Abstract
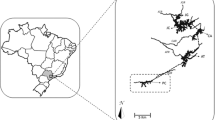
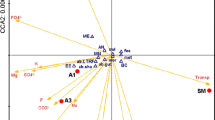
River basins are important for both industrial and agricultural activities. Pollution of air, water and soil is increasing owing to an insufficient number of treatment facilities; thus, most industrial and domestic wastewater either is directly discharged into water or is improperly treated. Here Chironomus spp. mentum deformities were used to determine environmental stress sources. A total of 4701 chironomid larvae were collected from 31 stations located in the Büyük Menderes River Basin. The mean mentum deformity incidence was 2.82%, and the frequency of deformities varied from 0 to 14.7%, with the highest frequencies calculated for the Dokuzsele (14.7%) and Banaz (9%) streams. The feature common among both stations is that they receive wastewater from textile, tannery and agricultural facilities. Our results show that mentum deformities are at least five times more pronounced at the most highly polluted sampling stations and indicate that mentum deformities of chironomid larvae are strongly related to ammonium-N and Cl is positively associated with agricultural and household wastewater.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akcay, H., Oguz, A., and Karapire, C., Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in B. Menderes and Gediz river sediments, Water Res., 2003, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 813–822.
Al-Shami, S., Rawi, C.S., Nor, S.A., et al., Morphological deformities in Chironomus spp. (Diptera: Chironomidae) larvae as a tool for impact assessment of anthropogenic and environmental stresses on three rivers in the Jury River System, Penang, Malaysia, Environ. Entom., 2010, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 210–222.
Al-Shami, S.A., Salmah, M.R.C., Hassan, A.A., et al., Evaluation of mentum deformities (Chironomidae: Diptera) larva using modified toxic score index (MTSI) to assess environmental stress in Juru River Basin Penang, Malaysia, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2011, vol. 177, nos. 1–4, pp. 233–244.
Arambourou, H., Beisel, J.N., Branchu, P., and Debat, V., Patterns of fluctuating asymmetry and shape variation in Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae) exposed to nonylphenol or lead, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 11. e48844.
Arslan, N., Ayik, O., and Şahin, Y., Diversity and structure of Chironomidae (Diptera) limnofauna of Lake Uluabat, a Ramsar site of Turkey, and their relation to environmental variables, Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2010, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 315–322.
Baird, D.J., Brown, S.S., Laqadic, L., et al., In situ-based effects measures: determining the ecological relevance of measured responses, Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag., 2007, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 259–267.
Beneberu, G., Mengistou, S., Eggermont, H., and Verschuren, D., Chironomid distribution along a pollution gradient in Ethiopian rivers, and their potential for biological water quality monitoring, Afr. J. Aquat. Sci., 2014, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 45–56.
Bervoets, L., Meregalli, G., De Cooman, W., et al., Caged midgelarvae (Chironomus riparius) for the assessment of metal bioaccumulation from sediments in situ, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2004, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 443–454.
Boyacioglu, H. and Boyacioglu, H., Su Kalitesinin İstatistiksel Yöntemlerle Değerlendirilmesi, Su Kirlenmesi Kontrolü Dergisi, 2004, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 9–17.
Brooks, S.J., Langdon, P.G., and Heiri, O., The Identification and Use of Palaearctic Chironomidae Larvae in Palaecology and Technical Guide, QRA Technical Guide No. 10, Quartenary Research Association, London, 2007, Büyük Menderes, Havza Atlası, Yaşayan Nehir, Yaşayan Ege, WWF Turkiye, 2013.
Choi, J., Biomarkes in environmental monitoring and its application in Chironomus sp., in Ecological Issues in a Changing World. Status, Response and Strategy, Dordrecht: Kluwer Acad. Publ., 2004, pp. 203–215.
Cortelezzi, A., Paggi, A.C., Rodriguez, M., and Capitulo, A.R., Taxonomic and nontaxonomic responses to ecological changes in an urban lowland stream through the use of Chironomidae (Diptera) larvae, Sci. Tot. Environ., 2011, vol. 409, no. 7, pp. 1344–1350.
