Abstract
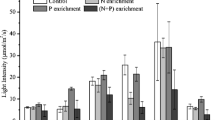
Experimental studies of the effect of phosphorus, nitrogen, and silicon on the phytoplankton of the shallow highly eutrophic Lake Nero have been carried out. It is shown that the enrichment of lake water with nitrogen leads to an increased concentration of chlorophyll a and the growth of the biomass of dominant algae species. Phosphorus limits the abundance of a certain species of algae; the limiting role of silicon in the development of spring phytoplankton has not been experimentaly confirmed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bikbulatov, E.S., Bikbulatova, E.M., Litvinov, A.S., and Poddubnyi, S.A., Gidrologiya i gidrokhimiya ozera Nero (Hydrology and Hydrochemistry of Lake Nero), Rybinsk: Dom Pechati, 2003.
Bikbulatov, E.S., Bikbulatova, E.M., and Stepanova, I.E., The Chemical Composition of Water, in Sostoyanie ekosistemy ozera Nero v nachale XXI veka (The State of the Ecosystem of Lake Nero at the Beginning of XXI Century), Moscow: Nauka, 2008, pp. 35–52.
Bul’on, V.V., Nikulina, V.N., and Fursenko, M.V., The Influence of Small Additions of River Water, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus on Lake Plankton, in Gidrobiologicheskie issledovaniya na reke Tyup i Tyupskom zalive ozera Issyk-Kul’ (Hydrobiological Studies on the Tyup River and Tyup Bay of Lake Issyk-Kul), Leningrad: Nauka, 1977, pp. 58–70.
Glants, S., Mediko-biologicheskaya statistika (Biomedical Statistics), Moscow: Praktika, 1999.
Guseva, K.A., Algal Blooms: Its Causes, Prediction, and Responses to It, Tr. Vsesoyuz. Gidrobiol. Obshch., 1952, vol. 4, pp. 3–92.
Elizarova, V.A. and Koroleva, M.B., Growth Rate of Phytoplankton in the Rybinsk Reservoir in Connection with Small Amounts of Phosphorus and Nitrogen, in Flora i produktivnost’ pelagicheskikh i litoral’nykh fitotsenozov vodoemov basseina Volgi (Flora and Productivity of Pelagic and Littoral Plant Communities of Water Bodies of the Volga River Basin), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990, pp. 189–200.
Kuz’min, G.V., Phytoplankton. Species Composition and Abundance, in Metodika izucheniya biogeotsenozov vnutrennikh vodoemov (The Method of Studying Biogeocenoses of Inland Water Bodies), Moscow: Nauka, 1975, pp. 73–87.
Lyashenko, O.A., Structure and Pigment Characteristics of Phytoplankton of Shallow Lakes (As Examplified by Lake Nero), Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation: St. Petersburg, 1995.
Maximov, V.N., Mnogofaktornyi experiment v biologii (Multifactorial Experiment in Biology), Moscow: Moscow Gos. Univ., 1980.
Nikulina, V.N., Effect of Supplementation of Biogenic Elements and Different Quality Waters on Phytoplankton of Lake Onega, in Limnologicheskie issledovaniya na zalive Onezhskogo ozera Bol’shoe Onego (Limnological Studies at Bol’shoe Onego Bay of Lake Onega), Leningrad: Zool. Inst. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1982, pp. 97–109.
Nikulina, V.N., Methods of Biological Tests in Hydrobiological Studies, Ekologiya, 1985, no. 3, pp. 55–63.
Nikulina, V.N., Biogenic Elements as a Limiting Factor of Phytoplankton, in Gidrobiologicheskie issledovaniya morskikh i presnykh vod (Hydrobiological Studies of Marine and Fresh Waters), Leningrad: Zool. Inst. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1988, pp. 11–19.
Pavlova, O.A., An Experimental Study of the Effect of Addition of Biogenic Elements on the Phytoplankton of an Eutrophic Polluted Lake, in Biologiya vnutrennikh vod: problemy ekologii i bioraznoobraziya: Mater. XII Mezhdunar. Konf. Molodykh Uchenykh (Inland Water Biology: Problems of Ecology and Biodiversity. Proc. XII Int. Conf. Young Sci.), Borok, 2002, pp. 166–173.
Petrova, N.A., Suktsessii fitoplanktona pri antropogennom evtrofirovanii bol’shikh ozer (Succession of Phytoplankton under Anthropogenic Eutrophication of Large Lakes), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
Petrova, N.A., Raspletina, G.F., and Gusakov, B.L., The Study of the Demands of the Phytoplankton of Lakes of Different Types in Biogenic Elements by the Method of Planned Additives, Bot. Zh., 1977, vol. 62, no. 7, pp. 984–989.
