Abstract
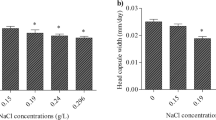
Threshold concentrations of sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium in water determining the borders of the Chironomus balatonicus range in waterbodies are 0.6–0.62, 0.11–0.12, 0.071–0.073, and 0.022–0.028 mmol/L, respectively. In the freshwater section of the Curonian Lagoon of the Baltic Sea and other waterbodies with weakly mineralized water where the content of ions is lower than the threshold values, larval Ch. balatonicus cannot dwell because of the impossibility of maintaining the ionic balance between the organism and environment. The threshold concentrations and rates of loss of ions from an organism in various species of aquatic organisms are comparatively analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vinogradov, G.A., Protsessy ionnoi regulyatsii u presnovodnykh ryb i bespozvonochnykh (Processes of Ion Regulation in Freshwater Fishes and Invertebrates), Moscow: Nauka, 2000.
Vinogradov, G.A., Klerman, A.K., and Komov, V.T., Characteristics of ion exchange in freshwater mollusks under conditions of high concentration of hydrogen ions and low ambient salinity, Ekologiya, 1987, no. 3, pp. 81–84.
Vinogradov, G.A. and Komov, V.T., Ion exchange in Prussian carp and common carp during acclimation to water with low salinity, Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1988, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 124–131.
Vinogradov, G.A. and Shobanov, N.A., Characteristics of sodium exchange in larvae of the genus Chironomus at different salinity and pH of the environment, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1990, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 308–315.
Markiyanova, M.F., Composition and distribution of sibling species of the genus Chironomus Meigen, 1803 (Diptera, Chironomidae) in Curonian Lagoon of the Baltic Sea, Povolzhsk. Ekol. Zh., 2015, no. 4, pp. 400–408.
Martemyanov, V.I., Threshold concentrations of cations in the external environment required for maintenance of the ionic balance between the organism of the invader Elodea canadensis Michaux and fresh water, Russ. J. Biol. Invas., 2014, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 265–274.
Martemyanov, V.I. and Shobanov, N.A., Sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium content in the hemolymph of larvae of the genus Chironomus, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1997, vol. 33, no. 4-5, pp. 443–448.
Prosser, C.L., Comparative Animal Physiology, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 1973.
Romanenko, V.D., Arsan, O.M., and Solomatina, V.D., Kal’tsii i fosfor v zhiznedeyatel’nosti gidrobiontov (Calcium and Phosphorus in the Life Activity of Aquatic Organisms), Kiev: Nauk. dumka, 1982.
Schmidt-Nielsen, K., Animal Physiology: Adaptation and Environment, Cambridge, New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1979.
Goldstein, L., Comparative physiology of osmoregulation: The legacies of August Krogh and Homer Smith, J. Exp. Zool., 1999, vol. 283, pp. 619–733.
Krogh, A., Osmotic Regulation in Aquatic Animals, London: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1939.
Shaw, J., Salt and water balance in the east African fresh-water crab, Potamon niloticus (M. Edw.), J. Exp. Biol., 1959, vol. 36, pp. 157–176.
Shaw, J., The absorption of sodium ions by the crayfish, Astacus pallipes Lereboullet. I. The effect of external and internal sodium concentrations, J. Exp. Biol., 1959, vol. 36, pp. 126–144.
Specziár, A., Life history patterns of Procladius choreus, Tanypus punctipennis and Chironomus balatonicus in Lake Balaton, Ann. Limnol., 2008, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 181–188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.I. Martemyanov, M.F. Markiyanova, 2018, published in Biologiya Vnutrennykh Vod, 2018, No. 1, pp. 80–87.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martemyanov, V.I., Markiyanova, M.F. Threshold Concentrations of Cations in the Water Necessary for Maintaining the Ionic Balance Between Organism of Chironomus balatonicus Devai et al. Larvae and Environment. Inland Water Biol 11, 81–86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082917040071
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082917040071