Abstract
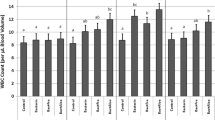
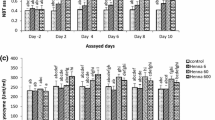
This paper provides a review of literature published in 2000–2016 on the responses of lysozyme in cyprinids, which was experimentally obtained based on substances of different origin. Ten species, representing objects of aquaculture, are studied. The effects of pathogenic and parasitic infection, vaccination, and immunization, as well as immunostimulants, including endotoxins, secondary metabolites, components of plant origin, and hormones administered by injection, are considered. The pathogenic challenge of carp Cyprinus carpio L. by Aeromonas hydrophila (Chester) shows multidirectional changes and their absence in the activity of lysozyme. The parasitic infection of different fish species usually has an immunosuppressive effect. Vaccination and immunization increase serum lysozyme activity, which is 7–8 times higher than that in the control fish. However, the immune responses differ in time and depend on some factors, including the structure of the active substance and composition of the vaccine. Most immunostimulants contribute to different growths in the activity and content of lysozyme in carp serum and organs. Immune responses can reverse, depending on the dose of the active substance. The diversity of units of lysozyme activity makes it difficult to systematize immune responses even within a single fish species. The range of variation in the serum lysozyme activity of Cyprinus carpio and Labeo rohita (Hamilton) is very wide in studies conducted by different researchers, which probably cannot correspond to adequate physiological values. There are data indicating the highest mortality among experimental fish that have the highest serum lysozyme activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abasali, H. and Mohamad, S., Immune response of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed with herbal immunostimulants diets, Agric. J., 2010, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01660.x
Alexander, C., Sahu, N.P., Pal, A.K., et al., Haemato-immunological and stress responses of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings: effect of rearing temperature and dietary gelatinized carbohydrate, J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutrit., 2011, vol. 95, no. 5, p. 653. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01096.x
Ardo, L., Jeney, Z., Adams, A., et al., Immune responses of resistant and sensitive common carp families following experimental challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila,Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2010, vol. 29, no. 1, p. 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.02.029
Baruah, A., Saha, R.K., and Kamilya, D., Interspecies transmission of the epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS) pathogen, Aphanomyces invadans, and associated physiological responses, Bamidgeh, 2012, vol. 64, p. 9.
Behera, T. and Swain, P., Antigen adsorbed surface modified poly-ε-caprolactone microspheres stimulates both adaptive and innate immune response in fish, Vaccine, 2012, vol. 30, no. 35, p. 5278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.05.028
Behera, T. and Swain, P., Alginate-chitosan-PLGA composite microspheres induce both innate and adaptive immune response through parenteral immunization in fish, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2013, vol. 35, no. 3, p. 785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.06.012
Behera, T. and Swain, P., Antigen encapsulated alginate-coated chitosan microspheres stimulate both innate and adaptive immune responses in fish through oral immunization, Aquacult. Int., 2014, vol. 22, no. 2, p. 673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9696-8
Betoulle, S., Etienne, J.C., and Vernet, G., Acute immunotoxicity of gallium to carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2002, vol. 68, no. 6, p. 817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-002-0028-3
Bols, N.C., Brubacher, J.L., Ganassin, R.C., et al., Ecotoxicology and innate immunity in fish, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 2001, vol. 25, nos. 8–9, p. 853. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0145-305x(01)00040-4
Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Yang, Y., et al., Effect of dietary lysozyme on growth, immune response, intestine microbiota, intestine morphology and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophilia in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio), Aquacult. Nutr., 2014, vol. 20, no. 3, p. 229. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12069
Das, B.K., Pradhan, J., and Sahu, S., The effect of Euglena viridis on immune response of rohu, Labeo rohita (Ham.), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2009, vol. 26, no. 6, p. 871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.03.016
Das, B.K., Pradhan, J., Sahu, S., et al., Microcystis aeruginosa (Kutz) incorporated diets increase immunity and survival of Indian major carp Labeo rohita (Ham.) against Aeromonas hydrophila infection, Aquacult. Res., 2013, vol. 44, no. 6, p. 918. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2012.03098.x
Das, R., Raman, R.P., Saha, H., et al., Effect of Ocimum sanctum Linn. (Tulsi) extract on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila,Aquacult. Res., 2015, vol. 46, no. 5, p. 1111. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12264
