Abstract
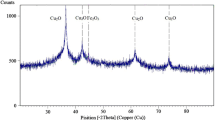
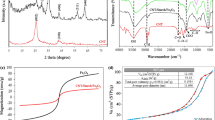
New starch coated zero-valent Fe/Cu nanoparticles were synthesized by borate reduction method. The surface profile of synthesized nanoparticles was studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM) imaging. Comparison of Infra red (IR) spectra of soluble starch and starch coated Fe/Cu nanoparticle revealed the complex formation between Fe/Cu nanoparticles and soluble starch. X-ray diffraction pattern and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) spectrum analysis exposed the composition of starch coated Fe/Cu nanoparticles. SEM imaging determined the size of Fe/Cu nanoparticle which was fallen into the size of 48 to 70 nm. In this study, the capability of starch coated Fe/Cu nanoparticle to degrade the low and high chlorinated biphenyls were studied extensively. It was observed that soluble starch and β-cyclodextrin have enhanced the polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) degradation by preventing iron nano-agglomeration and making the PCB as a soluble form, respectively. The dechlorination was further confirmed by the estimation of released chloride ion during the PCB degradation. The present study suggested that this new method could be an efficient and reliable method to treat PCB contaminated soil and sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, G., Brusseau, M.L., and Miller, R.L., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1997, vol. 63, p. 1866.
Biswas, P. and Wu, C.Y., J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., 2005, vol. 55, p. 708.
Cao, J., Xu, R., Tang, H., et al., Sci. Total Environ., 2011, vol. 409, p. 2336.
Cirwertny, D.M., Bransford, S.J., and Roberts, A.L., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 41, p. 3734.
Clark, C.J., Rao, P.S.C., and Annable, M.D., J. Hazard. Mater., 2003, vol. 96, p. 65.
Coleman, N.V., Mattes, T.E., Gossett, J.M., et al., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 68, p. 2726.
Cundy, A.B., Hopkinson, L., and Whitby, R.L.D., Sci. Total Environ., 2008, vol. 400, p. 42.
Dragunski, D.C. and Pawlicka, A., Mater. Res., 2001, vol. 4, p. 77.
Gusmao, A.D., Campos, T.M.P., Nobre, M.M.M., et al., J. Hazard. Mater., 2004, vol. 110, p. 105.
He, F. and Zhao, D., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, vol. 39, p. 3314.
He, F. and Zhao, D.Y., Appl. Catal., B, 2008, vol. 84, p. 533.
Henn, K. and Waddill, D.W., Rem. J., 2006, vol. 16, p. 57.
Kim, Y.H. and Carraway, E.R., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 34, p. 2014.
Li, L., Fan, M., Brown, R.C., et al., Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 36, p. 405.
Lien, H.L., Elliott, D.S., Sun, Y.P., et al., J. Environ. Eng. Manage., 2006, vol. 16, p. 71.
Lin, C.J., Liou, Y.H., and Lo, S.L., Chemosphere, 2009, vol. 74, p. 314.
Lowry, G.V. and Johnson, K.M., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 38, p. 5208.
Miehr, R., Tratnyek, P.G., Bandstra, J.Z., et al., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 38, p. 139.
Phenrat, T., Saleh, N., Sirk, K., et al., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 41, p. 284.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.J., Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters, New York: Wiley, 1996.
Tee, Y.H., Grulke, E., and Bhattacharyya, D., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2005, vol. 44, p. 7062.
Volkering, F., Breure, A.M., and Rulkens, W.H., Biodegradation, 1998, vol. 8, p. 401.
Wang, C.B. and Zhang, W.X., Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 31, p. 2154.
Xu, J. and Bhattacharyya, D., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, vol. 46, p. 2348.
Xu, Y. and Zhang, W.X., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2000, vol. 39, p. 2238.
Elliott, D.W. and Zhang, W.X., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 35, no. 24, pp. 4922–4926.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesh-Kumar, S., Kalimuthu, K. & Jebakumar, S.R.D. Characterization of newly synthesized starch coated Fe/Cu nanoparticles and its dechlorination efficiency on the low and high chlorinated biphenyls. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 53, 685–692 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117040074
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117040074