Abstract
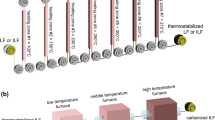
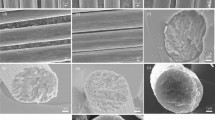
There is an increasing demand for lightweight composites reinforced with carbon fibers (CFs) that possess exceptional thermal characteristics, especially at high-temperature conditions. The focus of this study is primarily on the sequence of structural changes at the micro-nano level during the carbonization of cellulosic fibers collected from Northern Vietnam. The impact of various operational parameters in the carbonization process such as the heating temperature and the stabilization process also discussed. The chemical structure, morphology, and thermal conductivity of cellulose-based fiber were investigated. This investigation revealed that prepared CF-3 using cellulosic fibers collected from Northern Vietnam through the optimized parameters can be a potentials material for making outer ring insulation in high-temperature furnace environments.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Luning Chai, Bin Lou, Ran Yu, et al., J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 158, 105260 (2021).
P. Morgan, Carbon Fibers and Their Composites (CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 2005).
G. Dumanlı and A. H. Windle, Mater. Sci. 47, 4236–4250 (2012).
J. B. Donnet and R. C. Bansal, Carbon Fibers (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1990).
X. Huang, Materials 2, 2369–2403 (2009).
B. Tang, Y. Wang, L. Hu, et al., J. Eng. Fibers Fabrics 14, 1–9 (2019).
Bo Tang, Ying Wang, Jinhong Yu, et al., J. Chem. 2020, 1–15 (2020).
Ch. Wang, X. Jin, H. Cheng, et al., Mater. Des. 131, 177–185 (2017).
N. M. Puri, I. Kenny, et al., Polym. Degrad. Stab. 141, 84–96 (2017).
H. W. Wong, J. Peck, J. Assif, et al., J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 122, 258–267 (2016).
P. W. Gibson, C. Lee, and F. Ko, J. Eng. Fiber Fab. 2, 32–40 (2007).
E. Frank, F. Hermanutz, and M. R. Buchmeiser, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 297, 493–501 (2012).
W. Dang, J. Liu, X. Wang, et al., Polymers 12, 63 (2020).
A. Galiguzov, A. Malakho, V. Kulakov, et al., Carbon Lett. 14, 22–26 (2013).
J. M. Spörl, R. Beyer, F. Abels, et al., Macromol. Mater. Eng. 302, 1700195 (2017).
H. Kleinhans and L. Salmen, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 133, 43965 (2016).
E. Frank, L. M. Steudle, D. Ingildeev, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 5262–5298 (2014).
D. S. Karousos, L. Lei, and A. Lindbrathen, Sep. Purif. Technol. 253, 117473 (2020).
Mitsui and Co., Monthly Report (Mitsui & Co. Global Strategic Studies Inst., 2021).
K. George, B. P. Panda, S. Mohanty, and S. K. Nayak, Polym. Adv. Technol. 29, 8–21 (2017).
J. Y. Zhu, U. P. Agarwal, P. N. Ciesielski, et al., Biotechnol. Biofuels 14, 114 (2021).
A. A. Ogale, M. Zhang, and J. Jin, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 133, 43794 (2016).
S.-J. Park, Carbon Fibers (Springer, New York, 2015).
N.-D. Le, M. Trogen, Y. Ma, et al., Carbohydr. Polym. 250, 116918 (2020).
A. E. Lewandowska, C. Soutis, L. Savage, and S. J. Eichhorn, Compos. Sci. Technol. 116, 50–57 (2015).
Y.-H. Wang, S. Bayatpour, X. Qian, et al., Colloids Surf., A 612, 125908 (2021).
P. Guo, J. Li, S. Pang, et al., Carbon 183, 525–529 (2021).
Shigetaka Wada, Bongkoch Piempermpoon, Pao Na Nakorn, et al., J. Sci. Res. Chula. Univ. 30, 109–120 (2005).
M. A. Kedzierski, R. Brignoli, and K. T. Quine, Int. J. Ref. 74, 1–9 (2017).
L. Huang and M. Sel-Genk, Energy Convers. Manage. 42, 599–612 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, K.S., Dinh, N.N., Nam, N.P. et al. Carbon Fibers from Cellulosic Precursor for Thermal Insulation: An Insight Into the Effect of Stabilization and Carbonization Conditions on the Synthesis. Nanotechnol Russia 17, 372–379 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2635167622030090
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2635167622030090