Dash, S., Das, S.K., Samal, J., et al., Dose dependence specific and non-specific immune responses of indian major carp (L. rohita Ham) to intraperitoneal injection of formalin killed Aeromonas hydrophila whole cell vaccine, Vet. Res. Commun., 2011, vol. 35, no. 8, p. 541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-011-9498-2
Dautremepuits, C., Betoulle, S., Paris-Palacios, S., et al., Humoral immune factors modulated by copper and chitosan in healthy or parasitised carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) by Ptychobothrium sp. (Cestoda), Aquat. Toxicol., 2004, vol. 68, no. 4, p. 325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.04.003
Devi, T.B., Kamilya, D., and Abraham, T.J., Dynamic changes in immune-effector activities of Indian major carp, catla (Catla catla) infected with Edwardsiella tarda,Aquaculture, 2012, vols. 366-367, no. 5, p. 62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.09.002
Fatima, M., Mandiki, S.N.M., Douxfils, J., et al., Combined effects of herbicides on biomarkers reflecting immune-endocrine interactions in goldfish. Immune and antioxidant effects, Aquat. Toxicol., 2007, vol. 81, no. 2, p. 159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.11.013
Fawole, F.J., Sahu, N.P., Pal, A.K., et al., Haemato-immunological response of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings fed leaf extracts and challenged by Aeromonas hydrophila,Aquacult. Res., 2016, vol. 47, no. 12, p. 3788. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12829
Harikrishnan, R., Balasundaram, C., Kim, M.-C., et al., Innate immune response and disease resistance in Carassius auratus by triherbal solvent extracts, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2009a, vol. 27, no. 3, p. 508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.07.004
Harikrishnan, R., Balasundaram, C., Dharaneedharan, S., et al., Effect of plant active compounds on immune response and disease resistance in Cirrhina mrigala infected with fungal fish pathogen, Aphanomyces invadans,Aquacult. Res., 2009b, vol. 40, no. 10, p. 1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02213.x
Harikrishnan, R., Balasundaram, C., and Heo, M.-S., Herbal supplementation diets on hematology and innate immunity in goldfish against Aeromonas hydrophila,Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2010, vol. 28, no. 2, p. 354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.11.013
Jiang, X., Zhang, C., Zhao, Y., et al., Immune effects of the vaccine of live attenuated Aeromonas hydrophila screened by rifampicin on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), Vaccine, 2016, vol. 34, no. 27, p. 3087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.075
Jin, Y., Tian, L., Zeng, S., et al., Dietary lipid requirement on non-specific immune responses in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2013, vol. 34, no. 5, p. 1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.01.008
Kar, B., Mohanty, J., Hemaprasanth, K.P., et al., The immune response in rohu, Labeo rohita (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae) to Argulus siamensis (Branchiura: Argulidae) infection: kinetics of immune gene expression and innate immune response, Aquacult. Res., 2015, vol. 46, no. 6, p. 1292. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12279
Kozinska, A. and Guz, L., The effect of various Aeromonas bestiarum vaccines on non-specific immune parameters and protection of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2004, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2003.08.003
Kumar, V., Sahu, N.P., Pal, A.K., et al., Immunomodulation of Labeo rohita juveniles due to dietary gelatinized and non-gelatinized starch, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2007, vol. 23, no. 2, p. 341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2006.11.008
Kumar, R., Mukherjee, S.C., Ranjan, R., et al., Effect of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis on haematological and immunological parameters of Catla catla (Hamilton), Aquacult. Int., 2015, vol. 23, no. 5, p. 1275.
Kurovskaya, L.Ya. and Stril’ko, G.A., Effect of aquatic environment pH on the level of ectoparasite infestation, protein and lysozyme content in some cyprinid species (Cyprinidae), Ribogospodars’ka Nauka Ukraini, 2016, vol. 1, no. 35, p. 88. https://doi.org/10.15407/fsu2016.01.088
Liu, J., Lei, Y., Wang, F., et al., Immunostimulatory activities of specific bacterial secondary metabolite of Anoxybacillus flavithermus strain SX-4 on carp, Cyprinus carpio,J. Appl. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 110, no. 4, p. 1056. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.04963.x
Liu, B., Ge, X., Xie, J., et al., Effects of anthraquinone extract from Rheum officinale Bail on the physiological responses and HSP70 gene expression of Megalobrama amblycephala under Aeromonas hydrophila infection, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2012, vol. 32, no. 1, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2011.02.015
Maqsood, S., Samoon, M.H., and Singh, P., Immunomodulatory and growth promoting effect of dietary levamisole in Cyprinus carpio fingerlings against the challenge of Aeromonas hydrophila, Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2009, 2009, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 111.
