Abstract
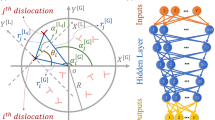
Two-dimensional discrete dislocation models exhibit complex dynamics in relaxation and under external loading. This is manifested both in the time-dependent velocities of individual dislocations and in the ensemble response, the strain rate. Here we study how well this complexity may be reproduced using so-called Interaction Networks, an artificial intelligence method for learning the dynamics of complex interacting systems. We test how to learn such networks using creep data, and show results on reproducing individual and collective dislocation velocities. The quality of reproducing the interaction kernel is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zdeborová, Nat. Phys. 13, 420 (2017)
J. Behler, J. Chem. Phys. 145, 170901 (2016)
V. Botu, R. Ramprasad, Phys. Rev. B 92, 094306 (2015)
T.D. Huan, R. Batra, J. Chapman, S. Krishnan, L. Chen, R. Ramprasad, NPJ Comput. Mater. 3, 37 (2017)
S. Wiewel, M. Becher, N. Thuerey, https://doi.org/arXiv:1802.10123 (2018)
J. Pathak, B. Hunt, M. Girvan, Z. Lu, E. Ott, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 024102 (2018)
M. Koch-Janusz, Z. Ringel, Nat. Phys. 14, 578 (2018)
J. Carrasquilla, R.G. Melko, Nat. Phys. 13, 431 (2017)
E.P.L. van Nieuwenburg, Y.H. Liu, S.D. Huber, Nat. Phys. 13, 435 (2017)
S.J. Wetzel, Phys. Rev. E, 96, 022140 (2017)
S. Papanikolaou NPJ Comput. Mater. 4, 27 (2018)
P. Battaglia, R. Pascanu, M. Lai, D.J. Rezende, inAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS, 2016), Vol. 29, p. 4502
M.C. Miguel, A. Vespignani, S. Zapperi, J. Weiss, J.R. Grasso, Nature 410, 667 (2001)
M. Zaiser, Adv. Phys. 55, 185 (2006)
J. Rosti, J. Koivisto, L. Laurson, M.J. Alava, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 100601 (2010)
P.D. Ispánovity, L. Laurson, M. Zaiser, I. Groma, S. Zapperi, M.J. Alava, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 235501 (2014)
S. Janićević, M. Ovaska, M.J. Alava, L. Laurson, J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2015, P07016 (2015)
S. Papanikolaou, Y. Cui, N. Ghoniem, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 26, 013001 (2017)
J.P. Hirth, J. Lothe,Theory of dislocations (Krieger, Malabar, FL, 1982)
P. Moretti, M.-C. Miguel, M. Zaiser, S. Zapperi, Phys. Rev. B 69, 214103 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contribution to the Topical Issue “Complex Systems Science meets Matter and Materials”, edited by Stefano Zapperi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salmenjoki, H., Alava, M.J. & Laurson, L. Mimicking complex dislocation dynamics by interaction networks. Eur. Phys. J. B 91, 275 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-90419-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-90419-7