Davies, L.J. and Hawkes, H.A., Some effects of organic pollution on the distribution and seasonal incidence of Chironomidae in riffles in the River Cole, Freshwater Biol., 1981, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 549–559.
De Bisthoven, L.J. and Gerhardt, A., Chironomidae (Diptera, Nematocera) fauna in three small streams of Skania, Sweden, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2003, vol. 83, no. 1, pp. 89–102.
De Bisthoven, L.J., Timmermans, K.R., and Ollevier, F., The concentration of cadmium, lead, copper, and zinc in Chironomus gr. thummi larvae (Diptera, Chironomidae) with deformed versus normal menta, Hydrobiologia, 1992, vol. 239, no. 3, pp. 141–149.
Di Veroli, A., Goretti, E., Paumen, M.L., et al., Induction of mouthpart deformities in Chironomus riparius larvae exposed to toxicants, Environ. Pollut., 2012, vol. 166, pp. 212–217.
Di Veroli, A., Santoro, F., and Pallottini, M., Deformities of chironomid larvae and heavy metal pollution: From laboratory to field studies, Chemosphere, 2014, vol. 112, pp. 9–17.
Di Veroli, A., Selvaggi, R., Goretti, E., et al., Chironomid mouthpart deformities as indicator of environmental quality: a case study in Lake Trasimeno (Italy), J. Environ. Monit., 2012, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 1473–1478.
Di Veroli, A., Selvaggi, R., Pellegrino, R.M., and Goretti, E., Sediment toxicity and deformities of chironomid larvae in Lake Piediluco (Central Italy), Chemosphere, 2010, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 33–39.
Duran, M., Büyük Menderes, Nehri’nin (Denizli) Su Kalitesinin Biyomarkörler ile Belirlenmesi, TUBITAK Project Report 108Y326, 2008.
Duran, M., Michailova, P., Adile, S., et al., Assessment of the sediment toxicity in Bulgarian and Turkish Rivers using the biomarkers in Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae), Acta Zool. Bulg., 2012, suppl. 4, pp. 167–173.
Galluba, S., Oetken, M., and Oehlmann, J., Comprehensive sediment toxicity assessment of Hessian surface waters using Lumbriculus variegatus and Chironomus riparius, J. Environ. Sci. Health A. Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng., 2012, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 507–521.
Grebenjuk, L.P. and Tomilina. I.I., Morphological deformations of hard chitinized mouthpart structures in larvae of the genus Chironomus (Diptera, Chironomidae) as the ındex of organic pollution in freshwater ecosystems, Inland Water Biol., 2014, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 273–285. doi. 10.1134/S1995082914030092
Groenendijk, D., Postma, J.F., Kraak, M.H.S., and Admiraal, W., Seasonal dynamics and larval drift of Chironomus riparius (Diptera) in a metal contaminated lowland river, Aquat. Ecol., 1998, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 341–351.
Güven, G., Analysis of some pollutants parameters of Büyük Menderes River in Aydın Region, in 4th Aegean Analytical Chemistry Days: Proc. Sci. Conf., Aydın, 2004, pp. 179–181.
Hamalainen, H., Critical appraisal of the indexes of chironomid larvae deformities and their use in bioindication, Ann. Zool. Fenn., 1999, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 179–186.
Hudson, L.A. and Ciborowski, J.J., Spatial and taxonomic variation in incidence of mouthpart deformities in midge larvae (Diptera: Chironomidae: Chironomini), Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1996, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 297–304.
Ingersoll, C.G. and Nelson, M.K., Testing sediment toxicity with Hyalella azteca (Amphipoda) and Chironomus riparius (Diptera), Aquat. Toxicol. Risk Assess., 1990, vol. 13, pp. 93–109.
Keser, B., Aydın ilinde Büyük Menderes Nehri ile sulanan bölgelerde yetişen bazı sebze ve meyvelerdeki ağır metal kirliliğinin araştırılması, Aydın: Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, 2008.
