Abstract
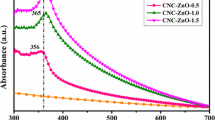
A low-temperature solution-based method for the production of hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposite films based on nanoscale cellulose and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (CNC/Fe3O4) was developed. The obtained nanomaterials were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), energy dispersive spectroscopy analysis (EDS) and X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and FT-IR spectroscopy. The formation of CNC/Fe3O4 nanocomposite was confirmed by the XRD analysis. According to SEM images, Fe3O4 nanoparticles are uniformly distributed on the surface of nanocellulose. The obtained nanocomposite material exhibits photocatalytic activity under visible light and UV irradiation in the rhodamine B degradation reaction. Thus, the developed biocompatible and environmentally friendly hybrid nanomaterials have great prospects of practical application in the field of biomedicine and photocatalysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hood, M., Mari, M., and Muñoz-Espí, R., Synthetic strategies in the preparation of polymer/inorganic hybrid nanoparticles, Materials, 2014, vol. 7, pp. 4057–4087.
Sanchez, C., Julián, B., Belleville, P., and Popall, M., Applications of hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposites, J. Mater. Chem., 2005, vol. 15, pp. 3559–3592.
Wicklein, B. and Salazar-Alvarez, G., Functional hybrids based on biogenic nanofibrils and inorganic nanomaterials, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, vol. 1, pp. 5469–5478.
Häffner, S.M. and Malmsten, H.M., Membrane interactions and antimicrobial effects of inorganic nanoparticles, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, vol. 248, pp. 105–128.
Azizi, S., Ahmad, M.B., Hussein, M.Z., Ibrahim, N.A., and Namvar, F., Preparation and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend bionanocomposites reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals/ZnO–Ag multifunctional nanosized filler, Int. J. Nanomed., 2014, vol. 9, pp. 1909–1917.
Cowger, A., Yang, Y., Rink, D.E., et al., Protein-adsorbed magnetic-nanoparticle-mediated assay for rapid detection of bacterial antibiotic resistance, Bioconjugate Chem., 2017, vol. 28, pp. 890–896.
Fernandes, E.M., Pires, R.A., Mano, J.F., and Reis, R.L., Bionanocomposites from lignocellulosic resources: properties, applications and future trends for their use in the biomedical field, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2013, vol. 38, pp. 1415–1441.
Allaker, R.P. and Ren, G., Potential impact of nanotechnology on the control of infectious disease, Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg., 2008, vol. 102, pp. 1–2.
Nagappan, S., Choi, M.-C., Sung, G., Park, S.S., Moorthy, M.S., Chu, S.-W., Lee, W.-K., and Ha, C.-S., Highly transparent, hydrophobic fluorinated polymethylsiloxane/silica organic-inorganic hybrids for anti-stain coating, Macromol. Res., 2013, vol. 21, pp. 669–680.
Samiey, B., Cheng, C.-H., and Wu, J., Organic-inorganic hybrid polymers as adsorbents for removal of heavy metal ions from solutions: a review, Materials, 2014, vol. 7, pp. 673–726.
Guise, C. and Fangueiro, R., Biomedical applications of nanocellulose, in Natural Fibres. Advances in Science and Technology towards Industrial Applications: From Science to Market, Fangueiro, R. and Rana, S., Eds., Dordrecht: Springer-Verlag, 2016, no. 12, pp. 155–169.
Lin, N. and Dufresne, A., Nanocellulose in biomedicine: current status and future prospect, Eur. Polym. J., 2014, vol. 59, pp. 302–325.
Wei, H., Rodriguez, K., Renneckar, S., and Vikesland, P.J., Environmental science and engineering applications of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014, vol. 1, pp. 302–316.
Islam, C.M.S., Sisler, L. Chen, J, and Tam, K.C., Cellulose nanocrystal (CNC)–inorganic hybrid systems: synthesis, properties and applications, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, vol. 6, pp. 864–883.
