Abstract
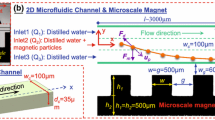
The design of a new hybrid magnetic MEMS for biology (Bio-Mag-MEMS) is presented. It combines magnetophoresis, dielectrophoresis and microfluidics. These phenomena are used to sort magnetically tagged and non-tagged objects. Magnetic objects are trapped by the use of high gradient magnetophoresis. Thanks to dielectrophoresis these objects, once trapped, can be successfully released in a buffer. Efficient sorting is performed in this hybrid Bio-Mag-MEMS by using magnetic beads. A high sorting efficiency is demonstrated. Magnetic, Stokes and dielectrophoretic forces in the microfluidic channel are simulated with both analytical tools and the finite element method (FEM). The trajectories of magnetically tagged objects are simulated. Finally the fabrication and optimization of this device are detailed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Jordan et al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 201, 413 (1999)
C. Plank et al., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63, 1300 (2011)
O. Osman et al., Biomed. Microdevices 14, 947 (2012)
N. Pamme, Lab Chip 6, 24 (2006)
M. Zborowski et al., Anal. Chem. 83, 8050 (2011)
D. Robert et al., Lab Chip 11, 1902 (2011)
P. Tseng, Nano Lett. 9, 3053 (2009)
K. Hoshino et al., Lab Chip 11, 3449 (2011)
R. Fulcrand et al., Sens. Actuators B 160, 1520 (2011)
O. Cugat et al., IEEE Trans. Magn. 39, 3607 (2003)
M. Kustov et al., J. Appl. Phys. 108, 063914 (2010)
F. Dumas-Bouchiat et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 102511 (2010)
L.F. Zanini et al., J. Appl. Phys. 111, (2012)
L.F. Zanini et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 232504 (2011)
N.M. Dempsey et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 092509 (2007)
T. Honeger et al., Micro Nanosystems 2, 239 (2010)
T. Honeger et al., Microelectron. Eng. 86, 1401 (2009)
S. Chigirinsky et al., Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 20, 85 (2009)
P. Kauffmann et al., IEEE Trans. Magn. 46, 3293 (2010)
T. Honeger et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 181906 (2011)
C. Mikkelsen et al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 293, 578 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contribution to the Topical Issue “New Trends in Magnetism and Magnetic Materials”, edited by Francesca Casoli, Massimo Solzi and Paola Tiberto.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blaire, G., Masse, A., Zanini, L.F. et al. Hybrid Bio-Mag-MEMS combining magnetophoresis and dielectrophoresis. Eur. Phys. J. B 86, 165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2013-30679-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2013-30679-1