Abstract
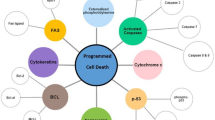
The data on the molecular mechanisms of normal and pathological apoptosis are summarized. Three phases of apoptosis are distinguished: signal, effector, and degradation. The signal phase includes the extrinsic (caspase-dependent) and extrinsic (mitochondrial) pathways. Molecular markers of extrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways play an important role in the diagnostics and treatment of immune, bronchopulmonary, excretory, and cardiovascular system pathologies, oncology, and senescence. This review considers the initiator caspases-8 and -9 and the effector caspase-3 as the molecular markers of the caspase-dependent apoptosis. The main molecular markers of the mitochondrial (or caspase-independent) apoptosis are p53, p21, and p16 proteins, which respond to DNA damage and are involved in cellular senescence, as well as chaperon prohibitin and flavoprotein apoptosis-inducing factor.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aken van, O., Mitochondrial type-I prohibitins of Arabidopsis thaliana are required for supporting proficient meristem development, Plant J., 2007, vol. 52, no. 5, pp. 850–864.
Baker, D.J., Wijshake, T., and Tchkonia, T., Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders, Nature, 2011, vol. 479, no. 7372, pp. 232–236.
Baris, O.R., Klose, A., Kloepper, J.E., et al., The mitochondrial electron transport chain is dispensable for proliferation and differentiation of epidermal progenitor cells, Stem Cells, 2011, vol. 29, pp. 1459–1468.
Baryshnikov, A.Yu. and Shishkin, Yu.V., Immunologicheskie problemy apoptoza (Immunological Problems of Apoptosis), Moscow: Editorial URSS, 2002.
Bedelbaeva, K., Snyder, A., and Gourevitch, D., Lack of p21 expression links cell cycle control and appendage regeneration in mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 30, pp. 45–50.
Bucchieri, F., Marino Gammazza, A., Pitruzzella, A., et al., Cigarette smoke causes caspase-independent apoptosis of bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatic donors, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 3, p. e0120510.
Bunz, F., Dutriaux, A., Lengauer, C., et al., Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage, Science, 1998, vol. 282, no. 5393, pp. 1497–1501.
Chiu, C.-F., Ho, M.-Y., and Peng, J.-M., Raf activation by Ras and promotion of cellular metastasis require phosphorylation of prohibitin in the raft domain of the plasma membrane, Oncogene, 2013, vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 777–787.
Coughlan, M.T., Higgins, G.C., Nguyen, T.V., et al., Deficiency in apoptosis-inducing factor recapitulates chronic kidney disease via aberrant mitochondrial homeostasis, Diabetes, 2016, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 1085–1098.
Creagh, E.M., Caspase crosstalk: integration of apoptotic and innate immune signaling pathways, Trends Immunol., 2014, vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 631–639.
Daszkiewicz, L., Vázquez-Mateo, C., Rackov, G., et al., Distinct p21 requirements for regulating normal and self-reactive T cells through IFN-γ production, Sci. Rep., 2015, vol. 5, pp. 76–91.
Dotto, G.P., p21 (WAF1/Cip1): more than a break to the cell cycle? Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2000, vol. 1471, no. 1, pp. M43–M56.
Eleftheriadis, T., Pissas, G., Antoniadi, G., et al., Malate dehydrogenase-2 inhibitor LW6 promotes metabolic adaptations and reduces proliferation and apoptosis in activated human T-cells, Exp. Ther. Med., 2015, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 1959–1966.
Farina, B., Di Sorbo, G., Chambery, A., et al., Structural and biochemical insights of CypA and AIF interaction, Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1138–1145.
Giannotta, M., Fragassi, G., Tamburro, A., et al., Prohibitin: a novel molecular player in KDEL receptor signaling, BioMed Res. Int., 2015, art. ID 319454.
Golubev, A.M., Moskaleva, E.Yu., Severin, S.E., et al., Apoptosis in critical states, Obshch. Reanimatol., 2006, no. 2, no. 6, pp. 184–190.
Gordeeva, A.V., Labas, Y.A., and Zvyagilskaya, R.A., Apoptosis in unicellular organisms: mechanisms and evolution, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2004, vol. 69, no. 10, pp. 1055–1066.
Gubskii, Yu.I., Smert’ kletki: svobodnye radikaly, nekroz, apoptoz (Death of a Cell: Free Radicals, Necrosis, and Apoptosis), Vinnitsa: Nova Kniga, 2015.
Hangen, E., Interaction between AIF and CHCHD4 regulates respiratory chain biogenesis, Mol. Cell, 2015, vol. 58, pp. 1001–1014.
Hasan, I., Sugawara, S., Fujii, Y., et al., MytiLec, a mussel R-type lectin, interacts with surface glycan Gb3 on Burkitt’s lymphoma cells to trigger apoptosis through multiple pathways, Mar. Drugs, 2015, vol. 13, no. 12, pp. 7377–7389.
Ho, M.Y., Liang, C.M., and Liang, S.M., MIG-7 and phosphorylated prohibitin coordinately regulate lung cancer invasion/metastasis, Oncotarget, 2015, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 381–393.
