Abstract
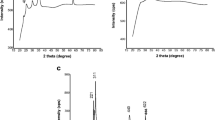
In the present work iron oxide nanoparticles have been prepared by microwave assisted synthesis with the influence of different precursor salts and synthesis of magnetite, hematite, Iron oxide hydroxide and maghemite nanoparticles. Synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles were characterized with Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM), and Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX). XRD measurements show that the peaks of diffractogram are in agreement with the theoretical data of magnetite, hematite, FeO(OH) (Iron oxide hydroxide) and maghemite. Crystallite size of the particles was found to be 33, 45, 36 and 43.5 nm for Fe3O4, α-Fe2O3, FeO(OH) and γ-Fe2O3. FESEM studies indicated that size of the particles is observed in the range of about 19.4 to 46.7 nm (Fig. 2a, average 32 nm), 29.1 to 67.6 nm (Fig. 2b average 45 nm), 29.1 to 40.8 (Fig. 2c average 36.6 nm), 29.1 to 80 nm (Fig. 2d average 43.5) for Fe3O4, α-Fe2O3, FeO(OH) and γ-Fe2O3 respectively. EDX spectral analysis reveals the presence of carbon, oxygen, iron in the synthesized nanoparticles. The FTIR graphs indicated absorption bands due to O–H stretching, C–O bending, C–H stretching and Fe–O stretching vibrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teja, A.S. and Koh, P.-Y., Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater., 2009, vol. 55, p. 22.
Rosenzweig, R.E., Ferrohydrodynamics, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1985.
Berry, C.C. and Curtis, A.S.G., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2003, vol. 36, p. 198.
Thach, C.V., Hai, N.H., and Chau, N.J., J. Korean Phys. Soc., 2008, vol. 52, p. 1332.
Leslie-Pelecky, D.L., Labhasetwar, V., and Kraus, R.H., in Advanced Magnetic Nanostructures, Sellmyer, D.J. and Skomski, R.S., Eds., New York: Kluwer, 2005.
Zboril, R., Mashlan, M., and Petridis, D., Chem. Mater., 2002, vol. 14, p. 969.
Cao, H. and Suib, S.L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, vol. 133, p. 460.
Mohapatra, M. and Anand, S., Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 2, p. 127.
Hasany, S.F., Ahmed, I., Rajan, J., and Rehman, A., Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2012, vol. 2, p. 148.
Cheng, Z., Tan, A.L.K., Tao, Y., et al., Int. J. Photoenergy, 2012, vol. 2012, pp. 1–5. Article ID608298. doi: doi 10.1155/2012/60829810.1155/2012/608298
Benyettou, F., Milosevic, I., Olsen, J.C., et al., J. Bioanal. Biomed., 2012, p. 5. doi 10.4172/1948-593X.S5-006
Parsons, J.G., Luna, C., Botez, C.E., et al., J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2009, vol. 70, p. 555.
Powder Diffraction File Alphabetical Index. Inorganic Phases, Swarthmore, PA: Int. Center for Diffraction Data, 1984, p. 1601.
Peng, Q., Dong, Y.J., and Li, Y.D., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, vol. 42, p. 3027.
Peng, Q., Xu, S., Zhuang, Z.B., et al., Small, 2005, vol. 1, p. 216.
Sun, X.M. and Li, Y.D., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, vol. 43, p. 3827.
Sun, X.M. and Li, Y.D., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, vol. 43, p. 597.
Wang, J.W., Wang, X., Peng, Q., and Li, Y.D., Inorg. Chem., 2004, vol. 43, p. 7552.
Zhang, Y. and Li, Y.D., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, vol. 108, p. 17805.
Phu, N.D., Ngo, D.T., Hoang, L.H., et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 44, p. 34.
Stuart, B.H., Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications, Chichester: Wiley, 2004.
Battisha, J.K., Afify, H.H., and Ibrahim, M., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2006, vol. 306, p. 211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guru, S., Mishra, D., Singh, M. et al. Effect of SO4 2-, Cl– and NO3 - anions on the formation of iron oxide nanoparticles via microwave synthesis. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 52, 627–631 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205116040146
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205116040146