Abstract
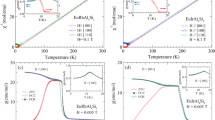
The Ru-Ru spin-singlet formation in La2 − x L n x RuO5 (Ln = Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd, Dy) was investigated by measurements of the specific heat and magnetic susceptibility. After subtraction of the lattice contribution from the specific heat (C p ), similar excess entropy values were obtained for all compounds. These entropies can be explained by the formation of antiferromagnetic Ru-spin dimers at low temperatures and provide a lower estimate for the intradimer exchange strength. Pronounced changes in the transition temperatures and a broadening of the corresponding peak in C p were observed. These changes depend on the rare-earth element and are due to local structural changes and heterogeneities caused by the substitution. The magnetic susceptibilities can be described by the sum of a rare-earth paramagnetic moment and the susceptibility of the unsubstituted La2RuO5. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed for various compounds to investigate the origin of the magnetic transition and the relationship between structural changes and the spin-dimerization temperature. The combination of the present results with previous structural investigations supports the model of a spin-pairing of the Ru moments which occurs as a reason of the structural phase transition in La2 − x L n x RuO5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J. Makowski, J.A. Rodgers, P.F. Henry, J.P. Attfield, J.-W.G. Bos, Chem. Mater. 21, 264 (2009)
Z.H. Han, H.E. Mohottala, J.I. Budnick, W.A. Hines, P.W. Klamut, B. Dabrowski, M. Maxwell, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18, 2273 (2006)
J.A. Rodgers, P.D. Battle, C.P. Grey, J. Sloan, Chem. Mater. 17, 4362 (2005)
W.G. Mumme, A.D. Wadsley, Acta Cryst. B 24, 1327 (1968)
G. Cao, S. McCall, Z.X. Zhou, C.S. Alexander, J.E. Crow, R.P. Guertin, C.H. Mielke, Phys. Rev. B 63, 144427 (2001)
P. Khalifah, R. Osborn, Q. Huang, H.W. Zandbergen, R. Jin, Y. Liu, D. Mandrus, R.J. Cava, Science 297, 2237 (2002)
S.G. Ebbinghaus, S. Riegg, T. Götzfried, A. Reller, Eur. Phys. J. ST 180, 91 (2010)
S. Riegg, U. Sazama, M. Fröba, A. Reller, S.G. Ebbinghaus, Phys. Rev. B 84, 014403 (2011)
D.I. Khomskii, T. Mizokawa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 156402 (2005)
H. Wu, Z. Hu, T. Burnus, J.D. Denlinger, P.G. Khalifah, D.G. Mandrus, L.-Y. Jang, H.H. Hsieh, A. Tanaka, K.S. Liang, J.W. Allen, R.J. Cava, D.I. Khomskii, L.H. Tjeng, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 256402 (2006)
S.J. Moon, W.S. Choi, S.J. Kim, Y.S. Lee, P.G. Khalifah, D. Mandrus, T.W. Noh, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 116404 (2008)
S. Riegg, A. Günther, H.-A. Krug von Nidda, A. Loidl, M.V. Eremin, A. Reller, S.G. Ebbinghaus, Phys. Rev. B 86, 115125 (2012)
P. Boullay, D. Mercurio, A. Bencan, A. Meden, G. Drazic, M. Kosec, J. Solid State Chem. 170, 294 (2003)
S.G. Ebbinghaus, Acta Cryst. C 61, i96 (2005)
S.K. Malik, D.C. Kundaliya, R.D. Kale, Solid State Commun. 135, 166 (2005)
V. Eyert, S.G. Ebbinghaus, T. Kopp, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 256401 (2006)
V. Eyert, S.G. Ebbinghaus, Prog. Solid State Chem. 35, 433 (2007)
E.C. Samulon, M.C. Shapiro, I.R. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 84, 054417 (2011)
K. Koepernick, H. Eschrig, Phys. Rev. B 59, 1743 (1999)
I. Opahle, K. Koepernick, H. Eschrig, Phys. Rev. B 60, 14035 (1999)
S. Riegg, A. Reller, S.G. Ebbinghaus, J. Solid State Chem. 188, 17 (2012)
R.P. Singh, C.V. Tomy, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 20, 235209 (2008)
C. Kant, J. Deisenhofer, A. Günther, F. Schrettle, A. Loidl, M. Rotter, D. Johrendt, Phys. Rev. B 81, 014529 (2010)
S. Layek, V.K. Anand, Z. Hossain, J. Magn. Magn. Mater 321, 3447 (2009)
A. Tari, The specific heat of matter at low temperatures (Imperial College Press, London, 2003)
M. Heinrich, H.-A. Krug von Nidda, V. Fritsch, A. Loidl, Phys. Rev. B 63, 193103 (2001)
B. Rivas-Murias, H.D. Zhou, J. Rivas, F. Rivadulla, Phys. Rev. B 83, 165131 (2011)
H. Lueken, Magnetochemie (Teubner, Stuttgart - Leipzig, 1999)
W.G. Penney, R. Schlapp, Phys. Rev. 41, 194 (1932)
A. Dittl, S. Krohns, J. Sebald, F. Schrettle, M. Hemmida, H.-A. Krug von Nidda, S. Riegg, A. Reller, S.G. Ebbinghaus, A. Loidl, Eur. Phys. J. B 79, 391 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riegg, S., Günther, A., Krug von Nidda, HA. et al. Spin-dimerization in rare-earth substituted La2RuO5 . Eur. Phys. J. B 85, 413 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2012-30840-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2012-30840-4