Hossen, M.N., Kajimoto, K., Akita, H., et al., Therapeutic assessment of cytochrome C for the prevention of obesity through endothelial cell-targeted nanoparticulate system, Mol. Ther., 2013, vol. 21, pp. 533–541.
Ising, C., Koehler, S., Brähler, S., et al., Inhibition of insulin/IGF-1 receptor signaling protects from mitochondria-mediated kidney failure, EMBO Mol. Med., 2015, vol. 3, pp. 275–287.
Kaushal, G.P. and Shah, S.V., Autophagy in acute kidney injury, Kidney Int., 2016, vol. 89, no. 4, pp. 779–791.
Kerr, J.F.R., Wyllie, A.H., and Currie, A.R., Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics, Br. J. Cancer, 1972, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 239–257.
Klein, J.A., Longo-Guess, C.M., and Rossmann, M.P., The harlequin mouse mutation downregulates apoptosis-inducing factor, Nature, 2002, vol. 419, pp. 367–374.
Koizumi, Y., Nagase, H., Nakajima, T., et al., Toll-like receptor 3 ligand specifically induced bronchial epithelial cell death in caspase dependent manner and functionally upregulated Fas expression, Allergol. Int., 2016, vol. 65, pp. 30–37.
Kolonin, M.G., Saha, P.K., Chan, L., et al., Reversal of obesity by targeted ablation of adipose tissue, Nat. Med., 2004, vol. 10, pp. 625–632.
Krishnamurthy, J., Torrice, C., Ramsey, M.R., et al., Ink4a/Arf expression is a biomarker of aging, J. Clin. Invest., 2004, vol. 114, no. 9, pp. 1299–1307.
Lee, J.Y., Tokumoto, M., Hattori, Y., et al., Different regulation of p53 expression by cadmium exposure in kidney, liver, intestine, vasculature, and brain astrocytes, Toxicol. Res., 2016, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 73–80.
Lewin, B., Cassimeris, L., and Plopper, G., Cells, Burlington, Ma: Jones & Bartlett Learning, 2007.
Li, Z.-J., Yao, C., Liu, S.-F., et al., Cytotoxic effect of icaritin and its mechanisms in inducing apoptosis in human Burkitt lymphoma cell line, BioMed. Res. Int., 2014, vol. 2014, art. ID 391512.
Li, F., Chen, Q., Song, X., et al., miR-30b is involved in the homocysteine-induced apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells by regulating the expression of caspase 3, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 682–695.
Li, J., Xiong, J., Yang, B., et al., Endothelial cell apoptosis induces TGF-β signaling-dependent host endothelial-mesenchymal transition to promote transplant arteriosclerosis, Am. J. Transplantol., 2015, vol. 15, no. 12, pp. 3095–3111.
Liggett, W.H., Jr. and Sidransky, D., Role of the p16 tumor suppressor gene in cancer, J. Clin. Oncol., 1998, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 1197–1206.
Lin, C.H., Hong, Y.C., and Kao, S.H., Aeroallergen Der p2 induces apoptosis of bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells via activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathway, Cell Biosci., 2015, vol. 5, pp. 1–11.
Liu, J., Yang, J.R., Chen, X.M., et al., Impact of ER stress-regulated ATF4/p16 signaling on the premature senescence of renal tubular epithelial cells in diabetic nephropathy, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 2015, vol. 308, no. 8, pp. 621–630.
Madapura, H.S., Salamon, D., Wiman, K.G., et al., cMyc-p53 feedback mechanism regulates the dynamics of T lymphocytes in the immune response, Cell Cycle, 2016, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 1267–1275.
Mahata, B., Biswas, S., Rayman, P., et al., GBM derived gangliosides induce T cell apoptosis through activation of the caspase cascade involving both the extrinsic and the intrinsic pathway, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 7, p. e0134425.
Maiboroda, A.A., Apoptosis: genes and proteins, Sib. Med. Zh., 2013, no. 3, pp. 130–135.
Martín-Caballero, J., Flores, J.M., García-Palencia, P., and Serrano, M., Tumor susceptibility of p21 (Waf1/Cip1)-deficient mice, Cancer Res., 2001, vol. 61, no. 16, pp. 6234–6238.
Martynova, E.A., Apoptotic regulation of caspase activity, Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem., 2003, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 471–495.
McIlwain, D.R., Berger, T., and Mak, T.W., Caspase functions in cell death and disease, Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol., 2013, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1–28.
Milasta, S., Dillon, C.P., Sturm, O.E., et al., Apoptosis-inducing-factor-dependent mitochondrial function is required for T cell but not B cell function, Immunity, 2016, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 88–102.
Mishiro, K., Imai, T., Sugitani, S., et al., Diabetes mellitus aggravates hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke via mitochondrial defects leading to endothelial apoptosis, PLoS One, 2014, vol. 9, no. 8, p. e103818.
Moskalev, A.A., Genetics of aging and life duration, Usp. Gerontol., 2009, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 92–103.
