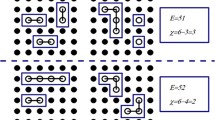
Abstract
We study the quantum self-organization of a few interacting particles with strong short-range interactions. The physical system is modeled via a 2D Hubbard square lattice model, with a nearest-neighbor interaction term of strength U and a second nearest-neighbor hopping t. For t=0, the energy of the system is determined by the number of bonds between particles that lie on adjacent sites in the Hubbard lattice. We find that this bond order persists for the ground and some of the excited states of the system, for strong interaction strength, at different fillings of the system. For our analysis, we use the Euler characteristic of the network/graph grid structures formed by the particles in real space (Fock states), which helps to quantify the energetical(bond) ordering. We find multiple ground and excited states, with integer Euler numbers, whose values persist from the \(t=0\) case, for strong interaction \(U>>t\). The corresponding quantum phases for the ground state contain either density-wave-order(DWO) for low fillings, where the particles stay apart form each other, or clustering-order(CO) for high fillings, where the particles form various structures as they condense into clusters. In addition, we find various excited states containing superpositions of Fock states, whose probability amplitudes are self-tuned in a way that preserves the integer value of the Euler characteristic from the \(t=0\) limit.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. All the numerical data from our calculations are displayed/plotted inside the figures.
References
M. Tsuchiizu, A. Furusaki, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 056402 (2002)
M. Murakami, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 69, 1113 (2000)
D.K. Campbell, J.T. Gammel, E.Y. Loh Jr., Phys. Rev. B 42, 475 (1990)
S.J. Gu, S.S. Deng, Y.Q. Li, H.-Q. Lin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 086402 (2004)
Guido Masella, Adriano Angelone, Fabio Mezzacapo, Guido Pupillo, V. Nikolay, Prokof’ev Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 045301 (2019)
I. Kleftogiannis, I. Amanatidis, Eur. Phys. J. B 92, 198 (2019)
I. Kleftogiannis, I. Amanatidis, J. Stat. Mech. 083108 (2020)
Ioannis Kleftogiannis, Ilias Amanatidis, Vladislav Popkov, J. Stat. Mech. 063102 (2019)
Ioannis Kleftogiannis, Ilias Amanatidis, Eur. Phys. J. B 93, 84 (2020)
Ioannis Kleftogiannis, Ilias Amanatidis, Eur. Phys. J. B 94, 41 (2021)
F.D.M. Haldane, Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 1358 (1980)
F.D.M. Haldane, Phys. Lett. A 93, 464 (1983)
I. Affleck, T. Kennedy, E.H. Lieb, H. Tasaki, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 799 (1987)
M. Levin, X.-G. Wen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 110405 (2006)
Chen X, Gu Z.-C., Wen X.-G., Phys. Rev. B. 82, 155138 (2010)
Kitaev A, Preskill J, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 110404 (2006)
A.Y. Kitaev, Ann. Phys. 303, 2 (2003)
V. Alba, M. Fagotti, P. Calabrese, J. Stat. Mech. P10020 (2009)
Alba V, Haque M, Luchli M, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(110), 260403 (2013)
I. Hen, M. Rigol, Phys. Rev. B 80, 134508 (2009)
A. Hamma, R. Ionicioiu, P. Zanardi, Phys. Rev. A 71, 022315 (2005)
P. Calabrese, A. Lefevre, Phys. Rev. A f78, 032329 (2008)
F. Pollmann, A.M. Turner, E. Berg, M. Oshikawa, Phys. Rev. B 81, 064439 (2010)
L. Amico, R. Fazio, A. Osterloh, V. Vedral, Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 517 (2008)
R. Horodecki, P. Horodecki, M. Horodecki, K. Horodecki, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865 (2009)
D.C. Tsui, H.L. Stormer, A.C. Gossard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 48(48), 1559 (1982)
E.B. Laughlin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 1395 (1983)
H.L. Stormer, D.C. Tsui, A.C. Gossard, Rev. Mod. Phys. 71(S298), S305 (1999)
H. Li, F.D.M. Haldane, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 010504 (2008)
F.D.M. Haldane, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 116801 (2011)
B. Chen, G. Chen, Gauss-Bonnet formula, finiteness condition, and asymptotic characterization for graphs embedded in surfaces Graphs. Combin. 24, 159–183 (2008)
O. Knill, A discrete Gauss-Bonnet type theorem, Elemente der Mathematik 67 (1): 1-44 (2012) arXiv:1009.2292 2010
O. Knill, A graph theoretical Gauss-Bonnet-Chern theorem, arXiv:1111.5395 (2011)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the resources, infrastructure and financial support provided by the Project HPC-EUROPA3 (INFRAIA-2016-1-730897), funded by the EC Research Innovation Action under the H2020 Programme, GRNET and the ARIS-GRNET computing network, along with the Physics Department at the University of Ioannina in Greece.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors I.K. and I.A. contributed equally to the design and implementation of the research, the analysis of the results and the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kleftogiannis, I., Amanatidis, I. Energetical self-organization of a few strongly interacting particles. Eur. Phys. J. B 96, 151 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-023-00613-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-023-00613-z