Klink, A.G. and Moller Pillot, H.K.M., Chironomidae Larvae, Key to Higher Taxa and Species of the Lowlands of Northwestern Europe, ETI, Amsterdam, CD-ROM, 2003.
Köhn, T. and Frank, C., Eject of thermal pollution on the chironomid fauna in an urban channel, in Chironomidae: Ecology, Systematics, Cytology, and Physiology, Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1980, pp. 187–194.
Langer-Jaesrich, M., Kohler, H.R., and Gerhardt, A., Can mouth part deformities of Chironomus riparius serve as indicators for water and sediment pollution. A laboratory approach, J. Soils Sediments, 2010, vol. 10, pp. 414–422.
Langton, P.H., A Key to Pupal Exuviae of West Palaearctic Chironomidae, Privately published by P.H. Langton, 3, St. Felix Road, Ramsey Forty Foot, Huntingdon, Cambridgeshire, 1984.
Langton, P.H., Visser, H., Chironomidae Exuviae. A Key to Pupal Exuviae of the West Palearctic Region, ETI, Amsterdam, CD-ROM, 2003.
Lenat, D.R., Using mentum deformities of Chironomus larvae to evaluate the effects of toxicity and organic loading in streams, J. N. Amer. Benthol. Soc., 1993, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 265–269.
Lenat, D.R., Water quality assessment of streams using a qualitative collection method for benthic macroinvertebrates, J. N. Amer. Benthol. Soc., 1988, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 222–233.
Liber, K., Goodfellow, W., Den Besten, P., et al., In situ-based effects measures: considerations for improving methods and approaches, Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag., 2007, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 246–258.
Meregalli, G., Bettinetti, R., Pluymers, L., et al., Mouthpart deformities and nucleolus activity in field-collected Chironomus riparius larvae, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2002, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 405–409.
Meregalli, G., Vermeulen, A.C., and Ollevier, F., The use of chironomide deformation in an in situ test for sediment toxicity, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2000, vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 231–238.
Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Duran, M., Karadurmus, E., Berber, R., and Sen, A., Structural and functional alterations in salivary gland chromosomes and enzyme activity of Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) from anthropogenically polluted sites in Bulgaria and Türkiye, Caryologia, 2012, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 157–169.
Michailova, P., Rearrangements in Chironomidae (Diptera), genomes induced by various environmental stress factors, Russ. J. Genet.: Appl. Res., 2011, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 10–20.
Moller Pillot, H.K.M., A Key to the Larvae of the Aquatic Chironomidae of the North-West European Lowlands, 2009 (private print, not published).
Moller Pillot, H.K.M., Chironomidae Larvae, vol. 2: Biology and Ecology of the Chironomini, Zeist: KNNV Publishing, 2009.
Moller Pillot, H.K.M., Chironomidae Larvae, vol. 3: Biology and Ecology of the Aquatic Orthocladiinae, Zeist: KNNV Publishing, 2013.
Morais, S.S., Molozzi, J., Viana, A.L., et al., Diversity of larvae of littoral Chironomidae (Diptera: Insecta) and their role as bioindicators in urban reservoirs of different trophic levels, Braz. J. Biol., 2010, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 995–1004.
Okur, B., Yener, H., Okur, N., and Irget, E., Büyük Menderes, Nehri’ndeki Bazı Kirletici Parametrelerin Aylık ve Mevsimsel Olarak Değişimi, Pamukkale Univ. Muh. Bilim. Derg., 2001, vol. 7, pp. 243–250.
Riani, E., Sudarso, Y., and Cordova, M.R., Heavy metals effect on unviable larvae of Dicrotendipes simpsoni (Diptera: Chironomidae), a case study from Saguling Dam, Indonesia, Aquacult. Aquarium Conserv. Legisl. Int. J. Bioflux Soc., 2014, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 76–84.
Rosenberg, D.M., Freshwater biomonitoring and Chironomidae, Netherlands J. Aquat. Ecol., 1992, vol. 26, pp. 101–122.
