Abstract
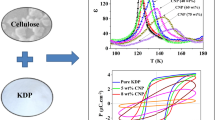
For the first time, a composite from polycrystals of KH2PO4 (KDP) with a filler of cellulose nanoparticles (CNP) was prepared to investigate the influence of cellulose on domain-wall freezing and ferroelectricity of KDP. The extrapolation of experimental data using Vogel–Fulcher law demonstrated a higher temperature of domain-wall freezing in KDP/CNP composite in comparison with pure KDP. In addition, the impact of CNP led to the expansion of ferroelectric phase in KDP and the red-shift of relaxation frequencies. Besides, the deformation of P–E hysteresis loops with the increase in coercive field as well as the decrease in saturated and remnant polarization was also detected.
Graphical abstract

Synthesis of KDP/CNP composite







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors' comment: The study provides initial results of electrophysical properties for the KDP/CNP composite, a deeper analysis of data is still in progress and will be reported with a dataset in next publications.]
References
E.I. Moses, Advances in inertial confinement fusion at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). Fusion Eng. Des. 85, 983 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2009.11.006
Q. Wang, W. Cong, Z.J. Pei, H. Gao, R. Kang, Rotary ultrasonic machining of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystal: an experimental investigation on surface roughness. J. Manuf. Process. 11, 66 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2009.09.001
K. Manimekalai, N. Padmamalini, G. Vinitha, P. Jayaprakash, Crystal growth and physico-chemical characterization of methyl ammonium chloride doping on the characteristics of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal for nonlinear optical applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 137, 109207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109207
Y. Wang, D. Sun, J. Chen, C. Shen, G. Liu, D. Wang, S. Wang, Linear and nonlinear optical characteristics effected by Na+ ions of low concentration for potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal. Optik 251, 168481 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168481
A. Ciżman, T. Marciniszyn, E. Rysiakiewicz-Pasek, A. Sieradzki, T.V. Antropova, R. Poprawski, Size effects in KDP-porous glass ferroelectric nanocomposites. Phase Transit. 86, 910 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2012.745537
S.A. Hayward, M.C. Gallardo, E.K.H. Salje, Ferroelectric phase transition in DKDP: a macroscopic order-disorder model. Ferroelectrics 255, 123 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190108225971
N.I. Uskova, E.V. Charnaya, D.Y. Podorozhkin, S.V. Baryshnikov, A.Y. Milinskiy, Impact of opal nanoconfinement on the ferroelectric transition in deuterated KDP. Results Phys. 26, 104354 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104354
H.T. Nguyen, M.T. Chau, Structural and dielectric studies of three-phase composite containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes, nanodispersed silica and KDP. Phase Transit. 93, 1080 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2020.1839753
H. Wang, Z. Li, M. Zuo, X. Zeng, X. Tang, Y. Sun, L. Lin, Stretchable, freezing-tolerant conductive hydrogel for wearable electronics reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals toward multiple hydrogen bonding. Carbohydr. Polym. 280, 119018 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.119018
J. Kawahara, P. Andersson Ersman, X. Wang, G. Gustafsson, H. Granberg, M. Berggren, Reconfigurable sticker label electronics manufactured from nanofibrillated cellulose-based self-adhesive organic electronic materials. Org. Electron. 14, 3061 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2013.07.013
D. Belaineh, R. Brooke, N. Sani, M.G. Say, K.M.O. Håkansson, I. Engquist, M. Berggren, J. Edberg, Printable carbon-based supercapacitors reinforced with cellulose and conductive polymers. J. Energy Storage 50, 104224 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.104224
E. Nakamura, K. Kuramoto, K. Deguchi, K. Hayashi, Mechanism of domain freezing in KDP type ferroelectrics. Ferroelectrics 98, 51 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150198908217569
Y.N. Huang, X. Li, Y. Ding, Y.N. Wang, H.M. Shen, Z.F. Zhang, C.S. Fang, S.H. Zhuo, P.C.W. Fung, Domain freezing in potassium dihydrogen phosphate, triglycine sulfate, and CuAlZnNi. Phys. Rev. B 55, 16159 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.55.16159
M.V. Talanov, A.A. Pavelko, L.S. Kamzina, Domain-wall freezing in Cd2Nb2O7 pyrochlore single crystal. Mater. Res. Bull. 145, 111548 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111548
N.I. Uskova, D.Y. Podorozhkin, E.V. Charnaya, S.V. Baryshnikov, A.Y. Milinskiy, D.Y. Nefedov, A.S. Bugaev, M.K. Lee, L.J. Chang, NMR and dielectric studies of ferroelectric nanocomposites with KDP. Ferroelectrics 514, 50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2017.1357980
B.D. Mai, H.T. Nguyen, D.H. Ta, Effects of moisture on structure and electrophysical properties of a ferroelectric composite from nanoparticles of cellulose and triglycine sulfate. Braz. J. Phys. 49, 333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-019-00658-5
C. Shi, X.-B. Han, W. Zhang, Structural phase transition-associated dielectric transition and ferroelectricity in coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 378, 561 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.09.020
E.V. Colla, A.V. Fokin, Y.A. Kumzerov, Ferroelectrics properties of nanosize KDP particles. Solid State Commun. 103, 127 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-1098(97)00132-4
M. Trainer, Ferroelectrics the Curie–Weiss law. Eur. J. Phys. 21, 459 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1088/0143-0807/21/5/312
R. Pirc, R. Blinc, Vogel–Fulcher freezing in relaxor ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 76, 020101 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.020101
M. Ikeda, M. Aniya, Understanding the Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann law in terms of the bond strength–coordination number fluctuation model. J. Non Cryst. Solids 371–372, 53 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.04.034
D.S. Bystrov, E.A. Popova, The molecular aspect of ferroelectricity in KDP crystals. Ferroelectrics 72, 147 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150198708017944
B.A. Strukov, S.A. Taraskin, A.B. Suvkhanov, Defects and ferroelectric phase transitions. Ferroelectrics 124, 189 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150199108209436
J.S. Zhu, K. Chen, W. Li, F. Yan, Y.R. Dai, X.M. Lu, Y.N. Wang, Mechanical and dielectric investigation on point defects and phase transition in ferroelectric ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 442, 49 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.04.139
B.D. Mai, H.T. Nguyen, M.T. Chau, Effects of hydrogen bonds on dielectric relaxation of composites based on hydrogen-bonded ferroelectrics. Phase Transit. 93, 228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2019.1709122
V.M. Rudyak, Dielectric viscosity and other properties of ferroelectrics. Ferroelectrics 35, 251 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150198108017701
N.M. Galiyarova, Critical slowing down of relaxing domain walls and interfaces in phase transition vicinities. Ferroelectrics 170, 111 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150199508014197
V.H. Schmidt, G. Bohannan, D. Arbogast, G. Tuthill, Domain wall freezing in KDP-type ferroelectrics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 61, 283 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(99)00294-2
K. Abe, Optical and X-ray studies of domain formation in KH2PO4 crystal. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 56, 757 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.56.757
A. Feisst, P. Koidl, Current induced periodic ferroelectric domain structures in LiNbO3 applied for efficient nonlinear optical frequency mixing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 47, 1125 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.96349
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, H.T. Anomalous domain-wall freezing and ferroelectricity of KDP polycrystals under influence of nanocellulose filler. Eur. Phys. J. B 95, 196 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00461-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00461-3