Abstract.
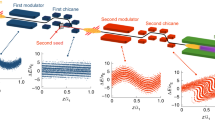
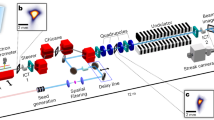
Many scientific disciplines ranging from physics, chemistry and biology to material sciences, geophysics and medical diagnostics need a powerful X-ray source with pulse lengths in the femtosecond range [1-4]. This would allow, for example, time-resolved observation of chemical reactions with atomic resolution. Such radiation of extreme intensity, and tunable over a wide range of wavelengths, can be accomplished using high-gain free-electron lasers (FEL) [5-10]. Here we present results of the first successful operation of an FEL at a wavelength of 32 nm, with ultra-short pulses (25 fs FWHM), a peak power at the Gigawatt level, and a high degree of transverse and longitudinal coherence. The experimental data are in full agreement with theory. This is the shortest wavelength achieved with an FEL to date and an important milestone towards a user facility designed for wavelengths down to 6 nm. With a peak brilliance exceeding the state-of-the-art of synchrotron radiation sources [4] by seven orders of magnitude, this device opens a new field of experiments, and it paves the way towards sources with even shorter wavelengths, such as the Linac Coherent Light Source [3] at Stanford, USA, and the European X-ray Free Electron Laser Facility [4] in Hamburg, Germany.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A VUV Free Electron Laser at the TESLA Test Facility at DESY. Conceptual Design Report, DESY, TESLA-FEL 95-03 (1995)
F. Richard et al., TESLA Technical Design Report, DESY 2001-11 (2001) and http://tesla.desy.de
The LCLS Design Study Group: LCLS Design Study Report, SLAC-R521, Stanford (1998) and http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/lcls/CDR
R. Brinkmann et al., TESLA XFEL: First stage of the X-ray laser laboratory-Technical design report, DESY 2002-167 (2002) and http://xfel.desy.de
A.M. Kondratenko, E.L. Saldin, Part. Accelerators 10, 207 (1980)
Ya.S. Derbenev, A.M. Kondratenko, E.L. Saldin, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 193, 415 (1982)
R. Bonifacio, C. Pellegrini, L.M. Narducci, Opt. Commun. 50, 373 (1984)
K.J. Kim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 1871 (1986)
S. Krinsky, L.H. Yu, Phys. Rev. A 35, 3406 (1987)
E.L. Saldin, E.A. Schneidmiller, M.V. Yurkov, The Physics of Free Electron Lasers (Springer, Berlin, 1999)
V. Ayvazyan et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 104802 (2002)
V. Ayvazyan et al., Eur. Phys. J. D 20, 149 (2002)
H. Wabnitz et al., Nature 420, 482 (2002)
L. Juha et al., Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 507, 577 (2003)
The TTF FEL team, SASE FEL at the TESLA Test Facility, Phase 2, DESY Print TESLA-FEL 2002-01 (2002)
M. Krasilnikov et al., Optimizing the PITZ Electron Source for the VUV FEL, Proc. EPAC 2004 Conference, Lucerne, Switzerland, 360 (2004)
S. Schreiber, Commissioning of the VUV-FEL Injector at TTF, Proc. EPAC 2004 Conference, Lucerne, Switzerland, 351 (2004)
K. Flöttmann, Ph. Piot, An Upgraded Injector for the TTF FEL User Facility, Proc. EPAC 2002 Conference, Paris, France, 1798 (2002)
H. Weise, Superconducting RF Structures - Test Facilities and Results, Proc. 2003 Part. Acc. Conf., Portland, Oregon, 673 (2003)
T. Limberg et al., Design and Performance Simulation of the TTF-FEL II Bunch Compression System, Proc. EPAC 2002 Conference, Paris, France, 811 (2002)
E.L. Saldin, E.A. Schneidmiller, M.V. Yurkov, Expected properties of the radiation from VUV-FEL at DESY (femtosecond mode of operation), DESY Print TESLA-FEL 2004-06 (2004)
J. Pflüger, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 445, 366 (2000)
M. Dohlus et al., Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 530, 217 (2004)
K. Flöttmann, Astra User Manual, http://www.desy.de/∼mpyflo/Astra_dokumentation/
M. Borland, elegant: A flexible SDDS-Compilant Code for Accelerator Simulation, APS LS-287 (September 2000)
B. Steffen et al., EOS Electro Optical Bunch Length Measurements at the VUV-FEL at DESY, Proc. 2005 Part. Acc. Conf., Knoxville, TN, USA (2005)
P. Krejcik et al., Commissioning of the SPPS Linac Bunch Compressor, Proc. 2003 Part. Acc. Conf., Portland, Oregon, 423 (2003)
R. Akre et al., Bunch length measurements using a transverse RF deflecting structure in the SLAC linac, Proc. EPAC 2002 Conference, Paris, France (2002)
E.L. Saldin, E.A. Schneidmiller, M.V. Yurkov, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 429, 233 (1999)
A. Bytchkov et al., Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 528, 254 (2004)
M. Richter et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2970 (2003)
E.L. Saldin, E.A. Schneidmiller, M.V. Yurkov, Opt. Commun. 148, 383 (1998)
P. Nicolosi et al., On-line spectral monitoring of the VUV-FEL beam at DESY, Proc. 2004 FEL Conference, Trieste, Italy, pp. 415-418 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayvazyan, V., Baboi, N., Bähr, J. et al. First operation of a free-electron laser generating GW power radiation at 32 nm wavelength. Eur. Phys. J. D 37, 297–303 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2005-00308-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2005-00308-1