Abstract—
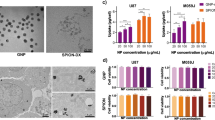
A binary cytopathic effect (CPE%) of synchrotron radiation (SR) and manganese oxide nanoparticles (MnO NP) on human glioblastoma U87MG, U-251MG, and A-172 cell lines was studied in vitro. After incubation of the cells with MnO NP at a concentration of 5 and 50 µmol for 18–24 h, irradiation of glioblastoma cells at the source of SR VEPP-4 was carried out. X-ray irradiation doses 0, 1, 2, 4 Gy were used. The results were estimated using a light microscopy, determination of CPE% on the counter (Countess, Invitrogen), and the clonogenic test. It was revealed that the preliminary incubation of glioblastoma cell lines with MnO NP causes an increase in CPE of external SR at a dose 1, 2, and 4 Gy on the glioblastoma cells by 25, 50, and 100%. This effect allows to reduce the radiation dose by 2–3 times, maintaining the efficiency of the effect. At the same time, the period of vital activity of tumor cells under a combined effect of SR and NP is reduced by 18–36 h. Probably, a synergism of the combination of MnO NP and SR will provide new opportunities for the development of a model for the treatment of brain tumors.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. Frosina, Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 96, 257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.05.013
R. M. Young, A. Jamshidi, G. Davis, and J. H. Sherman, Ann. Transl. Med. 9, 121 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.05.10
Q. T. Ostrom, H. Gittleman, P. Liao, et al., Neuro Oncol. 16, 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou223
Q. T. Ostrom, H. Gittleman, G. Truitt, et al., Neuro Oncol. 20, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy131
A. B. Mariotto, K. R. Yabroff, Y. Shao, et al., J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 103, 117 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djq495
S. E. Noda, A. El-Jawahri, D. Patel, et al., Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 19, 171 (2009). https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5851.103142
L. Khan, H. Soliman, A. Sahgal, et al., Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 19 (8), 1 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011475.pub2
V. Calugaru, N. Magné, J. Hérault, et al., Bull. Cancer 102, 83 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulcan.2014.10.002
A. Stepanovic and M. Nikitovic, J. BUON 23, 7 (2018).
M. Yamada, M. Foote, and T. W. Prow, Wiley Interdiscipl. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 7, 428 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1322
P. Liu, H. Jin, Z. Guo, et al., Int. J. Nanomed. 11, 5003 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S115473
H. Wu, J. Lin, P. Liu, et al., Biomaterials 101, 1 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.05.031
R. Raliya, C. T. Singh, K. Haddad, and P. Biswas, Curr. Pharm. Des. 22, 2481 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666160307151409
S. Aftab, A. Shaha, A. Nadhman, et al., Int. J. Pharm. 540, 132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.02.007
C. Ozada, V. Tekin, F. B. Barlas, et al., Chem. Sel. 5, 1987 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201901620
X. Cai, Q. Zhu, Y. Zeng, et al., Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 8321 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S218085
K. E. Kuper, E. L. Zavjalov, I. A. Razumov, et al., Phys. Proc. 84, 252 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2016.11.043
E. L. Zav’yalov, I. A. Razumov, L. A. Gerlinskaya, and A. V. Romashchenko, Vavilov. Zh. Genet. Selekts. 19 (4), 77 (2015). https://doi.org/10.18699/VJ15.061
I. A. Razumov, E. L. Zav’yalov, S. Yu. Troitskii, et al., Klet. Tekhnol. Biol. Med., No. 2, 114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3849-0
M. V. Petoukhov, P. V. Konarev, A. G. Kikhneya, and D. I. Svergun, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 223 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889807002853
G. Baranov, V. Borin, A. Zhuravlev, et al., J. Surf. Invest.: X-ray, Synchrotr. Neutron Tech. 14, 150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451020020032
O. Evdokov, V. Titov, B. Tolochko, and M. Sharafutdinov, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 603, 194 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2009.03.001
Guidelines for Experimental (Preclinical) Study of New Pharmacological Substances, Ed. by V. P. Fisenko (Remedium, Moscow, 2000) [in Russian].
N. A. P. Franken, H. M. Rodermond, J. Stap, et al., Nat. Protoc. 1, 2315 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.339
S. Y. Troitskii, A. L. Chuvilin, D. I. Kochubei, B. N. Novgorodov, V. N. Kolomiichuk, and V. A. Li-kholobov, Russ. Chem. Bull. 44, 1822 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707203
M. J. Ramírez-Expósito and J. M. Martínez-Martos, Curr. Neuropharmacol. 17, 342 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180302120925
G. Basati, M. Khaksarian, S. Abbaszadeh, et al., Stem Cell Invest. 6 (38), 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21037/sci.2019.10.07
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The studies were performed using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use “Center for Genetic Resources of Laboratory Animals” of Federal Research Center Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences. The studies of MnO NP were performed using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use “National Center for Catalyst Research.”
Funding
These studies were supported by Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russian Federation (project no. 0324-2019-0041, unique project identifier RFMEFI62119X0023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by A. Barkhash
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razumov, I.A., Troitsky, S.Y., Zavjalov, E.L. et al. Synergism of the Cytopathic Effect of Synchrotron Radiation and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles on the Growth of Human Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro. Nanotechnol Russia 15, 819–827 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078020060166
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078020060166