Abstract
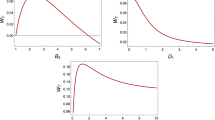
We construct an entangled quantum heat engine (EQHE) based on two two-spin systems with Dzyaloshinski-Moriya (DM) anisotropic antisymmetric interaction. By applying the explanations of heat transferred and work performed at the quantum level in Kieu’s work [Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 140403 (2004)], the basic thermodynamic quantities, i.e., heat transferred, net work done in a cycle and efficiency of EQHE are investigated in terms of DM interaction and concurrence. The validity of the second law of thermodynamics is confirmed in the entangled system. It is found that there is a same efficiency for both antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic cases, and the efficiency can be controlled in two manners: (1) only by spin-spin interaction J and DM interaction D; (2) only by the temperature T and concurrence C. In order to obtain a positive net work, we need not entangle all qubits in two two-spin systems and we only require the entanglement between qubits in a two-spin system not be zero. As the ratio of entanglement between qubits in two two-spin systems increases, the efficiency will approach infinitely the classical Carnot one. An interesting phenomenon is an abrupt transition of the efficiency when the entanglements between qubits in two two-spin systems are equal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.D. Kieu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 140403 (2004); T.D. Kieu, Eur. Phys. J. D 39, 115 (2006)
I. Zutic, J. Fabian, S. Das Sarma, Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323 (2004)
Q.F. Sun, X.C. Xie, J. Wang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 196801 (2007)
A. Einstein, B. Podolsky, N. Rosen, Phys. Rev. 47, 777 (1935)
E. Schrödinger, Proc. Cam. Phil. Soc. 32, 446 (1936)
J. Preskill, Lect. Notes. Quant. Inform. Comput. (2001) http://www.theory.caltech.edu/~preskill/ph219
R. Horodecki, P. Horodecki, M. Horodecki, K. Horodecki, arXiv:quant-ph/0702225 (2007)
C.H. Bennett, D.P. DiVincenzo, Nature 404, 247 (2000)
M.C. Arnesen, S. Bose, V. Vedral, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 277901 (2001)
D. Gunlycke et al., Phys. Rev. A 64, 042302 (2001)
X. Wang, P. Zanardi, Phys. Lett. A 301, 1 (2002)
M. Asoudeh, V. Karimipour, Phys. Rev. A 70, 052307 (2004); M. Asoudeh, V. Karimipour, Phys. Rev. A 71, 022308 (2005)
T. Zhang, W.-T. Liu, P.-X. Chen, C.-Z. Li, Phys. Rev. A 75, 062102 (2007)
I. Dzyaloshinskii, J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 4, 241 (1958)
T. Moriya, Phys. Rev. Lett. 4, 228 (1960); T. Moriya, Phys. Rev. 117, 635 (1960); T. Moriya, Phys. Rev. 120, 91 (1960)
X.G. Wang, Phys. Lett. A 281, 101 (2001)
S. Hill, W.K. Wootters, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 5022 (1997)
W.K. Wootters, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2245 (1998)
E. Schrödinger, Statistical Thermodynamics (Dover, New York, 1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G.F. Entangled quantum heat engines based on two two-spin systems with Dzyaloshinski-Moriya anisotropic antisymmetric interaction. Eur. Phys. J. D 49, 123–128 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2008-00133-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2008-00133-0