Abstract
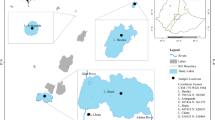
Results of a study of the water temperature and phytoplankton abundance in different regions of Lake Baikal according to 15 expeditions from 1994 to 2013 during late summer are present. The spatial distribution and interannual dynamics of phytoplankton are analyzed. The total abundance of phytoplankton in late summer is shown to be high. Its average long-term value for all of the open area of Lake Baikal is 532 ± 17 thousand cells/L. In Southern Baikal, the west coast is characterized by higher average phytoplankton abundance; in Middle and Northern Baikal, the east coast is rich. No significant differences were found between the hollows of the lake in terms of the development of late summer phytoplankton. The long-term average abundance of phytoplankton in the southern, middle, and northern hollows differs only by ≤1.2 times, but in the middle hollow it is significantly higher than in the northern. In the long-term dynamics, no significant increase in the abundance of late summer phytoplankton was recorded in any of the regions of the lake. The dependence of the total phytoplankton abundance on water temperature is weak; the correlation coefficients between the average annual values of these indicators are ≤0.50.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Antipova, N.L., Seasonal and annual changes in phytoplankton in Lake Baikal, Tr. Limnol. Inst. Sib. Otd. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1963, vol. 2 (22), part 2, p. 12.
Antipova, N.L., Interannual changes in the phytoplankton of Lake Baikal in the Bol’shie Koty region in the period 1960–1970, in Produktivnost’ Baikala i antropogennye izmeneniya ego prirody (Productivity of Lake Baikal and Anthropogenic Changes in Its Nature), Irkutsk: Izd. BGNII pri IGU, 1974, p. 75.
Antipova, N.L. and Kozhov, M.M., Data on seasonal and annual fluctuations in the abundance of dominant forms of phytoplankton of Lake. Baikal, Tr. Irkut. Gos. Univ.,Ser. Biol., 1953, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 63.
Baikalovedenie (Lake Baikal Science), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 2012.
Coats, R., Perez-Losada, J., Schladow, G., Richards, R., and Goldman, C., The warming of Lake Tahoe, Climatic Change, 2006, vol. 76, p. 121.
Goldman, C.R., Jassby, A., and Powell, T., Interannual fluctuations in primary production: meteorological forcing at two subalpine lakes, Limnol., Oceanogr., 1989, vol. 34, p. 310.
Hajnal, E. and Padisak, J., Analysis of long-term ecological status of lake balaton based on the almobal phytoplankton database, Hydrobiologia, 2008, vol. 599, no. 1, p. 227.
Huber, V., Adrian, R., and Gerten, D., Phytoplankton response to climate warming modified by trophic state, Limnol., Oceanogr., 2008, vol. 53, no. 1, p. 1.
Izmest’eva, L.R., Moore, M.V., Hampton, S.E., et al., 2016. Lake-wide physical and biological trends associated with warming in Lake Baikal, J. Great Lakes Res., vol. 42, p. 6.
Kalff, J., Limnology: Inland Water Ecosystems, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2002.
Kozhov, M.M., Ocherki po baikalovedeniyu (Essays on Lake Baikal Science), Irkutsk: Vost.-Sib. Knizhn. Izd., 1972.
Kozhova, O.M. and Kobanova, G.I., Abnormal phenomena in the structure of phytoplankton in Lake Baikal, in Otsenka sostoyaniya vodnykh i nazemnykh ekologicheskikh sistem (Assessment of the State of Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystems), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1974, p. 24.
Kozhova, O.M. and Mel’nik, N.G., Instruktsiya po obrabotke prob planktona schetnym metodom (Instruction on Processing Plankton Samples by the Counting Method), Irkutsk: Irkutsk. Univ., 1978.
Kraemer, B.M., Anneville, O., Chandra, S., Dix, M., et al., Morphometry and average temperature affect lake stratification responses to climate change, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2015, vol. 42, no. 12, p. 4981. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL064097
Kraemer, B.M., Chandra, S., Dell, A.I., et al., Global patterns in lake ecosystem responses to warming based on the temperature dependence of metabolism, Global Change Biol., 2017, vol. 23, no. 5, p. 1881. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13459
Meier, K.I., Introduction to the algal flora of Lake Baikal, Byull. Mosk. O-va Ispyt. Prir., Otd.Biol., 1930, vol. 39, p. 179.