Mikulcová, V., Bordes, R., and Kašpárková, V., On the preparation and antibacterial activity of emulsions stabilized with nanocellulose particles, Food Hydrocolloids, 2016, vol. 61, pp. 780–792
Cunha, A.G., Mougel, J.B., Cathala, B., Berglund, L.A., and Capron, I., Preparation of double pickering emulsions stabilized by chemically tailored nanocelluloses, Langmuir, 2014, vol. 30, pp. 9327–9335.
Gao, J., Gu, H., and Xu, B., Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: design, synthesis, and biomedical applications, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, vol. 42, pp. 1097–1107.
Sekhon, B.S. and Kamboj, S.R., Inorganic nanomedicine—Part 2, Nanomedicine, 2010, vol. 6, pp. 612–618.
Huh, A.J. and Kwon, Y.J., “Nanoantibiotics”: a new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era, J. Control Release, 2011, vol. 156, pp. 128–145.
Singh, R., Smitha, M.S., and Singh, S.P., The role of nanotechnology in combating multi-drug resistant bacteria, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2014, vol. 14, pp. 4745–4756.
Lee, N., Yoo, D., and Ling, D., Iron oxide based nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and magnetoresponsive therapy, Chem. Rev., 2015, vol. 115, pp. 10637–10689.
Mohammed, L., Gomaa, H.G., Ragab, D., and Zhu, J., Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: a review, Particuology, 2017, vol. 30, pp. 1–14.
Anghel, A.G., Grumezescu A.M., Chirea M., et al., MAPLE fabricated Fe3O4Cinnamomum verum antimicrobial surfaces for improved gastrostomy tubes, Molecules, 2014, vol. 19, pp. 8981–8994.
Galkina, O.L., Ivanov, V., Agafonov, A.V., Seisenbaeva, G.A., and Kessler, V.G., Cellulose nanofiber–titania nanocomposites as potential drug delivery systems for dermal applications, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015, vol. 3, pp. 1688–1698.
Galkina, O.L., Önneby, K., Huang, P., Ivanov, V.K., Agafonov, A.V., Seisenbaeva, G.A., and Kessler, V.G., Antibacterial and photochemical properties of cellulose nanofibers–titania nanocomposites loaded with two different types of antibiotic medicines, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015, vol. 3, pp. 7125–7134.
Evdokimova, O.L., Svensson, F.G., Agafonov, A.V., Håkansson, S., Seisenbaeva, G.A., and Kessler, V.G., Hybrid drug delivery patches based on spherical cellulose nanocrystals and colloid titania-synthesis and antibacterial properties, Nanomaterials (Basel, Switz.), 2018, vol. 8, no. 4, p. 228.
Ghaemi, N., Madaeni, S.S., and Daraei, P., Polyethersulfone membrane enhanced with iron oxide nanoparticles for copper removal from water: application of new functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles, Chem. Eng. J., 2015, vol. 263, pp. 101–112.
Poletto, M., Ornaghi, H.L., Jr., and Zattera, A.J., Native cellulose: structure, characterization and thermal properties, Materials, 2014, vol. 7, pp. 6105–6119.
Wang, L., Hu, C., and Shao, L., The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future, Int. J. Nanomed., 2017, vol. 12, pp. 1227–1249.
Wu, W., Wu, Z., Yu, T., Jiang, C., and Kim, W.S., Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2015, vol. 16, art. ID 023501.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The investigations were carried out using the equipment of the Upper Volga Regional Center for Physicochemical Studies.
Funding
The work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 18-33-00807 mol_a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by S. Efimov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evdokimova, O.L., Fedulova (Savicheva), A.D., Evdokimova, A.V. et al. Preparation of Hybrid Nanocomposites Based on Nanoscale Cellulose and Magnetic Nanoparticles with Photocatalytic Properties. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 11, 371–376 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113320020100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113320020100