Abstract.
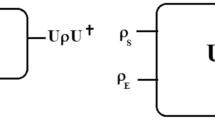
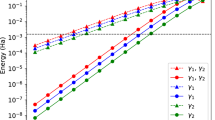
A general error correction method is presented which is capable of correcting coherent errors originating from static residual inter-qubit couplings in a quantum computer. It is based on a randomization of static imperfections in a many-qubit system by the repeated application of Pauli operators which change the computational basis. This Pauli-Random-Error-Correction (PAREC)-method eliminates coherent errors produced by static imperfections and increases significantly the maximum time over which realistic quantum computations can be performed reliably. Furthermore, it does not require redundancy so that all physical qubits involved can be used for logical purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Nielsen, I.L. Chuang, Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge UP, 2000)
D. Deutsch, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 400, 97 (1985)
P.W. Shor, In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, edited by S. Goldwasser (IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA, 1994), p. 124
L.K. Grover, Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 325 (1997)
S. Lloyd, Science 273, 1073 (1996)
R. Schack, Phys. Rev. A 57, 1634 (1998); B. Georgeot, D.L. Shepelyansky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 2890 (2001)
W.H. Zurek, Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 715 (2003)
For a comprehensive list of pioneering work on quantum error correction see, e.g., reference Nielsen00
For some more recent developments see, e.g., G. Alber, Th. Beth, Ch. Charnes, A. Delgado, M. Grassl, M. Mussinger, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4402 (2001); Ch. Ahn, H.M. Wiseman, G.J. Milburn, Phys. Rev. A 67, 052310 (2003); A.M. Steane, preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0304016; E. Knill, preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0404104
B. Georgeot, D.L. Shepelyansky, Phys. Rev. E 62, 3504 (2000); B. Georgeot, D.L. Shepelyansky, Phys. Rev. E 62, 6366 (2000)
G. Benenti, G. Casati, S. Montangero, D.L. Shepelyansky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 227901 (2001)
K.M. Frahm, R. Fleckinger, D.L. Shepelyansky, Eur. Phys. J. D 29, 139 (2004)
S.-J. Chang, K.-J. Shi, Phys. Rev. A 34, 7 (1986)
F.M. Izrailev, Phys. Rep. 196, 299 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kern, O., Alber, G. & Shepelyansky, D. Quantum error correction of coherent errors by randomization. Eur. Phys. J. D 32, 153–156 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2004-00196-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2004-00196-9