Servia, M.J., Cobo, F., and Gonzalez, M.A., Seasonal and interannual variations in the frequency and severity of deformities in larvae of Chironomus riparius (Meigen. 1804) and Prodiamesa olivacea (Meigen. 1818) (Diptera, Chironomidae) collected in a polluted site, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2000, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 617–626.
Ter Braak, C.J.F. and Smilauer, P., CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5), Ithaca: Microcomputer Power, 2002.
Ter Braak,C.J.F. and Smilauer, P., CANOCO Release 4, Reference Manual and Users Guide to CANOCO for Windows: Software for Canonical Community Ordination, Ithaca: Microcomputer Power, 1998.
Tomilina, I.I., Grebenjuk, L.P., and Chuiko, G.M., Toxicological and teratogenic assessment of bottom sediments from the Rybinsk Reservoir, Inland Water Biol., 2011, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 373–382.
Tomilina, I.I., Grebenyuk, L.P., Lobus, N.V., Komov, V.T., Biological effects of contaminated bottom sediments of water bodies in Central and South Vietnam on aquatic organisms, Inland Water Biol., 2016, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 413–422. doi. 10.1134/S1995082916030196
Vallenduuk, H.J. and Moller Pillot, H.K.M., Chironomidae Larvae of the Netherlands and Adjacent Lowlands, General Ecology and Tanypodinae, Zeist: KNNV Publishing, 2007.
Vermeulen, A.C., Dall, P.C., Lindegaard, C., et al., Improving the methodology of chironomid deformation analysis for sediment toxicity assessment: a case study in three Danish lowland streams, Arch. Hydrobiol., 1988, vol. 144, no. 1, pp. 103–125.
Vermeulen A.C. Elaboration of chironomid deformities as bioindicators of toxic sediment stress: the potential application of mixture toxicity concepts, Ann. Zool. Fenn., 1995, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 265–285.
Vermeulen A.C., Head capsule deformation in Chironomus riparius larvae (Diptera): causality, ontogenesis and its application in biomonitoring, Ph. D. Thesis, Leuven, 1998.
Vermeulen, A.C., Liberloo, G., Dumont, P., et al., Exposure of Chironomus riparius larvae (Diptera) to lead, mercury, and bitosterol: effects on mouthpart deformation and moulting, Chemosphere, 2000, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1581–1591.
Veroli, A.D., Selvaggi, R., Pellegrino, R.M., and Goretti, E., Sediment toxicity and deformities of Chironomid larvae in Lake Piediluco, Chemosphere, 2010, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 33–39.
Warwick, W.F., Morphological abnormalities in Chironomidae (Diptera) larva as measures of toxic stress in fresh water ecosystems: indexing antennal deformities in Chironomus Meigen, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1985, vol. 42, no. 12, pp. 1881–1914.
Warwick, W.F., Morphological deformities in Chironomidae (Diptera) larvae as biological indicators of toxic stress, in Toxic Contaminants and Ecosystem Health. A Great Lakes Focus, New York: Wiley, 1988, pp. 281–320.
Warwick, W.F. and Tisdale, N.A., Morphological deformities in Chironomus, Cryptochironomus, and Procladius (Diptera: Chironomidae) from two differentially stressed sites in Tobin Lake, Saskatchewan, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1988, vol. 45, no. 7, pp. 1123–1144.
Wene, G., The soil as an ecological factor in the abundance of aquatic Chironomid larvae, Ohio J. Sci., 1940, vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 193–199.
Wiederholm, T., Chironomidae of the Holarctic region. Keys and diagnosis, part 1: larvae, Ent. Scand., 1983, Suppl., vol. 19, pp. 149–291.
Wilson, R.S., Ruse, L.P., A Guide to the Identification of Genera of Chironomid Pupal Exuviae Occurring in Britain and Ireland (Including Common Genera from Northern Europe) and Their Use in Monitoring Lotic and Lentic Fresh Waters, Ambleside: The Freshwater Biological Association, 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akyildiz, G.K., Bakir, R., Polat, S. et al. Mentum Deformities of Chironomid Larvae as an Indicator of Environmental Stress in Büyük Menderes River, Turkey. Inland Water Biol 11, 515–522 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082918040028
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082918040028