Nagy, N., Matskova, L., Kis, L.L., et al., The proapoptotic function of SAP provides a clue to the clinical picture of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2009, vol. 106, pp. 11966–11971.
Novik, A.A., Kamilova, T.A., and Tsygan, V.N., Vvedenie v molekulyarnuyu biologiyu kantserogeneza (Introduction to Molecular Biology of Carcinogenesis), Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2005.
Pastore, D., Della-Morte, D., Coppola, A., et al., SGK-1 protects kidney cells against apoptosis induced by ceramide and TNF-α, Cell Death Dis., 2015, vol. 6, p. e1890.
Peng, Y.T., Chen, P., Ouyang, R.Y., and Song, L., Multifaceted role of prohibitin in cell survival and apoptosis, Apoptosis, 2015, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 1135–1149.
Potapnev, M.P., Autophagy, apoptosis, cell necrosis and immune recognition of own and alien, Immunologiya, 2014, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 95–102.
Pustavoitau, A., Barodka, V., Sharpless, N.E., et al., Role of senescence marker p16 INK4a measured in peripheral blood T-lymphocytes in predicting length of hospital stay after coronary artery bypass surgery in older adults, Exp. Gerontol., 2016, vol. 74, pp. 29–36.
Read, A.P. and Strachan, T., Human Molecular Genetics, New York: Wiley, 1999, 2nd ed.
Rheinwald, J.G., Hahn, W.C., Ramsey, M.R., et al., A two-stage, p16(INK4A)- and p53-dependent keratinocyte senescence mechanism that limits replicative potential independent of telomere status, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2002, vol. 22, no. 14, pp. 5157–1572.
Ruiz-Magaña, M.J., Rodriguez-Vargas, J.M., Morales, J.C., et al., The DNA methyltransferase inhibitors zebularine and decitabine induce mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and DNA damage in p53 mutant leukemic T cells, Int. J. Cancer, 2011, vol. 130, pp. 1195–1207.
Ruiz-Magaña, M.J., Martínez-Aguilar, R., Lucendo, E., et al., The antihypertensive drug hydralazine activates the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and causes DNA damage in leukemic T cells, Oncotarget, 2016, vol. 7, no. 16, pp. 21875–21886.
Ryzhov, S.V. and Novikov, V.V., Molecular mechanisms of apoptotic processes, Ross. Bioter. Zh., 2002, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 27–33.
Salmena, L., Lemmers, B., Hakem, A., et al., Essential role for caspase-8 in T-cell homeostasis and T-cell-mediated immunity, Genes Dev., 2003, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 883–895.
Salmina, A.B., Komleva, Yu.K., Kuvacheva, N.V., et al., Inflammation and aging of the brain, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 2015, vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 17–25.
Samuilov, V.D., Oleskin, A.V., and Lagunova, E.M., Programmed cell death, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2000, vol. 65, no. 8, pp. 873–887.
Schäker, K., Bartsch, S., Patry, C., et al., The bipartite rac1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor engulfment and cell motility 1/dedicator of cytokinesis 180 (elmo1/dock180) protects endothelial cells from apoptosis in blood vessel development, J. Biol. Chem., 2015, vol. 290, no. 10, pp. 6408–6418.
Shirokova, A.V., Apoptosis. Signaling pathways and cell ion and water balance, Cell Tissue Biol., 2007, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 215–224.
Susin, S.A., Lorenzo, H.K., and Zamzami, N., Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic process, J. Exp. Med., 1999, vol. 189, pp. 381–394.
Thal, S.E., Zhu, C., Thal, S.C., et al., Role of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) for hippocampal neuronal cell death following global cerebral ischemia in mice, Neurosci. Lett., 2011, vol. 499, pp. 1–3.
Uyanik, B., Grigorash, B.B., Goloudina, A.R., and Demidov, O.N., DNA damage-induced phosphatase Wip1 in regulation of hematopoiesis, immune system and inflammation, Cell Death Discovery, 2017, vol. 3, pp. 17–18.
Vahsen, N., Candé, C., and Brière, J.J., AIF deficiency compromises oxidative phosphorylation, EMBO J., 2004, vol. 23, pp. 4679–4689.
Varga, O.Yu. and Ryabkov, V.A., Apoptosis: definition, mechanisms, and role, Ekol. Chel., 2006, no. 7, pp. 28–32.
Wu, G., Cai, J., Han, Y., et al., LincRNA-p21 regulates neointima formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, apoptosis, and atherosclerosis by enhancing p53 activity, Circulation, 2014, vol. 130, no. 17, pp. 1452–1465.
Yang, H.B., Song, W., Chen, L.Y., et al., Differential expression and regulation of prohibitin during curcumin-induced apoptosis of immortalized human epidermal HaCaT cells, Int. J. Mol. Med., 2014, vol. 33, pp. 507–514.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by M. Batrukova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diatlova, A.S., Dudkov, A.V., Linkova, N.S. et al. Molecular Markers of Caspase-Dependent and Mitochondrial Apoptosis: Role in the Development of Pathology and Cellular Senescence. Biol Bull Rev 8, 472–481 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086418060038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086418060038