Abstract
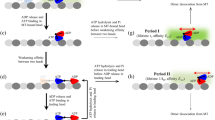
When the processive motor protein kinesin walks along the biopolymer microtubule it can occasionally make a backward step. Recent single molecule experiments on moving kinesin have revealed that the forward-to-backward step ratio decreases exponentially with the load force. Carter and Cross (Nature 435, 308-312, 2005) found that this ratio tightly followed 802 × exp[−0.95F], where F is the load force in piconewtons. A straightforward analysis of a Brownian step leads to L/(2k B T) as the factor in front of the load force, where L is the 8 nm stepsize, k B is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature. The factor L/(2k B T) does indeed equal 0.95 pN−1. The same analysis shows how the 802 prefactor derives from the power stroke energy G as exp[G/(2k B T)]. There are indications that the power stroke derives from the entropically driven coiling of the 30 amino acid neck linker that connects the two kinesin heads. This idea is examined and consequences are deduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Howard, Mechanics of motor proteins and the cytoskeleton (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland MA 2001) pp. 246–251
N.J. Carter, R.A. Cross, Nature 435, 308 (2005)
M. Nishiyama, H. Higuchi, T. Yanagida, Nature Cell Biol. 4, 790 (2002)
M. Bier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 1481041 (2003)
M. Bier, Contemporary Phys. 46, 41 (2005)
S.J. Hagen, L. Qiu, S.A. Pabit, J. Phys.: Condensed Matter 17, 1503 (2005)
K. Svoboda, C.F. Schmidt, B.J. Schnapp, S.M. Block, Nature 365, 721 (1993)
M. Bier, BioSystems 88, 301 (2007)
R.A. Cross, Trends in Biochem. Sci. 29, 301 (2004)
S. Rice, Y. Cui, C. Sindelar, N. Naber, M. Matuska, R. Vale, R. Cooke, Biophys. J. 84, 1844 (2003)
Y. Taniguchi, M. Nishiyama, Y. Ishii, T. Yanagida, Nature Chem. Biol. 1, 342 (2005)
R.D. Vale, R.A. Milligan, Sci. 288, 88 (2000)
Yu.A. Grosberg, A.R. Khokhlov, Giant Molecules (Academic Press, San Diego 1997) pp. 69–91
C. Tanford, K. Kawahara, S. Lapanje, J. Biol. Chem. 241, 1921 (1966)
T. Ohashi, C.A. Hale, P.A.J. De Boer, H.P. Erickson, J. Bacteriology, 184, 4313 (2002)
K. Kawaguchi, S. Ishiwata, Biochem. and Biophys. Res. Comm. 272, 895 (2000)
S.M. Block, Biophys. J. 92, 29862995 (2007)
P.G. de Gennes, Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics (Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY 1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bier, M. Accounting for the energies and entropies of kinesin’s catalytic cycle. Eur. Phys. J. B 65, 415–418 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2008-00271-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2008-00271-1