Abstract.
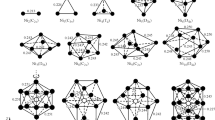
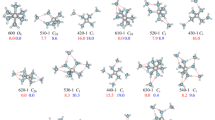
Optimized structures and cohesive energies of small mercury clusters (HgN; N = 3–7, 13, 19) are calculated with the spin-orbit diatomics-in-molecules method. The theory takes into account the effect of s-p mixing which tends to enhance the binding energies in the ground state. It is shown that excimer clusters have significantly short optimum bond lengths and their atomic geometries differ considerably from those in the ground state. Excitation energy gap depends sensitively on both cluster size and nearest-neighbor separation. Numerical results are compared with other theories and experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Hensel, W.W. Warren Jr, Fluid Metals (Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, 1999), Chap. 4
P. Schwerdtfeger, R. Wesendrup, G.E. Moyano, A.J. Sadlej, J. Grief, F. Hensel, J. Chem. Phys. 115, 7401 (2001)
E. Czuchaj, F. Rebentrost, H. Stoll, H. Preuss, Chem. Phys. 214, 277 (1997)
J. Koperski, Phys. Rep. 369, 177 (2002)
C.W. Eaker, C.A. Parr, J. Chem. Phys. 64, 1322 (1976); J.C. Tully, Adv. Chem. Phys. 42, 63 (1980)
H. Kitamura, Chem. Phys. Lett. 425, 205 (2006)
H. Kitamura, Chem. Phys. 325, 207 (2006)
M.R. Hoare, P. Pal, Adv. Phys. 20, 161 (1971)
M. Dolg, H.-J. Flad, Mol. Phys. 91, 815 (1997)
H. Haberland, H. Kornmeier, H. Langosch, M. Oschwald, G. Tanner, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 86, 2473 (1990)
B. Paulus, K. Rosciszewski, Chem. Phys. Lett. 394, 96 (2004)
G.E. Moyano, R. Wesendrup, T. Söhnel, P. Schwerdtfeger, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 103401 (2002)
R. Busani, M. Folkers, O. Cheshnovsky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3836 (1998)
R.E. Drullinger, M.M. Hessel, E.W. Smith, J. Chem. Phys. 66, 5656 (1977)
A.B. Callear, Chem. Rev. 87, 335 (1987)
M.A. Omary, P. Sinha, P.S. Bagus, A.K. Wilson, J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 690 (2005)
H. Kitamura, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15, 6427 (2003)
G. Raabe, R.J. Sadus, J. Chem. Phys. 119, 6691 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitamura, H. Cohesive properties of mercury clusters in the ground and excited states. Eur. Phys. J. D 43, 33–36 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2007-00069-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2007-00069-9