Misra, C.K., Das B.K., Mukherjee, S.C., et al., Effect of multiple injections of β-glucan on non-specific immune response and disease resistance in Labeo rohita fingerlings, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2006a, vol. 20, no. 3, p. 305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.05.007
Misra, S., Sahu, N.P., Pal, A.K., et al., Pre- and post-challenge immuno-haematological changes in Labeo rohita juveniles fed gelatinised or non-gelatinised carbohydrate with n-3 PUFA, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2006b, vol. 21, no. 4, p. 346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.12.010
Mohammadian, T., Alishahi, M., Tabandeh, M.R., et al., Probiotic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and L. delbrueckii ssp. bulguricus on some immune-related parameters in Barbus grypus,Aquacult. Int., 2016, vol. 24, no. 1, p. 225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9921-8
Mohanty, B.R. and Sahoo, P.K., Immune responses and expression profiles of some immune-related genes in Indian major carp, Labeo rohita to Edwardsiella tarda infection, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2010, vol. 28, no. 4, p. 613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.12.025
Mohanty, B.R., Sahoo, P.K., Mahapatra, K.D., et al., Innate immune responses in families of Indian major carp, Labeo rohita, differing in their resistance to Edwardsiella tarda infection, Curr. Sci. India, 2007, vol. 92, no. 9, p. 1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.06.008
Nayak, A.K., Das, B.K., Kohli, M.P.S., et al., The immunosuppressive effect of α-permethrin on Indian major carp, rohu (Labeo rohita Ham.), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2004, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1050-4648(03)00029-9
Nayak, S.K., Swain, P., Nanda, P.K., et al., Effect of endotoxin on the immunity of Indian major carp, Labeo rohita,Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2008, vol. 24, no. 4, p. 394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2007.09.005
Qi, X-Z., Li, D-L., Tu, X., et al., Preliminary study on the relationship between dexamethasone and pathogen susceptibility on crucian carp (Carassius auratus), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2016, vol. 48, p. 79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.10.017
Raa, J., The use of immunostimulatory substances in fish and shellfish farming, Rev. Fish. Sci., 1996, vol. 4, no. 3, p. 229. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641269609388587
Sahoo, P.K., Mahapatra, K.D., Saha, J.N., et al., Family association between immune parameters and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in the Indian major carp, Labeo rohita,Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2008, vol. 25, nos. 1–2, p. 163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.04.003
Sahu S., Das, B.K., Mishra, B.K., et al., Effect of Allium sativum on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita infected with Aeromonas hydrophila,J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2007, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00785.x
Sahu S., Das, B.K., Mishra, B.K., et al., Effect of dietary Curcuma longa on enzymatic and immunological profiles of rohu, Labeo rohita (Ham.), infected with Aeromonas hydrophila,Aquacult. Res., 2008, vol. 39, no. 16, pp. 1720–1730. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02048.x
Saikia, D. and Kamilya, D., Immune responses and protection in catla (Catla catla) vaccinated against epizootic ulcerative syndrome, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2012, vol. 32, no. 2, p. 353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2011.11.030
Saurabh, S. and Sahoo, P.K., Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system, Aquacult. Res., 2008, vol. 39, no. 3, p. 223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01883.x
Saurabh, S., Sahoo, P.K., Mohanty, B.R., et al., Modulation of the innate immune response of rohu Labeo rohita (Hamilton) by experimental freshwater lice Argulus siamensis (Wilson) infection, Aquacult. Res., 2010, vol. 41, no. 9, p. 326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02538.x
Sen, S.S., Giri, S.S., and Sukumaran, V., Immune responses and protection in rohu vaccinated against Aeromonas hydrophila infection, Aquacult. Int., 2014, vol. 22, no. 5, p. 1637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-014-9770-x
Shariff, M., Jayawandena, P.A.H.L., Yusoff, F.M., et al., Immunological parameters of Javanese carp Puntius gonionotus (Bleeker) exposed to copper and challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila, Fish Shellfish Immunol., vol. 11, no. 4, p. 281. https://doi.org/10.1006/fsim.2000.0309
Sharma, A., Deo, A.D., Riteshkumar, S.T., et al., Effect of Withania somnifera (L. Dunal) root as a feed additive on immunological parameters and disease resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2010, vol. 29, no. 3, p. 508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.05.005
Siwicki, A. and Studnicka, M., The phagocytic ability of neutrophils and serum lysozyme activity in experimentally infected carp, Cyprinus carpio L, J. Fish. Biol., 1987, vol. 31, suppl. A, p. 57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1987.tb05293.x
Siwicki, A.K., Cossarini-Dunier, M., Studnicka, M., et al., In vivo effect of the organophosphorus insecticide trichlorphon on immune response of carp (Cyprinus carpio). II. Effect of high doses of trichlorphon on nonspecific immune response, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 1990, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 99.
