. Mamun, Introduction to Dusty Plasma Physics (IOP, Bristol and Philadelphia, 2002)
A.A. Samarian, S.V. Vladimirov, Phys. Rev. E 67, 066404 (2003)
S.V. Vladimirov, N.F. Cramer, P.V. Schevchenko, Phys. Rev. E 60, 7369 (1999)
S.V. Vladimirov, S.A. Maiorov, N.F. Cramer, Phys. Rev. E 63, 045401(R) (2001)
A.A. Samarian, S.V. Vladimirov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 229501 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartoš, P., Blažek, J., Jelínek, P. et al. Hybrid computer simulations: electrical charging of dust particles in low-temperature plasma. Eur. Phys. J. D 54, 319–323 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00029-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00029-5