Parker, B.R., Vinebrooke, R.D., and Schindler, D.W., Recent climate change extreme salter alpine lake ecosystems, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, vol. 108, p. 12927.
Popovskaya, G.I., Dynamics of phytoplankton of the pelagic zone (1964–1974), in Biologicheskaya produktivnost' pelagiali Baikala i ee izmenchivost' (Biological Productivity of the Pelagic Zone of Lake Baikal and Its Variability), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1977, p. 5.
Popovskaya, G.I., Phytoplankton of Lake Baikal and its long-term changes (1958–1990), Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation, Novosibirsk, 1991.
Popovskaya, G.I., Usol’tseva, M.V., Domysheva, V.M., et al., Spring phytoplankton of the pelagic zone of Lake Baikal in 2007–2011, Geogr. Prir. Resur., 2015, no. 3, p. 74.
O’Reilly, C.M., Sharma, S., Gray, D.K., et al., Rapid and highly variable warming of lake surface waters around the globe, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2015, vol. 42. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL066235
Sachs, L., Statisticheskoe otsenivanie (Statistical Estimation), Moscow: Statistika, 1976.
Salmaso, N., Effects of climatic fluctuations and vertical mixing on the interannual trophic variability of Lake Garda, Italy, Limnol., Oceanogr., 2005, vol. 50, p. 553.
Schwoerbel, J. and Brendelberger, H., Einführung in die Limnologie.9 Auflage, München: Elsevier, 2005.
Sharma, S., Gray, D.K., Read, J.S., et al., A global database of lake surface temperatures collected by in situ and satellite methods from 1985–2009, Sci. Data, 2015, vol. 2, p. 19. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.8
Shitikov, V.K., Rozenberg, G.S., and Zinchenko, T.D., Kolichestvennaya gidroekologiya: metody, kriterii, resheniya (Quantitative Hydroecology: Methods, Criteria, and Decisions), Moscow: Nauka, 2005.
Tibby, J. and Tiller, D., Climate-water quality relationships in three Western Victorian (Australia) lakes 1984–2000, Hydrobiologia, 2007, vol. 591, p. 219.
Verburg, P., Hecky, R.E., and King, H., Ecological consequences of a century of warming in Lake Tanganyika, Science, 2003, vol. 301, p. 505.
Votintsev, K.K., Meshcheryakova, A.I., and Popovskaya, G.I., Krugovorot organicheskogo veshchestva v ozere Baikal (Circulation of Organic Matter in Lake Baikal), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1975.
Wetzel, R.G., Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, Tokyo: Academic, 2001.
Weyhenmeyer, G.A., Rates of change in physical and chemical lake variables—are they comparable between large and small lakes?, Hydrobiologia, 2008, vol. 599, p. 105.
Weyhenmeyer, G.A., Westöö, A.-K., and Willen, E., Increasingly ice-free winters and their effects on water quality in Sweden’s largest lakes, Hydrobiologia, 2008, vol. 599, no. 1, p. 111.
Winder, M. and Hunter, D.A., Temporal organization of phytoplankton communities linked to physical forcing, Oecologia, 2008, vol. 156, no. 1, p. 179.
Winder, M., Renter, J.E., and Schladow, S.G., Lake warming favours small-sized planktonic diatom species, Proc. R. Soc. B, 2008,vol. 276, no. 1656, p. 427.
Yasnitskii, V.N., Lake Baikal plankton near Kultuk and Slyudyanka, Zap. Sib. Otd. Russ. Geogr. O-va, 1924, no. 3, p. 142.
Zohary, T., Changes to the phytoplankton assemblage of Lake Kinneret after decades of a predictable, repetitive pattern, Freshwater Biol., 2004, vol. 49, no. 10, p. 1355.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the project of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation no. 6.1387.2017/4.6 and the Lake Baikal Foundation for Support of Applied Ecological Development and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by Z. Litvinenko
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krashchuk, L.S., Shimaraeva, S.V. & Silow, E.A. Spatiotemporal Changes in the Phytoplankton in Lake Baikal during Late Summer: I. Water Temperature and Phytoplankton Abundance. Inland Water Biol 13, 31–40 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082920010083
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082920010083