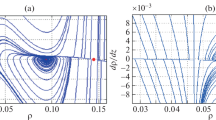
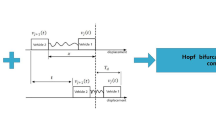
Abstract
Bifurcation of traffic flow involves complex dynamic characteristics of the system. In order to understand the complex traffic phenomenon, this work designed a macro traffic model considering the driver’s memory which plays an important role in the traffic flow. Based on this model, we investigate the effects of the driver’s memory and wave velocity on the stability of the traffic flow. By means of one and two parameter bifurcation analysis, we explore how these parameters affect the bifurcation structure of the system, and further investigate the dynamic mechanisms of traffic flow. We explain various traffic phenomena related to the different types of equilibrium points and limit cycles by phase plane analysis. We also study how the initial density and bifurcation structure affect the energy consumption in the system. The results show that the driver’s memory and wave velocity play an important role in the stability of the traffic flow. By considering the change of bifurcation structure, we can better understand the source of traffic congestion, and further predict and control the possible traffic congestion.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Data availability statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
W. Pan, X.L. Chen, X.J. Duan, Energy dissipation and particulate emission at traffic bottleneck based on NaSch model. Eur. Phys. J. B 95, 105 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00360-7
D. Helbing, M. Moussaid, Analytical calculation of critical perturbation amplitudes and critical densities by non-linear stability analysis of a simple traffic flow model. Eur. Phys. J. B 69, 571–581 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2009-00042-6
T.Q. Tang, J. He, Y.H. Wu, Propagating properties of traffic flow on a ring road without ramp. Phys. A 396, 164–172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2013.11.019
C. Gao, Y. Fan, S.H. Jiang, Y. Deng, J.M. Liu, X.H. Li, Dynamic robustness analysis of a two-layer rail transit network model. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23, 6509–6524 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3058185
T. Nagatani, TDGL and MKDV equation for jamming transition in the lattice models of traffic. Phys. A 264, 581–592 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4371(98)00466-X
K.K. Huang, S. Li, P.L. Dai, Z. Wang, Z.F. Yu, SDARE: A stacked denoising autoencoder method for game dynamics network structure reconstruction. Neural Netw. 126, 143–152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2020.03.008
K.K. Huang, Y.S. Liu, Y.C. Zhang, C.H. Yang, Z. Wang, Understanding cooperative behavior of agents with heterogeneous perceptions in dynamic networks. Phys. A 509, 234–240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.06.043
Z. Wang, S. Kokubo, M. Jusup, J. Tanimoto, Universal scaling for the dilemma strength in evolutionary games. Phys. Life Rev. 14, 1–30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2015.04.033
J.J. Ye, K.P. Li, X.M. Jin, Simulating train movement in an urban railway based on an improved car-following model. Chin. Phys. B 12, 65–69 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/22/12/120206
R. Jiang, Q.S. Wu, Z.J. Zhu, Full velocity difference model for a car-following theory. Phys. Rev. E 64, 017101 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.64.017101
H.M. Zhang, Driver memory traffic viscosity and a viscous traffic flow model. Transp. Res. Part B 37, 27–41 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-2615(01)00043-1
T.Q. Tang, H.J. Huang, S.G. Zhao, G. Xu, An extended OV model with consideration of driver’s memory. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 23, 743–752 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979209051966
B.G. Cao, A new car-following model considering driver’s sensory memory. Phys. A 427, 218–225 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.01.078
Y.Q. Sun, H.X. Ge, R.J. Cheng, An extended car-following model considering drivers memory and average speed of preceding vehicles with control strategy. Phys. A 521, 752–761 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.01.092
Z.P. Li, W.Z. Li, S.Z. Xu, Y.Q. Qian, Analyses of vehicle’s self-stabilizing effect in an extended optimal velocity model by utilizing historical velocity in an environment of intelligent transportation system. Nonlinear Dyn. 80, 529–540 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1886-z
W.X. Zhu, H.M. Zhang, Analysis of mixed traffic flow with human-driving and autonomous cars based on car-following model. Phys. A 496, 274–285 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.12.103
Q.T. Zhai, H.X. Ge, R.J. Cheng, An extended continuum model considering optimal velocity change with memory and numerical tests. Phys. A 490, 774–785 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.08.152
R.D. Kuhne, Macroscopic freeway model for dense traffic-stop-start waves and incident detection. International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory 21-42 (1984)
H.K. Lee, H.W. Lee, D. Kim, Steady-state solutions of hydrodynamic traffic models. Phys. Rev. E 69, 016118 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.69.016118
T. Li, Nonlinear dynamics of traffic jams. Phys. D 60, 550–556 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2005.05.011
P. Saavedra, R.M. Velasco, Phase-space analysis for hydrodynamic traffic models. Phy. Rev. E 79, 066103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.79.066103
F.A. Carrillo, J. Delgado, P. Saavedra, R.M. Velasco, F. Verduzco, Travling waves catastrophes and bifurcations in a generic second order traffic flow model. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 23, 1350191 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127413501915
B.S. Kerner, P. Konhauser, Cluster effect in initially homogeneous traffic flow. Phys. Rev. E 48, 2335–2338 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.48.R2335
J. Delgado, P. Saavedra, Global bifurcation diagram for the Kerner–Konhauser traffic flow model. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 25, 1550064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127415500649
W.H. Ai, Z.K. Shi, D.W. Liu, Bifurcation analysis of a speed gradient continuum traffic flow model. Phys. A 437, 418–429 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.06.004
W.R. Ren, R.J. Cheng, H.X. Ge, Bifurcation control in an optimal velocity model via double time-delay feedback method. IEEE Access 8, 216162 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3041794
W. Ren, H.X. Ge, Bifurcation analysis for a novel heterogeneous continuum model considering electronic throttle angle changes with memory. Appl. Math. Comput. 401, 126079 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2021.126079
W. Ren, H.X. Ge, Bifurcation analysis of a heterogeneous continuum traffic flow model. Appl. Math. Model. 94, 369–387 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.01.025
Q.T. Zhai, H.X. Ge, R.J. Cheng, An extended continuum model considering optimal velocity change with memory and numerical tests. Phys. A 490, 774–785 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.08.152
M. Herrmann, B.S. Kerner, Local cluster effect in different traffic flow models. Phys. A 255, 163–188 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4371(98)00102-2
X.Y. Guan, R.J. Cheng, H.X. Ge, Bifurcation control of optimal velocity model through anticipated effect and response time-delay feedback methods. Phys. A 574, 125972 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1886-z
T.Q. Tang, H.J. Huang, H.Y. Shang, An extended macro traffic flow accounting for the driver’s bounded rationality and numerical tests. Phys. A 468, 322–333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2016.10.092
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11872003) and North China University of Technology Research Fund Program for Key Discipline (No. 110052972027/014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SF designed the study, carried out the computations, analyzed the results, and wrote the first draft. LD supervised the project, contributed to the mathematical formulation. DL and ZH contributed to analysis of the results.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, L., Fan, S., Liu, D. et al. Two-parameter bifurcation and energy consumption analysis of the macro traffic flow model. Eur. Phys. J. B 95, 203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00469-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00469-9