Abstract.
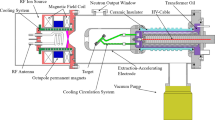
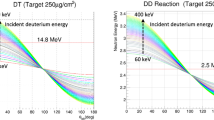
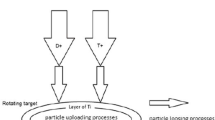
A high-intensity accelerator-based D-D/D-T fusion neutron source (ZF-400) with a thick adsorption target is designed with an intensity of \( 10^{13}\) n/s. A high-current microwave ion source is used to produce a large current deuteron beam, and neutrons are generated by irradiating the deuteron beam on a deuterium-adsorption target or tritium-adsorption target. According to the particle-in-cell (PIC) code, the length of the whole high-current D+ beam transport line is 500cm, the D+ beam transfer efficiency is up to 96%, and various components can match each other. On the rotating target, the D+ beam spot size is about 20.0 mm with energy of 450 keV. Based on the heat conduction theory, the thick adsorption rotating target with water-cooling can withstand the D+ ions beam with 450 kV/50 mA and ensure that the temperature is less than 200 °C. According to the multi-layer computing model, neutron energy spectra, angular distributions and yields for the thick target can be calculated with remarkable precision. The neutron energy spectra are non-mono-energetic neutrons for the ZF-400 neutron generator, the neutron angular distributions are anisotropic distributions, and they can provide neutrons with an intensity of \( 2.8\times 10^{11}\) n/s (D-D) and \( 1.4\times 10^{13}\) n/s (D-T), respectively, with the deuteron of 450 keV/50 mA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ojaruega, F.D. Becchetti, A.N. Villano et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 652, 397 (2011)
V.V. Shirokov, in Proceedings of EPAC, Lucerne, Switzerland 2004, edited by C. Petit-Jean-Genaz (JACoW, Geneva, 2004)
M. Febbraro, F.D. Becchetti, R.O. Torres-Isea et al., Phys. Rev. C 96, 024613 (2017)
Z.E. Yao, H.X. Du, X.J. Tan et al., Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 25, 744 (2008)
Z.E. Yao, W.M. Yue, P. Luo et al., At. Energy Sci. Technol. 42, 400 (2008)
M.E. Capoulat, A.J. Kreiner, Phys. Med. 33, 106 (2017)
L. Oláh, A.M. El-Megrab, A. Fenyvesi et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 404, 373 (1998)
H. Sadeghi, R. Amrollahi, M. Zare, S. Fazelpour, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 59, 125006 (2017)
V.M. Bystritsky, G.N. Dudkin, S.I. Kuanetsov et al., J. Surf. Investig. 11, 580 (2017)
C.L. Lan, J. Wang, T. Ye et al., Chin. Phys. C 34, 022401 (2017)
J.F. Zhang, X.C. Ruan, L. Hou et al., High Power Laser Part. Beams 23, 209 (2011)
Z. Wei, Y. Yan, Z.E. Yao et al., Phys. Rev. C 87, 054605 (2013)
Z. Wei, J.R. Wang, Y.L. Zhang et al., Chin. Phys. C 43, 054001 (2019)
A. Mattera, S. pomp, M. Lantz et al., Eur. Phys. J. A 53, 173 (2017)
M. Angelone, D. Flammini, S. Loreti et al., Fusion Eng. Des. 109, 843 (2016)
Y.L. Zhang, X.C. Ruan, H.X. Huang et al., Eur. Phys. J. A 53, 236 (2017)
J.P. Meulders, P. Leleux, P.C. Macq et al., Phys. Med. Biol. 20, 235 (1975)
S.Yu. Taskaev, V.V. Kanygin, V.A. Byvaltsev et al., Biomed. Eng. 52, 73 (2018)
S. Bishnoi, P.S. Sarkar, R.G. Thomas et al., J. Nondestruct. Eval. 38, 13 (2019)
K. Bergaoui, N. Reguigui, C.K. Gary et al., Appl. Radiat. Isotopes 94, 319 (2014)
P.V. Raja, N.V.L.N. Murty, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 60, 558 (2018)
Y. Cai, H. Hu, S. Lu, Q. Jia, App. Radiat. Isot. 135, 147 (2018)
D.W. Heikkinen, in The Second International Conference on Fusion Reactor Materials, Chicago, IL, USA 1986 (Elsevier, 1986)
R. Booth, J.C. Davis, C.L. Hanson et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods 145, 25 (1977)
G. Voronin, in Proceedings of the EPAC94, London, UK 1994, edited by V.P. Suller (World Scientific, Singapore, 1994)
Vit.D. Koval'chuk, A.V. Krasilʼnikov, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 77, 169 (1993)
M. Ohta, K. Takakura, K. Ochiai et al., Fusion Eng. Des. 89, 2164 (2014)
Sub Working Group of Fusion Reactor Physics Subcommittee, Collection of experimental data for fusion neutronics benchmark JAERI-M 94-014, Tokyo, Japan 1994 (Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Japan, 1994)
M.R. Cleland, B.P. Offermann, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 145, 41 (1977)
J.B. Hourst, M. Roche, J. Morin, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 145, 19 (1977)
T.L. Su, B.H. Su, B.T. Yang et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 287, 452 (1990)
K. B. Yuri, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 539, 455 (2005)
X.L. Lu, J.R. Wang, Y. Zhang et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 811, 76 (2016)
A. Goncharov, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84, 021101 (2013)
Q. Wu, L.T. Sun, B.Q. Cui et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 830, 214 (2016)
Z.E. Yao, S.W. Chen, T.L. Su et al., Nucl. Tech. 21, 787 (2004)
L. Horst, P. Arno, Nucl. Data Tables 11, 569 (1973)
J.F. Ziegler, M.D. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 268, 1818 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Motobayashi
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors' comment: All data generated during this study are contained in this published article.]
Publisher's Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Han, C., Peng, S.H. et al. Physical design and evaluation of a high-intensity accelerator-based D-D/D-T fusion neutron source. Eur. Phys. J. A 55, 162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2019-12848-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2019-12848-5