Abstract
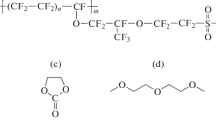
Ion-exchange membranes based on polymethylpentene and sulfonated polystyrene with different grafting degrees were obtained. Solvation and mobility of lithium ions depending on the composition of initial organic solvents were studied. The highest ionic conductivity at room temperature (30°C) are obtained for the membranes containing dimethylsulfoxide (σ = 1.31 × 10–4 S/cm for membrane with GD = 78%). Membranes containing dimethylformamide are characterized by a constant phase composition in a broad temperature range and the highest ionic conductivity at low temperature (σ = 9 × 10–6 S/cm at–20°C for a polymer with GD = 78%).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Quartarone and P. Mustarelli, “Electrolytes for solid-state lithium rechargeable batteries: recent advances and perspectives,” Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 2525–2540 (2011).
A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “Solid electrolytes: main prospects of research and development,” Russ. Chem. Rev. 85, 1255–1276 (2016).
Z. Gao, H. Sun, L. Fu, F. Ye, Y. Zhang, W. Luo, and Y. Huang, “Promises, challenges and recent progress of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries,” Adv. Mater. 30, 1705702 (2018).
I. A. Stenina, I. Y. Pinus, A. I. Rebrov, and A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “Lithium and hydrogen ions transport in materials with NASICON structure,” Solid State Ionics 175, 445–449 (2004).
Z. Jian, Y. S. Hu, X. Ji, and W. Chen, “NASICONstructured materials for energy storage,” Adv. Mater. 29, 1601925 (2017).
J. F. Nonemacher, C. Hüter, H. Zheng, J. Malzbender, M. Kruger, R. Spatschek, and M. Finsterbusch, “Microstructure and properties investigation of garnet structured Li7La3Zr2O12 as electrolyte for all-solidstate batteries,” Solid State Ionics 321, 126–134 (2018).
C. Li, Z. Xi, D. Guo, X. Chen, L. Yin, “Chemical immobilization effect on lithium polysulfides for lithium-sulfur batteries,” Smal. 14, 1701986 (2018).
Y. Xue and D. J. Quesnel, “Synthesis and electrochemical study of sodium ion transport polymer gel electrolytes,” RSC Adv. 6, 7504–7510 (2016).
H. Gao, W. Zhou, K. Park, and J. B. Goodenough, “A sodium-ion battery with a low-cost cross-linked gel-polymer electrolyte,” Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1600467 (2016).
L. Yue, J. Ma, J. Zhang, J. Zhao, S. Dong, Z. Liu, G. Cui, and L. Chen, “All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries,” Energy Storage Mater. 5, 139–164 (2016).
B. Sun, J. Mindemark, K. Edstrom, and D. Brandell, “Polycarbonate-based solid polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries,” Solid State Ionics 262, 738–742 (2014).
M. Armand, “Polymer electrolytes—an overview,” Solid State Ionics 9–10, 745–754 (1983).
V. di Noto, S. Lavina, G. A. Giffin, E. Negro, and B. Scrosati, “Polymer electrolytes: present, past and future,” Electrochim. Acta 57, 4–13 (2011).
K. Xu, “Nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithiumbased rechargeable batteries,” Chem. Rev. 104, 4303–4417 (2005).
A. Ghosh and P. Kofinas, “Nanostructured block copolymer dry electrolyte,” J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, A428–A431 (2008).
J. F. Snyder, M. A. Ratner, and D. F. Shriver, “Ion conductivity of comb polysiloxane polyelectrolytes containing oligoether and perfluoroether sidechains,” J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, A1090–A1094 (2003).
P. Han, Y. Zhu, and J. Liu, “An all-solid-state lithium ion battery electrolyte membrane fabricated by hot-pressing method,” J. Power Sources 284, 459–465 (2015).
Y. Liu, Z. Cai, L. Tan, and L. Li, “Ion exchange membranes as electrolyte for high performance li-ion batteries,” Energy Environ. Sci 5, 9007–9013 (2012).
Z. Cai, Y. Liu, S. Liu, L. Li, and Y. Zhang, “High performance of lithium-ion polymer battery based on nonaqueous lithiated perfluorinated sulfonic ion-exchange membranes,” Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 5690–5693 (2012).
P. Aldebert, M. Guglieimi, and M. Pineri, “Ionic conductivity of bulk, gels and solutions of perfluorinated ionomer membranes,” Polym. J. 23, 399–406 (1991).
M. Doyle, M. E. Lewittes, M. G. Roelofs, S. A. Perusich, and R. E. Lowrey, “Relationship between ionic conductivity of perfluorinated ionomeric membranes and nonaqueous solvent properties,” J. Membr. Sci. 184, 257–273 (2001).