Skouras, A., Lang, T., Vobach, M., et al., Assessment of some innate immune responses in dab (Limanda limanda L.) from the North Sea as part of an integrated biological effects monitoring, Helgoland Mar. Res., 2003, vol. 57, no. 3, p. 181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10152-003-0143-5
Sun, J., Wang, Q., Qiao, Z., et al., Effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and outer membrane protein (OMP) vaccines on protection of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) against Aeromonas hydrophila,Bamidgeh, 2011, vol. 63, p. 8.
Swain, P., Nayak, S.K., Nanda, P.K., et al., Biological effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) in fish: a review, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2008, vol. 25, no. 3, p. 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.04.009
Tassakka, A.C.M.A.R. and Sakai, M., CPG oligodeoxynucleotides enhance the non-specific immune responses on carp, Cyprinus carpio,Aquaculture, 2002, vol. 209, nos. 1–4, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00764-5
Thilagam, H., Gopalakrishnan, S., Bo, J., et al., Effect of 17 β-estradiol on the immunocompetence of Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus), Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2009, vol. 28, no. 8, p. 1722. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-642.1
Tort, L., Balasch, J.C., and Mackenzie, S., Fish immune system. A crossroads between innate and adaptive responses, Immunologia, 2003, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 277.
Vainikka, A., Jokinen, E.I., Kortet, R., et al., Effects of testosterone and β-glucan on immune functions in tench, J. Fish. Biol., 2005, vol. 66, no. 2, p. 348. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-1112.2005.00598.x
Wang, W.B., Li, A.H., Cai, T.Z., et al., Effects of intraperitoneal injection of cortisol on non-specific immune functions of Ctenopharyngodon idella,J. Fish. Biol., 2005, vol. 67, no. 3, p. 779. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-1112.2005.00779.x
Wang, G.-X., Liu, Y.-T., Li, F.-Y., et al., Immunostimulatory activities of Bacillus simplex DR-834 to carp (Cyprinus carpio), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2010, vol. 29, no. 3, p. 378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.03.014
Wang, G.-X., Wang, Y., Wu, Z.-F., et al., Immunomodulatory effects of secondary metabolites from thermophilic Anoxybacillus kamchatkensis XA-1 on carp, Cyprinus carpio,Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2011a, vol. 30, no. 6, p. 1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2011.03.011
Wang, G.-X., Li, F.-Y., Cui, J., et al., Immunostimulatory activities of a decapeptide derived from Alcaligenes faecalis FY-3 to crucian carp, Scand. J. Immunol., 2011b, vol. 74, no. 1, p. 14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02533.x
Wang, N., Yang, Z., Zang, M., et al., Identification of omp38 by immunoproteomic analysis and evaluation as a potential vaccine antigen against Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese breams, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2013, vol. 34, no. 1, p. 74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.10.003
Watanuki, H., Chakraborty, G., Korenaga, H., et al., Immunostimulatory effects of natural human interferon-alpha (huIFN-α) on carps Cyprinus carpio L., Vet. Immunol. Immunop., 2009, vol. 131, nos. 3–4, p. 273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.04.005
Wu, Z.X., Pang, S.F., Liu, J.J., et al., Coriolus versicolor polysaccharides enhance the immune response of crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) and protect against Aeromonas hydrophila,J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2013, vol. 29, no. 3, p. 562. https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.12105
Yang, X., Guo, J.L., Ye, J.Y., et al., The effects of Ficus carica polysaccharide on immune response and expression of some immune-related genes in grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2015, vol. 42, no. 1, p. 132.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.037
Yin, G., Ardo, L., Thompson, K.D., et al., Chinese herbs (Astragalus radix and Ganoderma lucidum) enhance immune response of carp, Cyprinus carpio, and protection against Aeromonas hydrophila,Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2009, vol. 26, no. 1, p. 140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.08.015
Zhang, L., Ma, J., Fan, Y., et al., Immune response and protection in gibel carp, Carassius gibelio, after vaccination with β-propiolactone inactivated cyprinid herpesvirus 2, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2016, vol. 49, p. 344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.01.003
Funding
This study was performed under State Assignment no. AAAA-A18-118012690222-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by D. Zabolotny
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subbotkin, M.F., Subbotkina, T.A. Effect of Infection and Injections of Substances of Different Origin on Lysozyme in Cyprinids (Family Cyprinidae) (Review). Inland Water Biol 13, 297–307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082920020133
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082920020133