Sidelev, S.I. and Babanazarova, O.V., The Dependence of the Seasonal Dynamics of Chlorophyll a on Certain Factors of Aquatic Environment in the Northern Part of Lake Nero, in Sovremennye problemy biologii, ekologii, khimii (Current Problems in Biology, Ecology, and Chemistry), Yaroslavl: Yaroslav. Gos. Univ., 2005, pp. 137–142.
Sidelev, S.I. and Babanazarova, O.V., The Structure of Phytoplankton of the Highly Eutrophic Lake Nero, Izv. Orenburg. Gos. Agrar. Univ., 2008, no. 4, pp. 187–190.
Sostoyanie ekosistemy ozera Nero v nachale XXI veka (The State of the Ecosystem of Lake Nero at the Beginning of the XXI Century), Moscow: Nauka, 2008.
Stroganov, N.S. and Buzinova, N.S., Prakticheskoe rukovodstvo po gidrokhimii (A Practical Guide to Hydrochemistry), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1980.
Trifonova, I.S., Ekologiya i suktsessiya ozernogo fitoplanktona (Ecology and Succession of Lacustrine Phytoplankton), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
Uspenskaya, V.I., Ekologiya i fiziologiya pitaniya presnovodnykh vodoroslei (Ecology and Physiology of Nutrition of Freshwater Algae), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1966.
Henderson-Sellers, B. and Markland, H.R., Decaying Lakes: The Origins And Control Of Cultural Eutrophication, Chichester: WIley, 1987.
Evolyutsiya krugovorota fosfora i evtrofirovanie prirodnykh vod (Evolution of the Phosphorus Cycle and Eutrophication of Natural Waters), Leningrad: Nauka, 1988, p. 204.
Elser, J.J., Marzolf, E.R., and Goldman, C.R., Phosphorus and Nitrogen Limitation of Phytoplankton Growth in the Freshwaters of North America: A Review and Critique of Experimental Enrichments, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1990, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 1468–1477.
Gibson, C.E., Silica Budgets and the Ecology of Planktonic Diatoms in an Unstratified Lake (Lough Neagh, N. Ireland), Int. Rev. gesàmt. Hydrobiol, 1981, vol. 66, pp. 641–664.
Golterman, H.L., Algal Bioassays and Algal Growth Controlling Factors in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes, Hydrobiologia, 1983, vol. 100, pp. 59–64.
Haan, H., Wanders, J.B.W., and Moed, J.R., Multiple Addition Bioassay of Tjeukemeer Water, Hydrobiologia, 1982, vol. 88, pp. 233–244.
Jeffrey, S.W. and Humphrey, G.F., New Spectrophotometric Equations for Determining Chlorophylls A, B, C1 and C2 in Higher Plants Algae and Natural Phytoplankton, Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz., 1975, vol. 167, no. 2, pp. 191–194.
Kilham, S.S., Silicon and Phosphorus Growth Kinetics and Competitive Interactions between Stephanodiscus minutus and Synedra sp., Verh. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol., 1984, vol. 22, pp. 435–439.
Meffert, M.-E., Planktic Unsheathed Filaments (Cyanophyceae) with Polar and Central Gas Vacuoles II. Biology, Population Dynamics and Biotopes of Limnothrix redekei (Van Goor) Meffert, Arch. Hydrobiol., 1989, vol. 116, no. 3, pp. 257–282.
Reynolds, C.S., Huszar, V., Kruk, C., et al., Towards a Functional Classification of the Freshwater Phytoplankton, J. Plankton Res., 2002, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 417–428.
Riddolls, A., Aspects of Nitrogen Fixation in Lough Neagh. II. Competition between Aphanizomenon flosaquae, Oscillatoria redekei, Oscillatoria agardhii, Freshwater Biol., 1985, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 299–306.
Schindler, D.W., Evolution of Phosphorus Limitation in Lakes. Natural Mechanisms Compensate for Deficiencies of Nitrogen and Carbon in Eutrophied Lakes, Science, 1977, vol. 195, no. 4275, pp. 260–262.
Sommer, U., Comparison between Steady State and Non-Steady State Competition: Experiments with Natural Phytoplankton, Limnol. Oceanogr, 1985, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 335–346.
Zevenboom, W., N2-Fixing Cyanobacteria: Why They Do Not Become Dominant in Shallow Hypertrophic Lakes, Aquat. Ecol., 1982, vol. 16, nos. 2–3, pp. 289–290.
Zevenboom, W., Bij De Vaate, A., and Mur, L.R., Assessment of Factors Limiting Growth Rate of Oscillatoria agardhii in Hypertrophic Lake Wolderwijd, 1978, by use Of Physiological Indicators, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1982, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 39–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.I. Sidelev, 2012, published in Biologiya Vnutrennikh Vod, No. 1, 2012, pp. 60–66.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidelev, S.I. Experimental study of the effect of nutrients on phytoplankton of the shallow highly eutrophic Lake Nero. Inland Water Biol 5, 54–60 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082911040171
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082911040171