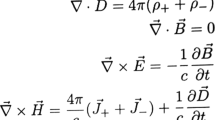Abstract
The role of the chiral magnetic effect (CME) in Weyl semimetals is considered within the framework of classical electrodynamics. The dispersion relation of electromagnetic waves is studied using their helical polarization. It has been shown that the refractive index in this class of materials becomes negative in the frequency range below the plasma frequency. The CME (a signature of chiral anomaly/ axial anomaly) which is due to the application of parallel electric and magnetic fields in Weyl semimetals thus opens up a new way of realizing negative refractive index (NRI). The relevance of the present work to negative refraction through chiral route where cross polarization (magnetization) induced by magnetic fields (electric fields) occurs in chiral materials is discussed. This novel phenomenon of negative refraction in Weyl semimetals might help in exploiting this class of materials in potential applications.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data, data sharing is not applicable.
References
V.G. Veselago, Electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative electrical and magnetic permeabilities. Sov. Phys. Usp. 10, 509 (1968)
J.B. Pendry et al., Magnetism from conductors and enhanced non-linear phenomena. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 47, 2075 (1999)
R.A. Shelby, D.R. Smith, S. Schultz, Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction. Science 292, 77 (2001)
V.M. Shalaev, Optical negative-index metamaterials. Nature Photonics. 1, 509 (2007)
S. Tretyakov et al., Waves and energy in chiral nihility. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 17, 695 (2003)
J.B. Pendry, A chiral route to negative refraction. Science 306, 1353 (2004)
C. Monzon, D.W. Forester, Negative refraction and focusing of circularly polarized waves in optically active media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 123904 (2005)
S. Zhang et al., Negative refractive index in chiral metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 023901 (2009)
X. Wan, A.M. Turner, A. Vishwanath, S.Y. Savrasov, Topological semimetal and Fermi-arc surface states in the electronic structure of pyrochlore iridates. Phys. Rev. B 83, 205101 (2011)
N. P. Armitage, E. J. Mele, Ashvin Viswanath, “Weyl and Dirac semimetals in three-dimensional solids”, Rev. Mod. Phys. 90, 015001 (2018)
H.B. Nielsen, M. Ninomiya, The Adler-Bell-Jackiw anomaly and Weyl Fermions in a crystal. Phys. Lett. B 130, 389 (1983)
Di. Xiao, Yugui Yao, Zhong Fang, Qian Niu, Berry phase effect in anomalous thermoelectric transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 026603 (2006)
P. Hosur, X.L. Qi, Recent developments in transport phenomena in Weyl semimetals. Comptes Rendus Physique 14, 857 (2013)
A.A. Burkov, Chiral anomaly and transport in Weyl metals. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 27, 113201 (2015)
S. Adler, Axial-vector vertex in spinor electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 177, 2426 (1969)
J.S. Bell, R. Jackiw, A PCAC puzzle: \(\pi ^0\rightarrow \gamma \gamma \) in the - model. Nuovo Cimento A 60, 47 (1969)
D.T. Son, B.Z. Spivak, Chiral anomaly and classical negative magnetoresistence of Weyl metals. Phys. Rev. B 88, 104412 (2013)
Xiaochun Huang et al., Observation of the chiral anomaly induced negative magnetoreistence in 3D Weyl semimetal \(TaAs\). Phys. Rev. X 5, 031023 (2015)
C. Zhang et al., Signature of the Adler-Bell-Jackiw chiral anomaly in a Weyl fermion semimetal. Nature Commun. 7, 10735 (2015)
Qiang Li et al., Chiral magnetic effect in \(ZrTe_5\). Nature Phys. 12, 550 (2016)
A.A. Zyuzin, S. Wu, A.A. Burkov, Weyl semimetal with broken time reversal and inversion symmetries. Phys. Rev. B 85, 165110 (2012)
A.A. Zyuzin, A.A. Burkov, Topological response in Weyl semimetals and the chiral anomaly. Phys. Rev. B 86, 115133 (2012)
P. Goswami, S. Tewari, Axionic field theory of (3+1) dimensional Weyl semimetals. Phys. Rev. B 88, 245107 (2013)
M.A. Stephanov, Y. Yin, Chiral kinetic theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 162001 (2012)
K. Fukushima, D.E. Kharzeev, H.J. Warringa, Chiral magnetic effect. Phys. Rev. D 78, 074033 (2008)
M.M. Vazifeh, M. Franz, Electromagnetic response of Weyl semimetals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 027201 (2013)
Y. Chen, Si Wu, A. A. Burkov, “Axion response in Weyl semimetals”, Phys. Rev. B 88, 125105 (2013)
See the text by J. D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, John Wiley and Sons. Inc., New York, (1962)
Due to the axion action mentioned in the introduction, the Gauss’s law and the Ampere’s law can respectively be written as, \(\vec{\nabla }.\vec{E}=4\pi (\rho +\frac{\alpha }{2\pi ^2}\vec{Q}.\vec{B}) \) and \(\vec{\nabla }\times \vec{B}=\frac{4\pi }{c} [\vec{J} +\frac{\alpha }{2\pi ^2}Q_0\vec{B}+\frac{\alpha }{2\pi ^2} (\vec{Q}\times \vec{E})]+\frac{1}{c}\frac{\partial \vec{E}}{\partial t}\). Since we are interested here in CME, the terms containing \(\vec{Q}\) have been neglected and the term related to \(Q_0\) has been absorbed in \({{ }_{ch}}\) as, \(\frac{\alpha }{2\pi ^2}Q_0 = {{ }_{ch}}\)
From the continuity equation (equation (5) in the text), \((\rho _{+}-\rho _{-})\) can be calculated as, \((\rho _{+}-\rho _{-})=\frac{2e^3}{4\pi ^2} E B \tau _{ch}\) for B parallel to E, where \(\tau _{ch}\) is the chirality changing scattering time. Thus, \({{ }_{ch}}\) becomes, \({{ }_{ch}}=\frac{e^2}{4\pi ^2}\frac{2e^3}{4\pi ^2}\frac{1}{e g_B} E B\tau _{ch}\). The CME conductivity \({{ }_{CME}}\) which is experimentally measured, is related to the chiral conductivity \({{ }_{ch}}\) as, \({{ }_{ch}}= {{ }_{CME}}\frac{E}{B}\)
Debanand Sa, Chiral magnetic effect and Maxwell-Chern-Simons electrodynamics in Weyl semimetals. Eur. Phys. J. B 94, 31 (2021)
M. Shoufie Ukhtary, Ahmad R. T. Nugraha, Riichiro Saito, “Nagative refraction in Weyl semimetals”, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 86, 104703 (2017)
T. Morimoto, N. Nagaosa, Chiral anomaly and giant magnetochiral anisotropy in noncentrosymmetric Weyl semimetals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 146603 (2016)
S. Nandy, D.A. Pesin, Chiral magnetic effect of hot electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 266601 (2020)
S. Nandy, G. Sharma, A. Taraphder, S. Tewari, Chiral anomaly as the origin of the planar Hall effect in Weyl semimetals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 176804 (2017)
R. D. Peccei, The strong CP problem and axions, Axions- Lecture notes in Physics, 741, 3-17 (2008), (eds.) M. Kuster, G. Raffelt and B. Beltran, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
F. Wilczek, Time’s (almost) reversible arrow, Quanta Magazine, 7 January (1016)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Prof. T. V. Ramakrishnan and Prof. V. S. Subrahmanyam for stimulating discussions and critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sa, D. Chiral magnetic effect in Weyl semimetals and negative refraction. Eur. Phys. J. B 95, 11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-021-00274-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-021-00274-w