Abstract
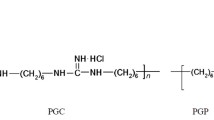
The introduction of Ca2+ and Zn2+ ions into solutions containing polyhexamethyleneguanidine derivatives leads to the increase of their inhibitory effect in the steel corrosion in neutral medium. It was shown, that inhibition effect has adsorption nature and linearly depends on the degree of filling of the electrode with an inhibitor. It was established, that in the consequences of complexation of modified polyhexamethyleneguanidines with Ca2+ and Zn2+ cations the structure, charge and hydrophilic-lipophilic balance of macromolecules are changing which lead to a change in the free energy of interaction of the macroparticles with the solvent and the growth of “displacement” on a free surface. In the high media hardness the most effective inhibitor is a zinc complex of carboxylated polihexamethyleneguanidine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chirkunov, A.A., Kuznetsov, Yu.I., and Tomin, V.P, Korroz.: Mater., Zashch., 2007, no. 4, p. 18.
Chirkunov, A.A., Kuznetsov, Yu.I., and Kazanskii, L.P, Korroz.: Mater., Zashch., 2007, no. 9, p. 27.
Antonnik, L.M., Lopyrev, V.A., Korchevin, N.A., and Tomin, V.P, Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2002, vol. 75, no. 2, p. 257.
Obraztsov, V.B., Rubl’ova, E.D., and Amirulloeva, N.V, Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 49, no. 3, p. 326.
Rublova, E.D., Obraztsov, V.B., and Danilov, F.I, Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2014, vol. 87, no. 12, p. 1836.
Obraztsov, V.B., Rubl’ova, E.D., Amirulloeva, N.V., et al, Visn. Skhidnoukr. Nats. Univ. im. V. Dalya, 2013, no. 13, p. 18.
Delahay, P. and Reinmuth, W.H, Anal. Chem., 1962, vol. 34, no. 10, p. 1344.
Obraztsov, V.B., Kapitonov, A.G., Parfenov, Yu.A., and Danilov, F.I, Elektrokhimiya, 1991, vol. 27, no. 10, p. 1378.
Danilov, F.I., Kapitonov, A.G., and Obraztsov, V.B, Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., 2000, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 611.
Leo, A., Hansch, C., and Elkins, D, Chem. Rev., 1971, vol. 71, no. 6, p. 525.
Damaskin, B.B., Nekrasov, L.N., Petrii, O.A., et al., Elektrodnye protsessy v rastvorakh organicheskikh soedinenii (Electrode Processes in Organic Compounds Solutions), Moscow: Moscow State Univ., 1985.
Afanas’ef, B.N., Akulova, Yu.P., and Yakovleva, O.R, Prot. Met., 2001, vol. 37, no. 3, p. 201.
Skopenko, V.V. and Zub, V.Ya., Koordinatsiina Khimiya (Coordination Chemistry), Kyiv: Kyivskii Universitet, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Y.D. Rublova, O.V. Velichko, F.I. Danilov, 2017, published in Fizikokhimiya Poverkhnosti i Zashchita Materialov, 2017, Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 556–560.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rublova, Y.D., Velichko, O.V. & Danilov, F.I. Effect of Ca2+ and Zn2+ ions on the adsorption and inhibitory properties of polyhexamethyleneguanidine derivatives. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 53, 916–919 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117050173
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117050173