Abstract
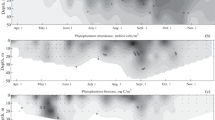
A study of the horizontal and vertical distribution of phytoplankton in Lake Sevan was conducted in mid-July 2018 during the maximum Cyanoprokaryota blooms. The summer biomass of algae in the pelagic zone of the lake corresponded to values of mesatrophic waters. The Cyanoprokaryota biomass in Lake Sevan has horizontal and vertical heterogeneity and is related to the depth, morphometry of the lake parts, distribution of currents, transparency, temperature, and biomass of Cladocera. The specific number of phytoplankton species and water transparency decreases in areas where water blooms occur. The following factors contribute to the increase in the average phytoplankton biomass when compared to 2013–2017: (1) increased water temperature, (2) weakening of zooplankton grazing pressure due to the disappearance of Daphnia magna, and (3) increased phosphorus load due to increased contribution of D. longispina and Diaphanosoma lacustris to the zooplankton biomass.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abakumov, A.I. and Izrailsky, Y.G., Environment influence on the phytoplankton distribution in a basin, Math. Biol. Bioinf., 2012, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 274–283. https://doi.org/10.17537/2012.7.274
Airapetyan, A.O., Krylov, A.V., and Gabrielyan, B.K., Zooplankton of two types of shallow water sites of the Sevan Lake formed during water level rise, Biol. Zh. Arm., 2014, vol. 66, no. 1, pp. 12–17.
Balushkina, E.B. and Vinberg, G.G., Dependence between weight and length of body in planktonic animals, in Obshchie osnovy izucheniya vodnykh ekosistem (General Principles of the Study of Aquatic Ecosystems), Leningrad: Nauka, 1979, pp. 169–172.
Chilingaryan, L.A. and Mnatsakanyan, B.A., Hydrology of the Sevan Lake basin, in Ekologiya ozera Sevan v period povysheniya ego urovnya (Ecology of the Sevan Lake during Water Level Rise), Makhachkala: Nauka, 2010, pp. 28–40.
Decamps, H., Pinay, G., Naiman, R., Petts, G.E., McClain, M. E., Hillbricht-Ilkowska, A., Hanley, T.A., Holmes, R.M., Quinn, J., Gibert, J., Planty Tabacchi, A., Schiemer, F., Tabacchi, E., and Zalewski, M., Riparian zones: where biogeochemistry meets biodiversity in management practice, Pol. J. Ecol., 2004, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 3–18.
Ekosistema ozera Pleshcheevo (Ecosystem of the Pleshcheevo Lake), Leningrad: Nauka, 1989.
Ferrante, J.G., The role of zooplankton in the intrabiocenotic phosphorus cycle and factors affecting phosphorus excretion in a lake, Hydrobiologia, 1976, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 203–214.
Filatov, N.N., Gidrodinamika ozer (Lake Hydrodynamics), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1991.
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Gabrielyan, B.K., Malin, N.I., and Rubenyan, A.R., Long-term dynamics and modern state of fish reserves in the Sevan Lake, in Ekologiya ozera Sevan v period povysheniya ego urovnya. Rezul’taty issledovanii Rossiisko-Armyanskoi biologicheskoi ekspeditsii po gidroekologicheskomu obsledovaniyu ozera Sevan (Armeniya) (2005–2009 gg.) (Ecology of the Sevan Lake during Water Level Increase. The Study Results of Russian-Armenian Biological Expedition on Hydroecological Observation of the Sevan Lake (Armenia) in 2005–2009), Makhachkala: Nauka, 2010, pp. 249–278.
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Borisenko, E.S., Malin, N.I., Rubenyan, A.R., Vardanyan, T.V., Barsegyan, N.E., Zhgareva, N.N., Bazarov, M.I., and Gabrielyan, B.K., Fishes, in Ozero Sevan. Ekologicheskoe sostoyanie v period izmeneniya urovnya vody (Lake Sevan: Ecological State during Water Level Dynamics), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2016, pp. 207–252.
Hanley, T.A. and Barnard, J.C., Spatial variation in population dynamics of Sitkamice in floodplain forests, J. Mammal., 1999, vol. 80, no. 3, pp. 866–879.
Integral’naya otsenka ekologicheskogo sostoyaniya ozera Sevan (GEO–Lake Sevan). Doklad Association For SHD”/UNEPCom (Integral Assessment of Ecological State of the Sevan Lake (GEO–Lake Sevan): A Report of For SHD”/UNEPCom Association), Yerevan, 2011.
Kitaev, S.P., Osnovy limnologii dlya gidrobiontov i ikhtiologov (Fundamentals of Limnology for Hydrobiologists and Ichthyologists), Petrozavodsk: Karel. Nauchn. Tsentr, Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2007.
Korneva, L.G., Phytoplankton of Rybinsk Reservoir: composition, Specific distribution, and eutrophication consequences, in Sovremennoe sostoyanie ekosistemy Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha (Modern State of Ecosystem of Rybinsk Reservoir), St. Petersburg: Gidrometeoizdat, 1993, pp. 50–113.
Korneva, L.G., Solov’eva, V.V., Zhakovskaya, Z.A., Ruskikh, Ya.V., and Chenova, E.N., Phytoplankton and content of cyanotoxins in Rybinsk, Gorky, and Cheboksary reservoirs during abnormally hot summer 2010, Voda: Khim. Ekol., 2014, no. 8, pp. 24–29.
