Abstract
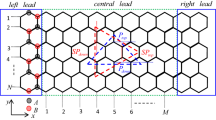
We have compared results of electronic transport using two different approaches: Dirac vs tight-binding (TB) Hamiltonians to assesses disorder-induced effects in graphene nanoribbons. We apply the proposed Hamiltonians to calculate the density of states, the transmission along the ribbon, and the pseudo-spin polarization (P(E)) in metallic armchair graphene nanoribbons. We clearly show differences between these two approaches in the interference processes, especially in the low-lying energy limit, when the systems are found in the presence of random impurities (disorder). This allows us to find fingerprints associated with each model used. As the disorder increases, more robust electronic transmission (through polarized states in a given sublattice) arises when one is dealing with the Dirac model only. We also find with this model unexpected peaks in the P(E) far from the Dirac point for wider nanoribbons. In the other hand, the model TB show the Dirac limit with disturbances of the hyperboloid subbands for certain potentials of the impurities. In general, our study is indicating that a P(E) spectroscopy (analyzing the line width and intensity) can be used to detect fingerprints of the increase of asymmetry in the scattering processes and the transport limits where hyperboloid subbands are important.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.H. Castro Neto, F. Guinea, N.M.R. Peres, K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 109 (2009)
M.Z. Hasan, C.L. Kane, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3045 (2010)
A. Kara, H. Enriquez, A.P. Seitsonen, L.C.L.Y. Voon, S. Vizzini, B. Aufray, H. Oughaddou, Surf. Sci. Rep. 67, 141 (2012)
Y. Xu, J. Dai, X.C. Zeng J. Phys. Chem. Lett 6, 1996 (2015)
L. Brey, H.A. Fertig, Phys. Rev. B 73, 235411 (2006)
M. Ezawa, N. Nagaosa, arXiv:1301.6337 (2013)
A.K. Geim, A.H. MacDonald, Phys. Today 60, 35 (2007)
S. Reich, J. Maultzsch, C. Thomsen, P. Ordejn, Phys. Rev. B 66, 035412 (2002)
Y. Hancock, A. Uppstu, K. Saloriutta, A. Harju, M.J. Puska, Phys. Rev. B 81, 245402 (2010)
L.I.A. López, A. Champi, S. Ujevic, M. Mendoza, Eur. Phys. J. B 88, 298 (2015)
L. Majidi, M. Zareyan, Phys. Rev. B 83, 115422 (2011)
H. Min, G. Borghi, M. Polini, A.H. MacDonald, Phys. Rev. B 77, 041407(R) (2008)
S.H. Abedinpour, M. Polini, A.H. MacDonald, B. Tanatar, M.P. Tosi, G. Vignale, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 206802 (2007)
E.R. Mucciolo, A.H. Castro Neto, C.H. Lewenkopf, Phys. Rev. B 79, 075407 (2009)
D. Pesin, A.H. MacDonald, Nat. Mater. 11, 409 (2012)
L.I.A. López, S.M. Yaro, A. Champi, S. Ujevic, M. Mendoza, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 26, 065301 (2014)
C. Lin, Y. Feng, Y. Xiao, M. Drr, X. Huang, X. Xu, R. Zhao, E. Wang, X.-Z. Li, Z. Hu, Nano Lett. 15, 903 (2015)
D.Y. Usachov, A.V. Fedorov, O.Y. Vilkov, A.E. Petukhov, A.G. Rybkin, A. Ernst, M.M. Otrokov, E.V. Chulkov, I.I. Ogorodnikov, M.V. Kuznetsov, L.V. Yashina, E.Yu. Kataev, A.V. Erofeevskaya, V.Y. Voroshnin, V.K. Adamchuk, C. Laubschat, D.V. Vyalikh, Nano Lett. 16, 4535 (2016)
J.A. Lawlor, P.D. Gorman, S.R. Power, C.G. Bezerra, M.S. Ferreira, Carbon 77, 645 (2014)
A. Zabet-Khosousi, L. Zhao, L. Plov, M.S. Hybertsen, D.R. Reichman, A.N. Pasupathy, G.W. Flynn, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 1391 (2014)
A. Celis, M.N. Nair, A. Taleb-Ibrahimi, E.H. Conrad, C. Berger, W.A. de Heer, A. Tejeda, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49, 143001 (2016)
Y.W. Son, M.L. Cohen, S.G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 216803 (2006)
R. Stacey, Phys. Rev. D 26, 468 (1982)
L. Susskind, Phys. Rev. D 16, 3031 (1977)
H. Gausterer, C.B. Lang, Phys. Rev. D 36, 1229 (1987)
J.R. Klauder, S. Lee, Phys. Rev. D 45, 2101 (1992)
K. Wakabayashi, M. Fujita, H. Ajiki, M. Sigrist, Phys. Rev. B 59, 8271 (1999)
A.V. Rozhkov, S. Savel’ev, F. Nori, Phys. Rev. B 79, 125420 (2009)
H. Zheng, Z.F. Wang, T. Luo, Q.W. Shi, J. Chen, Phys. Rev. B 75, 165414 (2007)
S. Datta, Quantum transport: atom to transistor (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2005)
S. Ujevic, M. Mendoza, Phys. Rev. B 82, 035432 (2010)
C.H. Lewenkopf, E.R. Mucciolo, J. Comput. Electron. 12, 203 (2013)
A.L.C. Pereira, P.A. Schulz, Phys. Rev. B 77, 075416 (2008)
M. Mendoza, P.A. Schulz, Phys. Rev. B 68, 205302 (2003)
M.A. Topinka et al., Science 289, 2323 (2000)
D. Ferry, S.M. Goodnick, Transport in nanostructures (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López, L.I.A., Mendoza, M. Electronic transport in graphene nanoribbons with disorder look at the pseudo-spin polarization: Dirac versus tight-binding model. Eur. Phys. J. B 91, 157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-80594-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-80594-x