J. Gao, C. Sun, L. Xu, J. Chen, C. Wang, D. Guo, and H. Chen, “Lithiated nafion as polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium sulfur batteries using carbon-sulfur composite cathode,” J. Power Sources 382, 179–189 (2018).
E. A. Sanginov, E. Yu. Evshchik, R. R. Kayumov, and Yu. A. Dobrovol’skii, “Lithium-ion conductivity of the nafion membrane swollen in organic solvents,” Russ. J. Electrochem. 51, 986–990 (2015).
A. I. Karelin, R. R. Kayumov, and Yu. A. Dobrovol’skii, “Structure of lithium ion-conducting polymer membranes based on nafion plasticized with dimethylsulfoxide,” Pet. Chem. 56, 1020–1026 (2017).
M. Nasef, “Preparation and applications of ion exchange membranes by radiation-induced graft copolymerization of polar monomers onto non-polar films,” Prog. Polym. Sci. 29, 499–561 (2004).
T. Zhou, R. Shao, S. Chen, X. He, J. Qiao, and J. Zhang, “A review of radiation-grafted polymer electrolyte membranes for alkaline polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells,” J. Power Sources 293, 946–975 (2015).
E. Y. Safronova, D. V. Golubenko, N. V. Shevlyakova, M. G. D’yakova, V. A. Tverskoi, L. Dammak, D. Grande, and A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “New cationexchange membranes based on cross-linked sulfonated polystyrene and polyethylene for power generation systems,” J. Membr. Sci. 515, 196–203 (2016).
D. V. Golubenko, E. Y. Safronova, A. B. Ilyin, N. V. Shevlyakova, V. A. Tverskoi, G. Pourcelly, and A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “Water state and ionic conductivity of grafted ion exchange membranes based on polyethylene and sulfonated polystyrene,” Mendeleev Commun. 27, 380–381 (2017).
Z. Xu, J. Wang, L. Shen, D. Men, and Y. Xu, “Microporous polypropylene hollow fiber membrane. Part I. Surface modification by the graft polymerization of acrylic acid,” J. Membr. Sci. 196, 221–229 (2002).
Y. Ding, X. Shen, J. Zeng, X. Wang, L. Peng, P. Zhang, and J. Zhao, “Pre-irradiation grafted single lithiumion conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinylidene fluoride),” Solid State Ionics 323, 16–24 (2018).
N. Walsby, F. Sundholm, T. Kallio, and G. Sundholm, “Radiation-grafted ion-exchange membranes: influence of the initial matrix on the synthesis and structure,” J. Polym. Sci., Part A 39, 3008–3017 (2001).
J. A. Horsfall and K. V. Lovell, “Synthesis and characterization of sulfonic acid-containing ion exchange membranes based on hydrocarbon and fluorocarbon polymers,” Eur. Polym. J. 38, 1671–1682 (2002).
D. V. Golubenko and A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “New approach to the preparation of grafted ion exchange membranes based on UV-oxidized polymer films and sulfonated polystyrene,” Mendeleev Commun. 27, 572–573 (2017).
V. Gutmann, “Empirical parameters for donor and acceptor properties of solvents,” Electrochim. Acta 21, 661–670 (1976).
E. Pasgreta, R. Puchta, M. Galle, N. van Eikema Hommes, A. Zahl, and R. van Eldik, “Ligand-exchange processes on solvated lithium cations: DMSO and water/DMSO mixtures,” ChemPhysChem 8, 1315–1320 (2007).
V. I. Volkov, E. V. Volkov, S. V. Timofeev, E. A. Sanginov, A. A. Pavlov, E. Yu. Safronova, I. A. Stenina, and A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “Diffusion mobility of alkali metals in perfluorinated sulfocationic and carboxylic membranes as probed by 1H, 7Li, 23Na, and 133Cs NMR spectroscopy,” Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 55, 318–324 (2010).
D. Yu. Voropaeva, S. A. Novikova, T. L. Kulova, and A. B. Yaroslavtsev, “Conductivity of Nafion-117 membranes intercalated by polar aprotonic solvents,” Ionics 24, 1685–1692 (2018).
V. I. Volkov and A. A. Marinin, “NMR methods for studying ion and molecular transport in polymer electrolytes,” Russ. Chem. Rev. 82, 248–272 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.Yu. Voropaeva, D.V. Golubenko, S.A. Novikova, A.B. Yaroslavtsev, 2018, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2018, Vol. 13, Nos. 5–6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voropaeva, D.Y., Golubenko, D.V., Novikova, S.A. et al. Lithium-Ion Conductivity of Polymers Based on Sulfonated Polystyrene and Polymethylpentene Intercalated by Organic Solvents. Nanotechnol Russia 13, 256–260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018030199
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018030199