Abstract
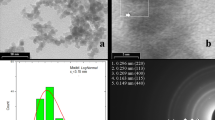
The kinetics of reduction of α-Fe2O3 nanopowder with hydrogen in an electromagnetic field with power mechanical treatment (PMT) in a vortex layer of ferromagnetic particles rotating in the field has been investigated. The kinetic parameters are calculated under the conditions of linear heating and isothermal conditions in accordance with the Freeman–Carroll and McKewan models, respectively. It is established that the electromagnetic field reduces the rate of reduction of the α-Fe2O3 nanopowder to 19% at 400°C, and PMT in a vortex layer intensifies the reduction process up to 4 times. The properties of the starting material and reduction products are studied using the thermogravimetry, X-ray diffraction, and electron microscopy methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Pankhurst, P.Q.A., Connolly, J., Jones, S.K., and Dobson, J., Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine, J. Phys. D, 2003, vol. 36, pp. 167–181.
Bengoa, J.F., Alvarez, A.M., Cagnoli, M.V., et al., Fischer–Tropsch reaction on Fe/zeolite-L system. Structure and catalytic behavior, Mater. Lett., 2002, vol. 53, pp. 6–11.
Wei, Y., Fang, Zh., Zheng, L., and Tsang, E.P., Biosynthesized iron nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and its mechanism in the hexavalent chromium removal, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, vol. 399, pp. 322–329.
Getmantsev, S.V., Nechaev, I.A., and Gandurina, L.V., Ochistka promyshlennykh stochnykh vod koagulyantami i flokulyantami (Cleaning of Industrial Wastewater by Coagulants and Flocculants), Moscow: Assots. Stroit. Vuzov, 2008.
Ryzhonkov, D.I., Levina, V.V., and Dzidziguri, E.L., Nanomaterialy (Nanomaterials), Moscow: BINOM. Laboratoriya Znanii, 2012.
Devatha, C.P., Thalla, A.K., and Shweta, Y.K., Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using different leaf extracts for treatment of domestic waste water, J. Clean. Prod., 2016, vol. 139, pp. 1425–1435.
Fan, M., Zhang, L., Wang, R., Guo, H., and Jia, Sh., Facile and controllable synthesis of iron nanoparticles directed by montmorillonite and polyvinylpyrrolidone, Appl. Clay Sci., 2017, vol. 144, pp. 1–8.
Gai, C., Zhang, F., Lang, Q., Liu, T., Peng, N., and Liu, Zh., Facile one-pot synthesis of iron nanoparticles immobilized into the porous hydrochar for catalytic decomposition of phenol, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, vol. 204, pp. 566–576.
Ravikumar, K.V.G., Dubey, S., Pulimi, M., et al., Scale-up synthesis of zero-valent iron nanoparticles and their applications for synergistic degradation of pollutants with sodium borohydride, J. Mol. Liq. A, 2016, vol. 224, pp. 589–598.
Lin, L., Starostin, S.A., et al., Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles in microplasma under atmospheric pressure, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2017, vol. 168, pp. 360–371.
Ryzhonkov, D.I., Arsent’ev, P.P., and Yakovlev, V.V., Teoriya metallurgicheskikh protsessov (Theory of Metallurgical Processes), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1989.
Logvinenko, D.D. and Shelyakov, O.P., Intensifikatsiya tekhnologicheskikh protsessov v apparatakh s vikhrevym sloem (Intensification of Technological Processes in Apparatuses with Eddy Layer), Kiev: Tekhnika, 1976.
Umanskii, Ya.S., Skakov, Yu.A., et al., Kristallografiya, rentgenografiya i elektronnaya mikroskopiya (Crystallography, X-ray, and Electron Microscopy), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1982.
Freeman, E.S. and Carroll, B., The application of thermoanalytical techniques to reaction kinetics: The thermogravimetric evaluation of the kinetics of the decomposition of calcium oxalate monohydrate, J. Phys. Chem., 1958, vol. 62, pp. 394–397.
Brown, M., Dollimore, D., and Galwey, A., Reactions in the Solid State, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1980.
McKewan, W.M., Kinetics of iron oxide reduction, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 1960, vol. 218, pp. 2–6.
Buchachenko, A.L., Sagdeev, R.Z., and Salikhov, K.M., Magnitnye i spinovye effekty v khimicheskikh reaktsiyakh (Magnetic and Spin Effects in Chemical Reactions), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1978.
Rahimi, M. and Dehkordi, A.M., Reactive absorption in packed bed columns in the presence of magnetic nanoparticles and magnetic field: modeling and simulation, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2017, vol. 45, pp. 131–144.
Nguyen, V.M., Konyukhov, Yu.V., Ryzhonkov, D.I., and Kotov, S.I., Peculiarities of nanodisperse and micron-size nickel powders produced by hydrogen reduction in the eddy magnetic field, Izv. VUZov, Poroshk. Metall. Funkts. Pokrytiya, 2016, no. 1, pp. 4–11.
Ryzhonkov, D.I., Kostyrev, S.B., and Gorchakov, Yu.A., Kinetic of reduction of Fe–NiO–CuO mixtures in a rotating electromagnetic field, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., 1990, no. 5, pp. 101–102.
Mishchenko, M.V., Bokov, M.M., and Grishaev, M.E., Activation of materials treatment in the devices with rotating electromagnetic field, Fundam. Issled., 2015, no. 2-16, pp. 3508–3512.
Bezzubtseva, M.M. and Volkov, V.S., Teoreticheskie osnovy elektromagnitnoi mekhanoaktivatsii (Theory of Electromagnetic Mechanical Activation), St. Petersburg: S.-Peterb. Gos. Agrar. Univ., 2011.
Chernavskii, P.A., Pankina, G.V., Turakulova, A.O., Zaikovskii, V.I., and Perov, N.S., The effect of a magnetic field on the thermal destruction of cobalt formate, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, vol. 83, no. 3, pp. 499–502.
Hans, E., Crystallization of calcium carbonate in magnetic field in ordinary and heavy water, J. Cryst. Growth, 2004, vol. 267, pp. 251–255.
Awaji, S., Ma, Y., Watanabe, K., and Motokawa, M., Magnetic field effects on growth process of YBa2Cu3O7 films by chemical vapor deposition in high magnetic fields, Materia Jpn., 2003, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 115–123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by O. Kadkin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konyukhov, Y.V., Nguyen, V.M. & Ryzhonkov, D.I. Kinetics of Reduction of α-Fe2O3 Nanopowder with Hydrogen under Power Mechanical Treatment in an Electromagnetic Field. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 10, 706–712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113319030171
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113319030171