Kozitskaya, V.N., Influence of temperature on growth and reproduction of algae with various types of pigment systems, Gidrobiol. Zh., 1991, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 62–71.
Krylov, A.V., Gerasimov, Yu.V., Gabrielyan, B.K., Borisenko, E.S., Hakobyan, S.A., Nikogosyan, A.A., Malin, M.I., and Ovsepyan, A.A., Zooplankton in Lake Sevan during the period of high water level and low fish density, Inland Water Biol., 2013, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082913030085
Krylov, A.V., Hayrapetyan, A.O., Gerasimov, Yu.V., and Malin, M.I., Changes in the structural parameters of the summer zooplankton in the pelagic zone of Lake Sevan (Armenia) during an increase in fish abundance and biomass, Inland Water Biol., 2016, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 73–78. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082916010090
Krylov, A.V., Kosolapov, D.B., Kosolapova, N.G., Hovsepyan, A.A., and Gerasimov, Yu.V., The plankton community of Sevan Lake (Armenia) after invasion of Daphnia (Ctenodaphnia) magna Straus, 1820, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2018, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 505–511. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0002332918050089
Legovich, N.A., About water blooming in the Sevan Lake, in Ekologiya gidrobiontov ozera Sevan (Ecology of Hydrobionts of the Sevan Lake), Yerevan: Akad. Nauk Arm. SSR, 1979, no. 17, pp. 51–74.
Metodika izucheniya biogeotsenozov vnutrennikh vodoemov (A Method of Analysis of Biogeocenosises of Inland Reservoirs), Moscow: Nauka, 1975.
Naiman, R.J., Bechtold, J.S., Drake, D., Latterell, J.J., O’Keefe, T.C., and Balian, E.A., Origins, patterns, and importance of heterogeneity in riparian systems, in Ecosystem Function in Heterogeneous Landscapes, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2005, pp. 279–309.
Ovsepyan, A.A. and Gambaryan, L.R., The data on development of phytoplanktonic community of the Sevan Lake, Tr. Bryansk.Gos. Univ., 2013, vol. 2, pp. 193–195.
Ovsepyan, A.A. and Khachikyan, T.G., Pelagial phytoplankton of the Sevan Lake, in Ozero Sevan. Ekologicheskoe sostoyanie v period izmeneniya urovnya vody (Lake Sevan: Ecological State during Water Level Dynamics), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2016, pp. 39–60.
Ovsepyan, A.A., Gambaryan, L.R., Oganesyan, R.O., and gusev, E.S., Planktonic algae of the Sevan Lake, in Ekologiya ozera Sevan v period povysheniya ego urovnya (Ecology of the Sevan Lake during Water Level Rise), Makhachkala: Nauka, 2010, pp. 90–104.
Paerl, H.W. and Huisman, J., Blooms like it hot, Science, 2008, vol. 320, pp. 57–58. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1155398
Paerl, H.W. and Huisman, J., Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms, Environ. Microbiol. Rep., 2009, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-2229.2008.00004.x
Pokrovskaya, T.N., Mironova, N.Ya., and Shil’krot, G.S., Makrofitnye ozera i ikh evtrofirovanie (Eutrophication of Macrophytic Lakes), Moscow: Nauka, 1983.
Pollock, M.M., Naiman, R.J., and Hanley, T.A., Plant species richness in riparian wetlands—a test of biodiversity theory, Ecology, 1998, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 94–105.
Sakharova, E.G. and Korneva, L.G., Phytoplankton communities of Volga Reach open shallows of Rybinsk Reservoir at the area affected by the vital activity products of grey heron (Ardea cinerea L.), Contemp. Probl. Ecol., 2017, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 140–146. https://doi.org/10.1134/S199542551702010X
Sakharova, E.G. and Korneva, L.G., Phytoplankton in the littoral and pelagial zones of the Rybinsk Reservoir in years with different temperature and water level regimes, Inland Water Biol., 2018, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 6–12. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082918010157
Schlosser, I.J. and Karr, J.R., Water quality in agricultural watersheds: impact of riparian vegetation during baseflow, Water Resour. Bull., 1981, vol. 17, pp. 233–240.
Sirenko, L.A. and Gavrilenko, M.Ya., Tsvetenie vody i evtrofirovanie (Water Blooming and Eutrophication), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1978.
Sládečeková, A. and Sládeček, V., Bioindication within the aquatic environment, Acta Environ. Univ. Comenianae, 1993, vol. 7, nos. 1–2, pp. 3–69.
Trifonova, I.S., Ekologiya i suktsessiya ozernogo fitoplanktona (Ecology and Succession of Lake Phytoplankton), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
Vollenweider, R.A., Scientific Fundamentals of the Eutrophication of Lakes and Flowing Waters with Particular Reference to Nitrogen and Phosphorus as Factors in Eutrophication, Paris: Org. Econ. Co-op. Dev., 1971.
FUNDING
We are grateful to the crew of the Gidrolog expeditionary vessel for assistance in collecting the material. This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-54-05003 Arm_а) and was performed within the framework of a state assignment (project nos. АААА-А18-118012690096-1, АААА-А18-118012690106-7, and АААА-А18-118012690104-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals.
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by N. Ruban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakharova, E.G., Krylov, A.V., Sabitova, R.Z. et al. Horizontal and Vertical Distribution of Phytoplankton in the Alpine Lake Sevan (Armenia) during the Summer Cyanoprokaryota Bloom. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 13, 60–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425520010072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425520010072